Rapid Urine Test Evaluated for Helicobacter Pylori Infection
|
By LabMedica International staff writers Posted on 26 Jun 2014 |
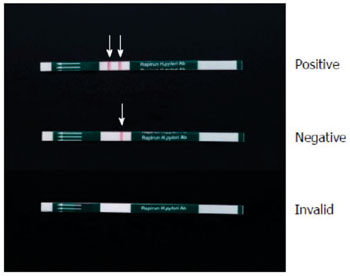
Image: Rapirun Helicobacter pylori Antibody Stick. The urine sample is considered positive when two red bands at the test line and control line (arrows) are observed after 15 minutes and is considered negative when only the control line is observed. The absence of a control line indicates an invalid result (Photo courtesy of Duc T Quach).
Image: The PyloriTek rapid urease test to detect Helicobacter pylori (Photo courtesy of Serim Research Co.).
A rapid urine test based on enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) has been developed for the detection of anti-Helicobacter Pylori antibodies in urine.
Several methods to diagnose H. pylori infection have been developed, among which the urea breath test (UBT) is currently regarded as the most accurate assay, but the UBT is still expensive and not widely available in many countries.
Scientists at the Ho Chi Minh City Medicine and Pharmacy University (Vietnam) working with Japanese colleagues, enrolled 200 patients undergoing upper gastrointestinal endoscopy from October 2012 to December 2012. Three biopsies were taken from each patient: two for histologic examination and one for the rapid urease test (RUT).
The biopsy for RUT was taken from the greater curvature of the corpus, about 2 cm above the atrophic border. This biopsy location has been reported to optimize the sensitivity of the PyloriTek RUT to detect H. pylori (Serim Research Co.; Elkhart, IN, USA). Urine samples were collected and were processed within one hour of collection for the detection of antibodies against H. pylori using the Rapirun Helicobacter pylori Antibody Stick (Otsuka Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd.; Tokyo, Japan). The test measures human immunoglobulin G (IgG) antibodies against H. pylori in urine using the principle of immunochromatography.
Of the 200 patients, 111 (55.5%) were diagnosed as being H. pylori positive. The sensitivity, specificity, and accuracy of the Rapirun Stick test were 84.7%, 89.9%, and 87.0%, respectively. There were 17 (8.5%) false-negative patients and 9 (4.5%) false-positive patients. Of the 24 patients with gastro-duodenal ulcer, 22 (91.7%) had H. pylori infection. However, 7 of 22 (31.8%) patients with reflux esophagitis also had the infection.
The authors demonstrated the usefulness of the Rapirun Stick test for the diagnosis of H. pylori infection in a Vietnamese population and the sensitivity, specificity, and accuracy of the Rapirun Stick test were high. In several patients, RUT and histologic examination produced false-negative or false-positive results, leading to the possible misdiagnosis of H. pylori infection. The study was published on May 7, 2014, in the World Journal of Gastroenterology.
Related Links:
Ho Chi Minh University of Medicine
Serim Research Co.
Otsuka Pharmaceutical Co.
Several methods to diagnose H. pylori infection have been developed, among which the urea breath test (UBT) is currently regarded as the most accurate assay, but the UBT is still expensive and not widely available in many countries.
Scientists at the Ho Chi Minh City Medicine and Pharmacy University (Vietnam) working with Japanese colleagues, enrolled 200 patients undergoing upper gastrointestinal endoscopy from October 2012 to December 2012. Three biopsies were taken from each patient: two for histologic examination and one for the rapid urease test (RUT).
The biopsy for RUT was taken from the greater curvature of the corpus, about 2 cm above the atrophic border. This biopsy location has been reported to optimize the sensitivity of the PyloriTek RUT to detect H. pylori (Serim Research Co.; Elkhart, IN, USA). Urine samples were collected and were processed within one hour of collection for the detection of antibodies against H. pylori using the Rapirun Helicobacter pylori Antibody Stick (Otsuka Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd.; Tokyo, Japan). The test measures human immunoglobulin G (IgG) antibodies against H. pylori in urine using the principle of immunochromatography.
Of the 200 patients, 111 (55.5%) were diagnosed as being H. pylori positive. The sensitivity, specificity, and accuracy of the Rapirun Stick test were 84.7%, 89.9%, and 87.0%, respectively. There were 17 (8.5%) false-negative patients and 9 (4.5%) false-positive patients. Of the 24 patients with gastro-duodenal ulcer, 22 (91.7%) had H. pylori infection. However, 7 of 22 (31.8%) patients with reflux esophagitis also had the infection.
The authors demonstrated the usefulness of the Rapirun Stick test for the diagnosis of H. pylori infection in a Vietnamese population and the sensitivity, specificity, and accuracy of the Rapirun Stick test were high. In several patients, RUT and histologic examination produced false-negative or false-positive results, leading to the possible misdiagnosis of H. pylori infection. The study was published on May 7, 2014, in the World Journal of Gastroenterology.
Related Links:
Ho Chi Minh University of Medicine
Serim Research Co.
Otsuka Pharmaceutical Co.
Latest Immunology News
- New Biomarker Predicts Chemotherapy Response in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
- Blood Test Identifies Lung Cancer Patients Who Can Benefit from Immunotherapy Drug
- Whole-Genome Sequencing Approach Identifies Cancer Patients Benefitting From PARP-Inhibitor Treatment
- Ultrasensitive Liquid Biopsy Demonstrates Efficacy in Predicting Immunotherapy Response
- Blood Test Could Identify Colon Cancer Patients to Benefit from NSAIDs
- Blood Test Could Detect Adverse Immunotherapy Effects
- Routine Blood Test Can Predict Who Benefits Most from CAR T-Cell Therapy
- New Test Distinguishes Vaccine-Induced False Positives from Active HIV Infection
- Gene Signature Test Predicts Response to Key Breast Cancer Treatment
- Chip Captures Cancer Cells from Blood to Help Select Right Breast Cancer Treatment
- Blood-Based Liquid Biopsy Model Analyzes Immunotherapy Effectiveness
- Signature Genes Predict T-Cell Expansion in Cancer Immunotherapy
- Molecular Microscope Diagnostic System Assesses Lung Transplant Rejection
- Blood Test Tracks Treatment Resistance in High-Grade Serous Ovarian Cancer
- Luminescent Probe Measures Immune Cell Activity in Real Time
- Blood-Based Immune Cell Signatures Could Guide Treatment Decisions for Critically Ill Patients
Channels
Clinical Chemistry
view channel
Simple Blood Test Offers New Path to Alzheimer’s Assessment in Primary Care
Timely evaluation of cognitive symptoms in primary care is often limited by restricted access to specialized diagnostics and invasive confirmatory procedures. Clinicians need accessible tools to determine... Read more
Existing Hospital Analyzers Can Identify Fake Liquid Medical Products
Counterfeit and substandard medicines remain a serious global health threat, with World Health Organization estimates suggesting that 10.5% of medicines in low- and middle-income countries are either fake... Read moreMolecular Diagnostics
view channel
New Genome Sequencing Technique Measures Epstein-Barr Virus in Blood
The Epstein–Barr virus (EBV) infects up to 95% of adults worldwide and remains in the body for life. While usually kept under control, the virus is linked to cancers such as Hodgkin’s lymphoma and autoimmune... Read more
Blood Test Boosts Early Detection of Brain Cancer
Brain and central nervous system (CNS) tumors are often diagnosed at an advanced stage, when treatment options are limited, and survival rates remain low. Around 300,000 new cases are diagnosed each year... Read moreHematology
view channel
Rapid Cartridge-Based Test Aims to Expand Access to Hemoglobin Disorder Diagnosis
Sickle cell disease and beta thalassemia are hemoglobin disorders that often require referral to specialized laboratories for definitive diagnosis, delaying results for patients and clinicians.... Read more
New Guidelines Aim to Improve AL Amyloidosis Diagnosis
Light chain (AL) amyloidosis is a rare, life-threatening bone marrow disorder in which abnormal amyloid proteins accumulate in organs. Approximately 3,260 people in the United States are diagnosed... Read moreImmunology
view channel
New Biomarker Predicts Chemotherapy Response in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
Triple-negative breast cancer is an aggressive form of breast cancer in which patients often show widely varying responses to chemotherapy. Predicting who will benefit from treatment remains challenging,... Read moreBlood Test Identifies Lung Cancer Patients Who Can Benefit from Immunotherapy Drug
Small cell lung cancer (SCLC) is an aggressive disease with limited treatment options, and even newly approved immunotherapies do not benefit all patients. While immunotherapy can extend survival for some,... Read more
Whole-Genome Sequencing Approach Identifies Cancer Patients Benefitting From PARP-Inhibitor Treatment
Targeted cancer therapies such as PARP inhibitors can be highly effective, but only for patients whose tumors carry specific DNA repair defects. Identifying these patients accurately remains challenging,... Read more
Ultrasensitive Liquid Biopsy Demonstrates Efficacy in Predicting Immunotherapy Response
Immunotherapy has transformed cancer treatment, but only a small proportion of patients experience lasting benefit, with response rates often remaining between 10% and 20%. Clinicians currently lack reliable... Read morePathology
view channel
Single Sample Classifier Predicts Cancer-Associated Fibroblast Subtypes in Patient Samples
Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) remains one of the deadliest cancers, in part because of its dense tumor microenvironment that influences how tumors grow and respond to treatment.... Read more
New AI-Driven Platform Standardizes Tuberculosis Smear Microscopy Workflow
Sputum smear microscopy remains central to tuberculosis treatment monitoring and follow-up, particularly in high‑burden settings where serial testing is routine. Yet consistent, repeatable bacillary assessment... Read more
AI Tool Uses Blood Biomarkers to Predict Transplant Complications Before Symptoms Appear
Stem cell and bone marrow transplants can be lifesaving, but serious complications may arise months after patients leave the hospital. One of the most dangerous is chronic graft-versus-host disease, in... Read moreTechnology
view channel
Blood Test “Clocks” Predict Start of Alzheimer’s Symptoms
More than 7 million Americans live with Alzheimer’s disease, and related health and long-term care costs are projected to reach nearly USD 400 billion in 2025. The disease has no cure, and symptoms often... Read more
AI-Powered Biomarker Predicts Liver Cancer Risk
Liver cancer, or hepatocellular carcinoma, causes more than 800,000 deaths worldwide each year and often goes undetected until late stages. Even after treatment, recurrence rates reach 70% to 80%, contributing... Read more
Robotic Technology Unveiled for Automated Diagnostic Blood Draws
Routine diagnostic blood collection is a high‑volume task that can strain staffing and introduce human‑dependent variability, with downstream implications for sample quality and patient experience.... Read more
ADLM Launches First-of-Its-Kind Data Science Program for Laboratory Medicine Professionals
Clinical laboratories generate billions of test results each year, creating a treasure trove of data with the potential to support more personalized testing, improve operational efficiency, and enhance patient care.... Read moreIndustry
view channel
QuidelOrtho Collaborates with Lifotronic to Expand Global Immunoassay Portfolio
QuidelOrtho (San Diego, CA, USA) has entered a long-term strategic supply agreement with Lifotronic Technology (Shenzhen, China) to expand its global immunoassay portfolio and accelerate customer access... Read more