Sensitive Nanozyme Test May Provide Rapid Point-of-Care Diagnosis of Ebola
|
By LabMedica International staff writers Posted on 24 Sep 2015 |
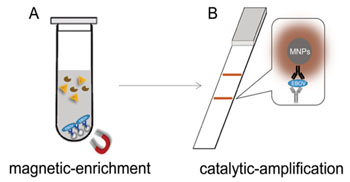
Image: In the new nanozyme immunochromatographic strip test for Ebolavirus (EBOV), the magnetic (A) and catalytic (B) properties of the nanozymes (Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles (MNPs)) make the signal 100 times stronger than standard strips with colloidal-gold nanoparticles, generating a deeper color reaction that can be more clearly seen by the naked eye (Image courtesy of Duan D et al., 2015, and Elsevier).
Researchers have developed a simple low-cost Ebolavirus (EBOV) test based on detection technology using magnetic nanoparticles that has shown 100x higher sensitivity than the standard immunochromatographic ELISA gold strip test.
In a new study led by Xiyun Yan, professor at the Institute of Biophysics, Chinese Academy of Sciences (Beijing, China), a nanozyme strip test was developed that is similar to the gold strip test but instead uses Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles (nanozymes) that enhance the signal via their intrinsic enzyme-like activity. Results showed 100x higher sensitivity than the gold strip test—the new test detects EBOV glycoprotein at concentrations as low as 1 nanogram/mL. Also, to concentrate the virus particles in the sample, the tube bottom is simply held against a magnet, so no expensive lab equipment is needed.
Early accurate detection is a key to controlling the Ebola outbreak as patients can then be isolated and treated. Current tests are either too expensive to be useful where they are most needed, or not sensitive enough to provide accurate diagnosis. PCR testing is highly sensitive but expensive and complicated, requiring specialized skills and equipment. Testing with the ELISA gold strip is inexpensive, but sensitivity is low.
“Our new strip test is a simple, one-step test that is cheap and easy to use, and provides a visible signal, which means people don’t need training to use it. We think it will be especially helpful in rural areas,” said Prof. Yan, “We’re very excited about our new nanozyme test, as it is much more sensitive and you don’t need any specialist equipment to get a quick, accurate result.” Her colleagues at the Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) will field-test it in West Africa for its EBOV diagnostic and screening potential. The researchers are also developing automatic equipment to reduce risk of test contamination from hand-contact.
The nanozyme test is the result of an interdisciplinary collaboration of scientists and clinicians. The researchers are collaborating to develop this robust technology further as it can be applied for detection of other biological molecules, making it useful to diagnose additional infectious diseases and to potentially detect cancer tumors. It is also being tested for its potential to help in decontamination for wastewater treatment.
“We had an idea and talked to many people about it, and the result is a test that will overcome a problem,” said Prof. Yan, “We have built strong collaborations that have finally made this method successful, and we’re looking forward to applying it to many other areas.”
The study, by Duan D et al., was published online ahead of print 11 May 2015, in the journal Biosensors and Bioelectronics.
Related Links:
Chinese Academy of Sciences
Elsevier
In a new study led by Xiyun Yan, professor at the Institute of Biophysics, Chinese Academy of Sciences (Beijing, China), a nanozyme strip test was developed that is similar to the gold strip test but instead uses Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles (nanozymes) that enhance the signal via their intrinsic enzyme-like activity. Results showed 100x higher sensitivity than the gold strip test—the new test detects EBOV glycoprotein at concentrations as low as 1 nanogram/mL. Also, to concentrate the virus particles in the sample, the tube bottom is simply held against a magnet, so no expensive lab equipment is needed.
Early accurate detection is a key to controlling the Ebola outbreak as patients can then be isolated and treated. Current tests are either too expensive to be useful where they are most needed, or not sensitive enough to provide accurate diagnosis. PCR testing is highly sensitive but expensive and complicated, requiring specialized skills and equipment. Testing with the ELISA gold strip is inexpensive, but sensitivity is low.
“Our new strip test is a simple, one-step test that is cheap and easy to use, and provides a visible signal, which means people don’t need training to use it. We think it will be especially helpful in rural areas,” said Prof. Yan, “We’re very excited about our new nanozyme test, as it is much more sensitive and you don’t need any specialist equipment to get a quick, accurate result.” Her colleagues at the Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) will field-test it in West Africa for its EBOV diagnostic and screening potential. The researchers are also developing automatic equipment to reduce risk of test contamination from hand-contact.
The nanozyme test is the result of an interdisciplinary collaboration of scientists and clinicians. The researchers are collaborating to develop this robust technology further as it can be applied for detection of other biological molecules, making it useful to diagnose additional infectious diseases and to potentially detect cancer tumors. It is also being tested for its potential to help in decontamination for wastewater treatment.
“We had an idea and talked to many people about it, and the result is a test that will overcome a problem,” said Prof. Yan, “We have built strong collaborations that have finally made this method successful, and we’re looking forward to applying it to many other areas.”
The study, by Duan D et al., was published online ahead of print 11 May 2015, in the journal Biosensors and Bioelectronics.
Related Links:
Chinese Academy of Sciences
Elsevier
Latest Microbiology News
- Comprehensive Review Identifies Gut Microbiome Signatures Associated With Alzheimer’s Disease
- AI-Powered Platform Enables Rapid Detection of Drug-Resistant C. Auris Pathogens
- New Test Measures How Effectively Antibiotics Kill Bacteria
- New Antimicrobial Stewardship Standards for TB Care to Optimize Diagnostics
- New UTI Diagnosis Method Delivers Antibiotic Resistance Results 24 Hours Earlier
- Breakthroughs in Microbial Analysis to Enhance Disease Prediction
- Blood-Based Diagnostic Method Could Identify Pediatric LRTIs
- Rapid Diagnostic Test Matches Gold Standard for Sepsis Detection
- Rapid POC Tuberculosis Test Provides Results Within 15 Minutes
- Rapid Assay Identifies Bloodstream Infection Pathogens Directly from Patient Samples
- Blood-Based Molecular Signatures to Enable Rapid EPTB Diagnosis
- 15-Minute Blood Test Diagnoses Life-Threatening Infections in Children
- High-Throughput Enteric Panels Detect Multiple GI Bacterial Infections from Single Stool Swab Sample
- Fast Noninvasive Bedside Test Uses Sugar Fingerprint to Detect Fungal Infections
- Rapid Sepsis Diagnostic Device to Enable Personalized Critical Care for ICU Patients
- Microfluidic Platform Assesses Neutrophil Function in Sepsis Patients
Channels
Clinical Chemistry
view channel
New PSA-Based Prognostic Model Improves Prostate Cancer Risk Assessment
Prostate cancer is the second-leading cause of cancer death among American men, and about one in eight will be diagnosed in their lifetime. Screening relies on blood levels of prostate-specific antigen... Read more
Extracellular Vesicles Linked to Heart Failure Risk in CKD Patients
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) affects more than 1 in 7 Americans and is strongly associated with cardiovascular complications, which account for more than half of deaths among people with CKD.... Read moreMolecular Diagnostics
view channel
Fully Automated Immunoassay Test Detects HDV Co‑Infection and Super-Infection
Hepatitis delta, also known as hepatitis D, is caused by the hepatitis delta virus (HDV). It is a viral liver infection that can result in one of the most severe forms of viral hepatitis.... Read more
Abdominal Fluid Testing Can Predict Ovarian Cancer Progression
Ovarian cancer kills more women than any other gynecological cancer, largely because it is usually diagnosed only after it has spread widely within the abdomen. Unlike many other cancers, it does not rely... Read more
POC Test Uses Fingerstick Blood, Serum, Or Plasma Sample to Detect Typhoid Fever
Typhoid fever is an acute febrile illness caused by Salmonella enterica serovar Typhi (S. Typhi) and affects an estimated 11–21 million people globally each year, resulting in approximately 128,000–161,000... Read more
Rapid Testing Panel Simultaneously Detects 15 Drugs of Abuse in Urine Within 21 Minutes
Illicit drug use and excessive use of prescription medicine is growing across the US amid a severe opioid crisis. Although overdose fatalities were reported to have declined by nearly 27% in 2024, many... Read moreHematology
view channel
New Guidelines Aim to Improve AL Amyloidosis Diagnosis
Light chain (AL) amyloidosis is a rare, life-threatening bone marrow disorder in which abnormal amyloid proteins accumulate in organs. Approximately 3,260 people in the United States are diagnosed... Read more
Fast and Easy Test Could Revolutionize Blood Transfusions
Blood transfusions are a cornerstone of modern medicine, yet red blood cells can deteriorate quietly while sitting in cold storage for weeks. Although blood units have a fixed expiration date, cells from... Read more
Automated Hemostasis System Helps Labs of All Sizes Optimize Workflow
High-volume hemostasis sections must sustain rapid turnaround while managing reruns and reflex testing. Manual tube handling and preanalytical checks can strain staff time and increase opportunities for error.... Read more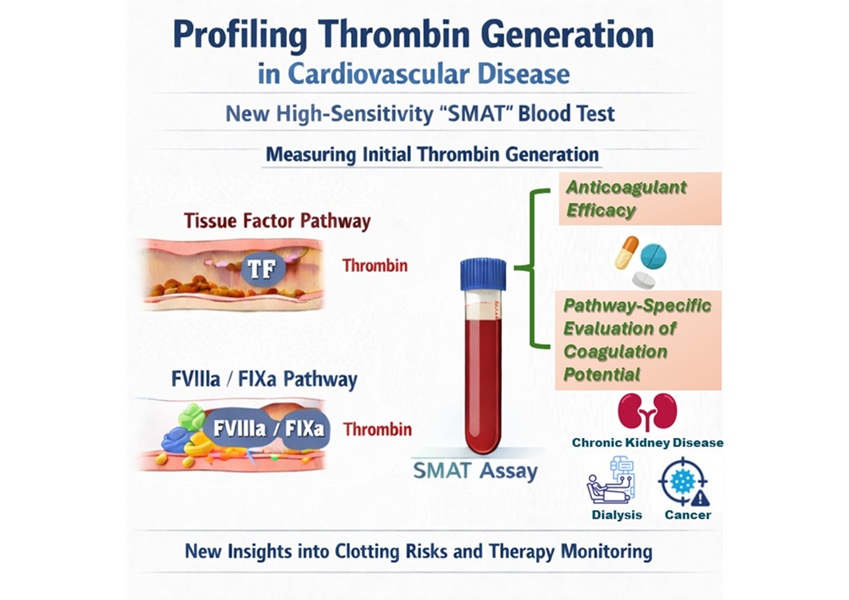
High-Sensitivity Blood Test Improves Assessment of Clotting Risk in Heart Disease Patients
Blood clotting is essential for preventing bleeding, but even small imbalances can lead to serious conditions such as thrombosis or dangerous hemorrhage. In cardiovascular disease, clinicians often struggle... Read moreImmunology
view channelBlood Test Identifies Lung Cancer Patients Who Can Benefit from Immunotherapy Drug
Small cell lung cancer (SCLC) is an aggressive disease with limited treatment options, and even newly approved immunotherapies do not benefit all patients. While immunotherapy can extend survival for some,... Read more
Whole-Genome Sequencing Approach Identifies Cancer Patients Benefitting From PARP-Inhibitor Treatment
Targeted cancer therapies such as PARP inhibitors can be highly effective, but only for patients whose tumors carry specific DNA repair defects. Identifying these patients accurately remains challenging,... Read more
Ultrasensitive Liquid Biopsy Demonstrates Efficacy in Predicting Immunotherapy Response
Immunotherapy has transformed cancer treatment, but only a small proportion of patients experience lasting benefit, with response rates often remaining between 10% and 20%. Clinicians currently lack reliable... Read morePathology
view channel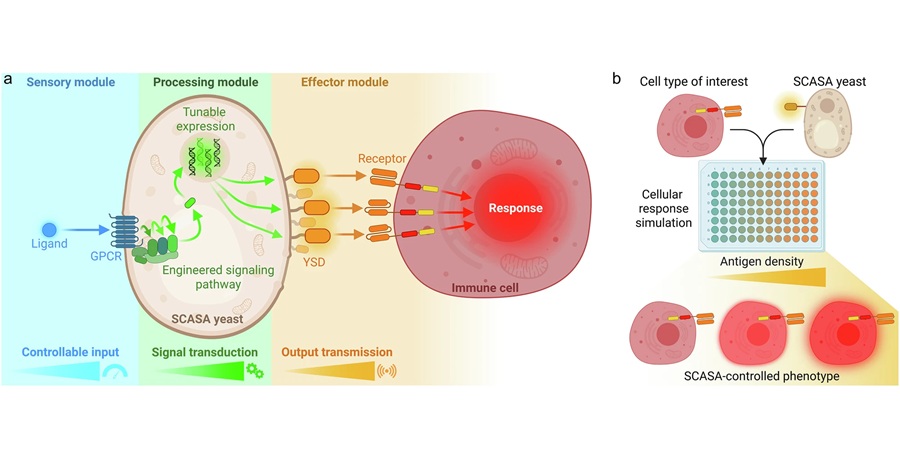
Engineered Yeast Cells Enable Rapid Testing of Cancer Immunotherapy
Developing new cancer immunotherapies is a slow, costly, and high-risk process, particularly for CAR T cell treatments that must precisely recognize cancer-specific antigens. Small differences in tumor... Read more
First-Of-Its-Kind Test Identifies Autism Risk at Birth
Autism spectrum disorder is treatable, and extensive research shows that early intervention can significantly improve cognitive, social, and behavioral outcomes. Yet in the United States, the average age... Read moreTechnology
view channel
Robotic Technology Unveiled for Automated Diagnostic Blood Draws
Routine diagnostic blood collection is a high‑volume task that can strain staffing and introduce human‑dependent variability, with downstream implications for sample quality and patient experience.... Read more
ADLM Launches First-of-Its-Kind Data Science Program for Laboratory Medicine Professionals
Clinical laboratories generate billions of test results each year, creating a treasure trove of data with the potential to support more personalized testing, improve operational efficiency, and enhance patient care.... Read moreAptamer Biosensor Technology to Transform Virus Detection
Rapid and reliable virus detection is essential for controlling outbreaks, from seasonal influenza to global pandemics such as COVID-19. Conventional diagnostic methods, including cell culture, antigen... Read more
AI Models Could Predict Pre-Eclampsia and Anemia Earlier Using Routine Blood Tests
Pre-eclampsia and anemia are major contributors to maternal and child mortality worldwide, together accounting for more than half a million deaths each year and leaving millions with long-term health complications.... Read moreIndustry
view channel
WHX Labs in Dubai spotlights leadership skills shaping next-generation laboratories
WHX Labs in Dubai (formerly Medlab Middle East), held at Dubai World Trade Centre (DWTC) from 10–13 February, brings together international experts to discuss the factors redefining laboratory leadership,... Read moreNew Collaboration Brings Automated Mass Spectrometry to Routine Laboratory Testing
Mass spectrometry is a powerful analytical technique that identifies and quantifies molecules based on their mass and electrical charge. Its high selectivity, sensitivity, and accuracy make it indispensable... Read more
AI-Powered Cervical Cancer Test Set for Major Rollout in Latin America
Noul Co., a Korean company specializing in AI-based blood and cancer diagnostics, announced it will supply its intelligence (AI)-based miLab CER cervical cancer diagnostic solution to Mexico under a multi‑year... Read more