HbA1c Point-of-Care Test Reliably Diagnoses Diabetes
|
By LabMedica International staff writers Posted on 11 Apr 2019 |
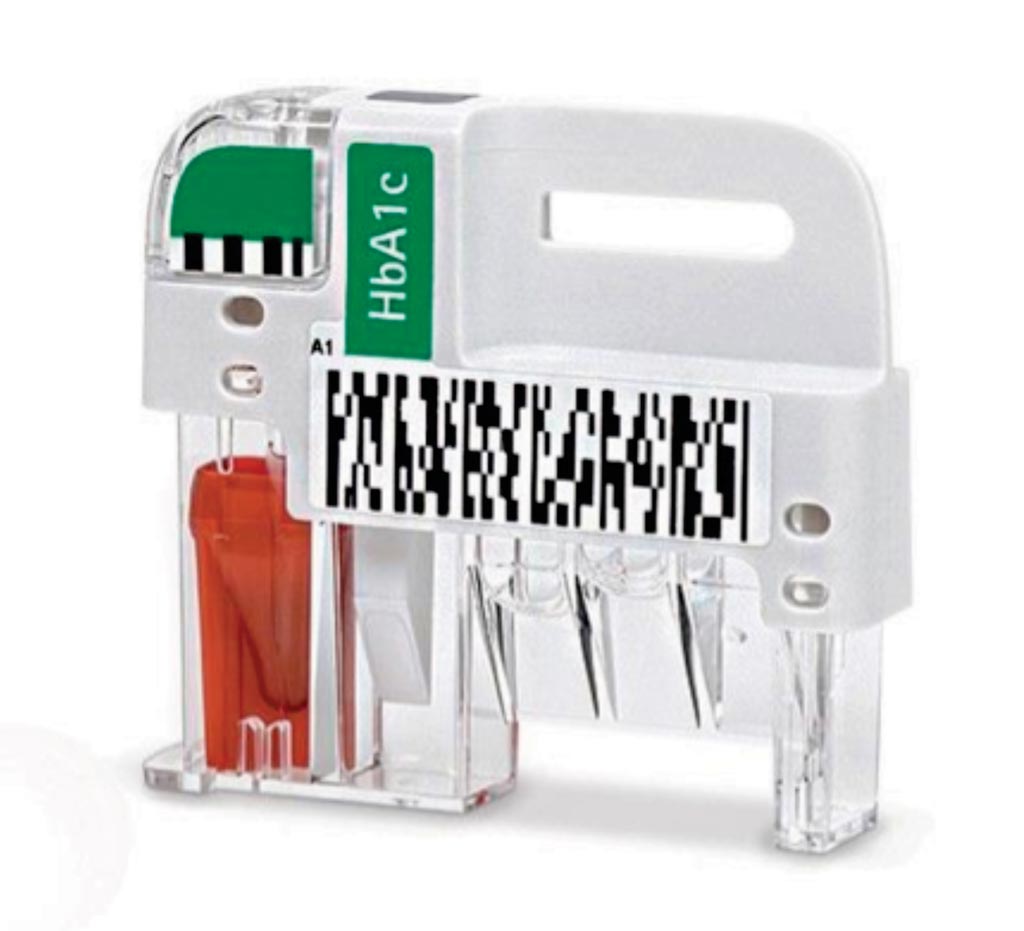

Image: The AfinionHbA1c assay cartridge is used to test for quantitative determination of glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) in human whole blood, which is used to monitor metabolic control in patients with diabetes (Photo courtesy of Alere).
Glycated hemoglobin is a form of hemoglobin that is covalently bound to glucose. It is formed in a non-enzymatic glycation pathway by hemoglobin's exposure to plasma glucose.
By measuring glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c), clinicians are able to get an overall picture of what the average blood sugar levels have been over a period of weeks/months. Point-of-care (POC) hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) testing has advantages over laboratory testing, but some questions have remained regarding the accuracy and precision of these methods.
Scientists collaborating with Abbott Rapid Diagnostics (San Diego, CA, USA) carried out a prospective and observational study using samples from 120 adults (mean age, 57 years; 56% women) across a range of HbA1c levels (4%-15%) that were taken by finger stick at three clinical sites in the USA. Four groups were formed based on HbA1c levels and categorized as low (4%-5.99%), threshold (6%-6.99%), medium (7%-9.99%) and high (more than 10%).
Venous blood samples were also taken from each participant, and three from each HbA1c group were analyzed using a POC test. The POC test assessed in the study was the Afinion HbA1c Dx test (Alere Technologies, Waltham, MA, USA). The precision of the POC test using venous blood was evaluated from samples run in four replicates on each of three test cartridge lots, twice per day for 10 consecutive days. The SD and CV by study site and overall were calculated.
The investigators found that using the point-of-care test with finger-stick and venous blood samples was “highly correlated” with the National Glycohemoglobin Standardization Program (NGSP) values. They also noted small bias results when comparing point-of-care testing by finger-stick testing (mean differential bias, –0.021%) and venous blood samples (mean differential bias, –0.005%). In addition, 97.5% of results from the finger-stick point-of-care tests and 97.1% of the venous blood point-of-care tests fell within 6% of the reference method from the Diabetes Control and Complications Trial. At least 92.5% of results are currently required to fall within this range by the NGSP, although the program will adjust the requirements to be 90% within 5% of the reference result this year. They noted that 95% of the finger-stick point-of-care test results and 93.3% of the venous blood POC test results fell within 5% of the reference in these new requirements.
The authors concluded that point-of-care HbA1c testing has the potential to expand patient access to diabetes diagnostic testing and expedite medical decisions and interventions aimed at the prevention of diabetes and its complications, particularly for those who face challenges in accessing traditional health care settings or attending multiple laboratory and physician follow-up appointments. The study was published on March 10, 2019, in the Journal of Diabetes Science and Technology.
By measuring glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c), clinicians are able to get an overall picture of what the average blood sugar levels have been over a period of weeks/months. Point-of-care (POC) hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) testing has advantages over laboratory testing, but some questions have remained regarding the accuracy and precision of these methods.
Scientists collaborating with Abbott Rapid Diagnostics (San Diego, CA, USA) carried out a prospective and observational study using samples from 120 adults (mean age, 57 years; 56% women) across a range of HbA1c levels (4%-15%) that were taken by finger stick at three clinical sites in the USA. Four groups were formed based on HbA1c levels and categorized as low (4%-5.99%), threshold (6%-6.99%), medium (7%-9.99%) and high (more than 10%).
Venous blood samples were also taken from each participant, and three from each HbA1c group were analyzed using a POC test. The POC test assessed in the study was the Afinion HbA1c Dx test (Alere Technologies, Waltham, MA, USA). The precision of the POC test using venous blood was evaluated from samples run in four replicates on each of three test cartridge lots, twice per day for 10 consecutive days. The SD and CV by study site and overall were calculated.
The investigators found that using the point-of-care test with finger-stick and venous blood samples was “highly correlated” with the National Glycohemoglobin Standardization Program (NGSP) values. They also noted small bias results when comparing point-of-care testing by finger-stick testing (mean differential bias, –0.021%) and venous blood samples (mean differential bias, –0.005%). In addition, 97.5% of results from the finger-stick point-of-care tests and 97.1% of the venous blood point-of-care tests fell within 6% of the reference method from the Diabetes Control and Complications Trial. At least 92.5% of results are currently required to fall within this range by the NGSP, although the program will adjust the requirements to be 90% within 5% of the reference result this year. They noted that 95% of the finger-stick point-of-care test results and 93.3% of the venous blood POC test results fell within 5% of the reference in these new requirements.
The authors concluded that point-of-care HbA1c testing has the potential to expand patient access to diabetes diagnostic testing and expedite medical decisions and interventions aimed at the prevention of diabetes and its complications, particularly for those who face challenges in accessing traditional health care settings or attending multiple laboratory and physician follow-up appointments. The study was published on March 10, 2019, in the Journal of Diabetes Science and Technology.
Latest Clinical Chem. News
- 3D Printed Point-Of-Care Mass Spectrometer Outperforms State-Of-The-Art Models
- POC Biomedical Test Spins Water Droplet Using Sound Waves for Cancer Detection
- Highly Reliable Cell-Based Assay Enables Accurate Diagnosis of Endocrine Diseases
- New Blood Testing Method Detects Potent Opioids in Under Three Minutes
- Wireless Hepatitis B Test Kit Completes Screening and Data Collection in One Step
- Pain-Free, Low-Cost, Sensitive, Radiation-Free Device Detects Breast Cancer in Urine
- Spit Test Detects Breast Cancer in Five Seconds
- Electrochemical Sensors with Next-Generation Coating Advances Precision Diagnostics at POC
- First-Of-Its-Kind Handheld Device Accurately Detects Fentanyl in Urine within Seconds
- New Fluorescent Sensor Array Lights up Alzheimer’s-Related Proteins for Earlier Detection
- Automated Mass Spectrometry-Based Clinical Analyzer Could Transform Lab Testing
- Highly Sensitive pH Sensor to Aid Detection of Cancers and Vector-Borne Viruses
- Non-Invasive Sensor Monitors Changes in Saliva Compositions to Rapidly Diagnose Diabetes
- Breakthrough Immunoassays to Aid in Risk Assessment of Preeclampsia
- Urine Test for Monitoring Changes in Kidney Health Markers Can Predict New-Onset Heart Failure
- AACC Releases Comprehensive Diabetes Testing Guidelines
Channels
Molecular Diagnostics
view channel
Blood Test Accurately Predicts Lung Cancer Risk and Reduces Need for Scans
Lung cancer is extremely hard to detect early due to the limitations of current screening technologies, which are costly, sometimes inaccurate, and less commonly endorsed by healthcare professionals compared... Read more
Unique Autoantibody Signature to Help Diagnose Multiple Sclerosis Years before Symptom Onset
Autoimmune diseases such as multiple sclerosis (MS) are thought to occur partly due to unusual immune responses to common infections. Early MS symptoms, including dizziness, spasms, and fatigue, often... Read more
Blood Test Could Detect HPV-Associated Cancers 10 Years before Clinical Diagnosis
Human papilloma virus (HPV) is known to cause various cancers, including those of the genitals, anus, mouth, throat, and cervix. HPV-associated oropharyngeal cancer (HPV+OPSCC) is the most common HPV-associated... Read moreHematology
view channel
Next Generation Instrument Screens for Hemoglobin Disorders in Newborns
Hemoglobinopathies, the most widespread inherited conditions globally, affect about 7% of the population as carriers, with 2.7% of newborns being born with these conditions. The spectrum of clinical manifestations... Read more
First 4-in-1 Nucleic Acid Test for Arbovirus Screening to Reduce Risk of Transfusion-Transmitted Infections
Arboviruses represent an emerging global health threat, exacerbated by climate change and increased international travel that is facilitating their spread across new regions. Chikungunya, dengue, West... Read more
POC Finger-Prick Blood Test Determines Risk of Neutropenic Sepsis in Patients Undergoing Chemotherapy
Neutropenia, a decrease in neutrophils (a type of white blood cell crucial for fighting infections), is a frequent side effect of certain cancer treatments. This condition elevates the risk of infections,... Read more
First Affordable and Rapid Test for Beta Thalassemia Demonstrates 99% Diagnostic Accuracy
Hemoglobin disorders rank as some of the most prevalent monogenic diseases globally. Among various hemoglobin disorders, beta thalassemia, a hereditary blood disorder, affects about 1.5% of the world's... Read moreImmunology
view channel
Diagnostic Blood Test for Cellular Rejection after Organ Transplant Could Replace Surgical Biopsies
Transplanted organs constantly face the risk of being rejected by the recipient's immune system which differentiates self from non-self using T cells and B cells. T cells are commonly associated with acute... Read more
AI Tool Precisely Matches Cancer Drugs to Patients Using Information from Each Tumor Cell
Current strategies for matching cancer patients with specific treatments often depend on bulk sequencing of tumor DNA and RNA, which provides an average profile from all cells within a tumor sample.... Read more
Genetic Testing Combined With Personalized Drug Screening On Tumor Samples to Revolutionize Cancer Treatment
Cancer treatment typically adheres to a standard of care—established, statistically validated regimens that are effective for the majority of patients. However, the disease’s inherent variability means... Read moreMicrobiology
view channel
New CE-Marked Hepatitis Assays to Help Diagnose Infections Earlier
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), an estimated 354 million individuals globally are afflicted with chronic hepatitis B or C. These viruses are the leading causes of liver cirrhosis, liver... Read more
1 Hour, Direct-From-Blood Multiplex PCR Test Identifies 95% of Sepsis-Causing Pathogens
Sepsis contributes to one in every three hospital deaths in the US, and globally, septic shock carries a mortality rate of 30-40%. Diagnosing sepsis early is challenging due to its non-specific symptoms... Read morePathology
view channelAI-Powered Digital Imaging System to Revolutionize Cancer Diagnosis
The process of biopsy is important for confirming the presence of cancer. In the conventional histopathology technique, tissue is excised, sliced, stained, mounted on slides, and examined under a microscope... Read more
New Mycobacterium Tuberculosis Panel to Support Real-Time Surveillance and Combat Antimicrobial Resistance
Tuberculosis (TB), the leading cause of death from an infectious disease globally, is a contagious bacterial infection that primarily spreads through the coughing of patients with active pulmonary TB.... Read moreTechnology
view channel
New Diagnostic System Achieves PCR Testing Accuracy
While PCR tests are the gold standard of accuracy for virology testing, they come with limitations such as complexity, the need for skilled lab operators, and longer result times. They also require complex... Read more
DNA Biosensor Enables Early Diagnosis of Cervical Cancer
Molybdenum disulfide (MoS2), recognized for its potential to form two-dimensional nanosheets like graphene, is a material that's increasingly catching the eye of the scientific community.... Read more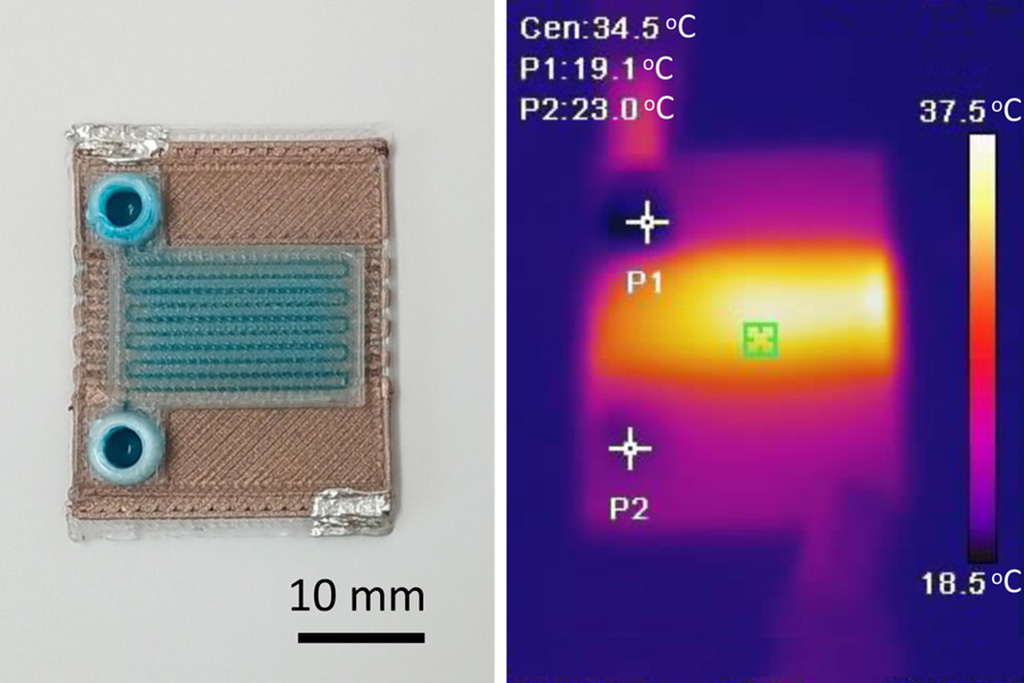
Self-Heating Microfluidic Devices Can Detect Diseases in Tiny Blood or Fluid Samples
Microfluidics, which are miniature devices that control the flow of liquids and facilitate chemical reactions, play a key role in disease detection from small samples of blood or other fluids.... Read more
Breakthrough in Diagnostic Technology Could Make On-The-Spot Testing Widely Accessible
Home testing gained significant importance during the COVID-19 pandemic, yet the availability of rapid tests is limited, and most of them can only drive one liquid across the strip, leading to continued... Read moreIndustry
view channel
ECCMID Congress Name Changes to ESCMID Global
Over the last few years, the European Society of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases (ESCMID, Basel, Switzerland) has evolved remarkably. The society is now stronger and broader than ever before... Read more
Bosch and Randox Partner to Make Strategic Investment in Vivalytic Analysis Platform
Given the presence of so many diseases, determining whether a patient is presenting the symptoms of a simple cold, the flu, or something as severe as life-threatening meningitis is usually only possible... Read more
Siemens to Close Fast Track Diagnostics Business
Siemens Healthineers (Erlangen, Germany) has announced its intention to close its Fast Track Diagnostics unit, a small collection of polymerase chain reaction (PCR) testing products that is part of the... Read more












.jpg)