Exhaled Breath Test Discriminates COPD
|
By LabMedica International staff writers Posted on 28 Jun 2017 |

Image: A patient undergoing a breath test for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and other lung diseases (Photo courtesy of Professor Malcolm Kohler, MD).
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is a type of obstructive lung disease characterized by long-term poor airflow. The main symptoms include shortness of breath and cough with sputum production. COPD is a progressive disease, meaning it typically worsens over time.
Analysis of exhaled breath by real-time mass spectrometry helps discriminate between patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), healthy controls, and patients with asthma. COPD is presently diagnosed based upon airflow restriction in spirometry, respiratory symptoms, and history of exposure to risk factors.
Scientists at the University Hospital Zurich (Switzerland) compared 49 patients with COPD whose mean age was 64 years 59.2% were male; 53 healthy control subjects whose mean age was 43 years and 52.8%were female, and 31 patients with asthma whose mean age was 41 years and 64.5% were male. The team used secondary electrospray ionization/high-resolution mass spectrometry to define a series of potential markers in exhaled breath with the potential to discriminate patients with COPD from healthy controls.
The team identified 57 specific COPD discriminatory markers, with a further 56 that overlapped with the control subjects, and 17 with the subjects with asthma, all 17 of which were common to all of these patients. Identification of 23 compounds using real-time mass spectrometry that best defined signals significantly correlated with forced expiratory volume in one second predicted (FEV1%-predicted) in terms of the FEV1/ forced vital capacity (FVC-predicted) ratio. These compounds generally belong to the oxidative stress cascade and the lipolysis cascade. Patients with COPD showed FEV1 44.6, FVC 75.8, and FEV1/FVC ratio of 44. The healthy control subjects showed FEV1 101.2, FVC 105.3, and FEV1/FVC ratio of 81. Patients with asthma had FEV1 84.4, FVC 99.5, and FEV1/FVC ratio of 70.
Yvonne Nussbaumer-Ochsner, MD, the lead author, said, “There are more biomarkers overlapping with the control group than with asthma, which is actually also a kind of chronic obstructive airways disorder. Asthmatics appear to have different biomarkers in their exhaled breath compared with both controls and patients with COPD.” The study was presented on June 8, 2017, at the Joint CHEST-Swiss Society of Pneumology Congress (CHEST-SGP) held in Basel, Switzerland.
Related Links:
University Hospital Zurich
Analysis of exhaled breath by real-time mass spectrometry helps discriminate between patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), healthy controls, and patients with asthma. COPD is presently diagnosed based upon airflow restriction in spirometry, respiratory symptoms, and history of exposure to risk factors.
Scientists at the University Hospital Zurich (Switzerland) compared 49 patients with COPD whose mean age was 64 years 59.2% were male; 53 healthy control subjects whose mean age was 43 years and 52.8%were female, and 31 patients with asthma whose mean age was 41 years and 64.5% were male. The team used secondary electrospray ionization/high-resolution mass spectrometry to define a series of potential markers in exhaled breath with the potential to discriminate patients with COPD from healthy controls.
The team identified 57 specific COPD discriminatory markers, with a further 56 that overlapped with the control subjects, and 17 with the subjects with asthma, all 17 of which were common to all of these patients. Identification of 23 compounds using real-time mass spectrometry that best defined signals significantly correlated with forced expiratory volume in one second predicted (FEV1%-predicted) in terms of the FEV1/ forced vital capacity (FVC-predicted) ratio. These compounds generally belong to the oxidative stress cascade and the lipolysis cascade. Patients with COPD showed FEV1 44.6, FVC 75.8, and FEV1/FVC ratio of 44. The healthy control subjects showed FEV1 101.2, FVC 105.3, and FEV1/FVC ratio of 81. Patients with asthma had FEV1 84.4, FVC 99.5, and FEV1/FVC ratio of 70.
Yvonne Nussbaumer-Ochsner, MD, the lead author, said, “There are more biomarkers overlapping with the control group than with asthma, which is actually also a kind of chronic obstructive airways disorder. Asthmatics appear to have different biomarkers in their exhaled breath compared with both controls and patients with COPD.” The study was presented on June 8, 2017, at the Joint CHEST-Swiss Society of Pneumology Congress (CHEST-SGP) held in Basel, Switzerland.
Related Links:
University Hospital Zurich
Latest Clinical Chem. News
- 3D Printed Point-Of-Care Mass Spectrometer Outperforms State-Of-The-Art Models
- POC Biomedical Test Spins Water Droplet Using Sound Waves for Cancer Detection
- Highly Reliable Cell-Based Assay Enables Accurate Diagnosis of Endocrine Diseases
- New Blood Testing Method Detects Potent Opioids in Under Three Minutes
- Wireless Hepatitis B Test Kit Completes Screening and Data Collection in One Step
- Pain-Free, Low-Cost, Sensitive, Radiation-Free Device Detects Breast Cancer in Urine
- Spit Test Detects Breast Cancer in Five Seconds
- Electrochemical Sensors with Next-Generation Coating Advances Precision Diagnostics at POC
- First-Of-Its-Kind Handheld Device Accurately Detects Fentanyl in Urine within Seconds
- New Fluorescent Sensor Array Lights up Alzheimer’s-Related Proteins for Earlier Detection
- Automated Mass Spectrometry-Based Clinical Analyzer Could Transform Lab Testing
- Highly Sensitive pH Sensor to Aid Detection of Cancers and Vector-Borne Viruses
- Non-Invasive Sensor Monitors Changes in Saliva Compositions to Rapidly Diagnose Diabetes
- Breakthrough Immunoassays to Aid in Risk Assessment of Preeclampsia
- Urine Test for Monitoring Changes in Kidney Health Markers Can Predict New-Onset Heart Failure
- AACC Releases Comprehensive Diabetes Testing Guidelines
Channels
Molecular Diagnostics
view channel
Simple Blood Test Could Enable First Quantitative Assessments for Future Cerebrovascular Disease
Cerebral small vessel disease is a common cause of stroke and cognitive decline, particularly in the elderly. Presently, assessing the risk for cerebral vascular diseases involves using a mix of diagnostic... Read more
New Genetic Testing Procedure Combined With Ultrasound Detects High Cardiovascular Risk
A key interest area in cardiovascular research today is the impact of clonal hematopoiesis on cardiovascular diseases. Clonal hematopoiesis results from mutations in hematopoietic stem cells and may lead... Read moreHematology
view channel
Next Generation Instrument Screens for Hemoglobin Disorders in Newborns
Hemoglobinopathies, the most widespread inherited conditions globally, affect about 7% of the population as carriers, with 2.7% of newborns being born with these conditions. The spectrum of clinical manifestations... Read more
First 4-in-1 Nucleic Acid Test for Arbovirus Screening to Reduce Risk of Transfusion-Transmitted Infections
Arboviruses represent an emerging global health threat, exacerbated by climate change and increased international travel that is facilitating their spread across new regions. Chikungunya, dengue, West... Read more
POC Finger-Prick Blood Test Determines Risk of Neutropenic Sepsis in Patients Undergoing Chemotherapy
Neutropenia, a decrease in neutrophils (a type of white blood cell crucial for fighting infections), is a frequent side effect of certain cancer treatments. This condition elevates the risk of infections,... Read more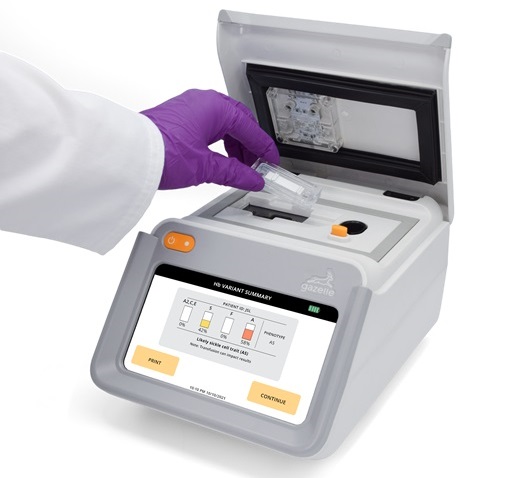
First Affordable and Rapid Test for Beta Thalassemia Demonstrates 99% Diagnostic Accuracy
Hemoglobin disorders rank as some of the most prevalent monogenic diseases globally. Among various hemoglobin disorders, beta thalassemia, a hereditary blood disorder, affects about 1.5% of the world's... Read moreImmunology
view channel
Diagnostic Blood Test for Cellular Rejection after Organ Transplant Could Replace Surgical Biopsies
Transplanted organs constantly face the risk of being rejected by the recipient's immune system which differentiates self from non-self using T cells and B cells. T cells are commonly associated with acute... Read more
AI Tool Precisely Matches Cancer Drugs to Patients Using Information from Each Tumor Cell
Current strategies for matching cancer patients with specific treatments often depend on bulk sequencing of tumor DNA and RNA, which provides an average profile from all cells within a tumor sample.... Read more
Genetic Testing Combined With Personalized Drug Screening On Tumor Samples to Revolutionize Cancer Treatment
Cancer treatment typically adheres to a standard of care—established, statistically validated regimens that are effective for the majority of patients. However, the disease’s inherent variability means... Read moreMicrobiology
view channelEnhanced Rapid Syndromic Molecular Diagnostic Solution Detects Broad Range of Infectious Diseases
GenMark Diagnostics (Carlsbad, CA, USA), a member of the Roche Group (Basel, Switzerland), has rebranded its ePlex® system as the cobas eplex system. This rebranding under the globally renowned cobas name... Read more
Clinical Decision Support Software a Game-Changer in Antimicrobial Resistance Battle
Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) is a serious global public health concern that claims millions of lives every year. It primarily results from the inappropriate and excessive use of antibiotics, which reduces... Read more
New CE-Marked Hepatitis Assays to Help Diagnose Infections Earlier
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), an estimated 354 million individuals globally are afflicted with chronic hepatitis B or C. These viruses are the leading causes of liver cirrhosis, liver... Read more
1 Hour, Direct-From-Blood Multiplex PCR Test Identifies 95% of Sepsis-Causing Pathogens
Sepsis contributes to one in every three hospital deaths in the US, and globally, septic shock carries a mortality rate of 30-40%. Diagnosing sepsis early is challenging due to its non-specific symptoms... Read morePathology
view channel.jpg)
Use of DICOM Images for Pathology Diagnostics Marks Significant Step towards Standardization
Digital pathology is rapidly becoming a key aspect of modern healthcare, transforming the practice of pathology as laboratories worldwide adopt this advanced technology. Digital pathology systems allow... Read more
First of Its Kind Universal Tool to Revolutionize Sample Collection for Diagnostic Tests
The COVID pandemic has dramatically reshaped the perception of diagnostics. Post the pandemic, a groundbreaking device that combines sample collection and processing into a single, easy-to-use disposable... Read moreAI-Powered Digital Imaging System to Revolutionize Cancer Diagnosis
The process of biopsy is important for confirming the presence of cancer. In the conventional histopathology technique, tissue is excised, sliced, stained, mounted on slides, and examined under a microscope... Read more
New Mycobacterium Tuberculosis Panel to Support Real-Time Surveillance and Combat Antimicrobial Resistance
Tuberculosis (TB), the leading cause of death from an infectious disease globally, is a contagious bacterial infection that primarily spreads through the coughing of patients with active pulmonary TB.... Read moreTechnology
view channel
New Diagnostic System Achieves PCR Testing Accuracy
While PCR tests are the gold standard of accuracy for virology testing, they come with limitations such as complexity, the need for skilled lab operators, and longer result times. They also require complex... Read more
DNA Biosensor Enables Early Diagnosis of Cervical Cancer
Molybdenum disulfide (MoS2), recognized for its potential to form two-dimensional nanosheets like graphene, is a material that's increasingly catching the eye of the scientific community.... Read more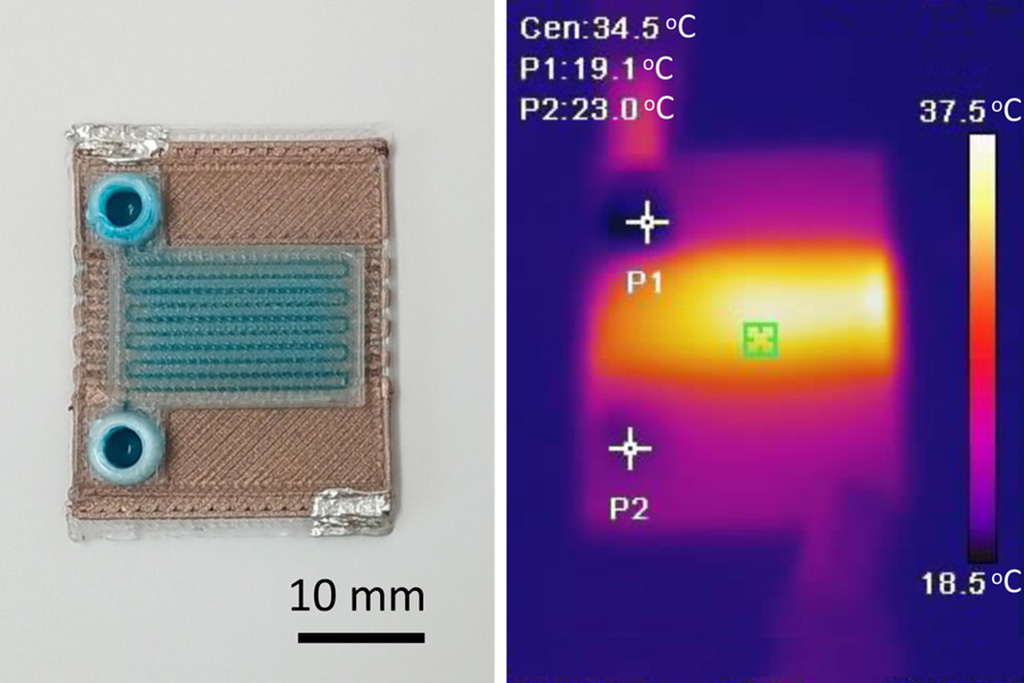
Self-Heating Microfluidic Devices Can Detect Diseases in Tiny Blood or Fluid Samples
Microfluidics, which are miniature devices that control the flow of liquids and facilitate chemical reactions, play a key role in disease detection from small samples of blood or other fluids.... Read more
Breakthrough in Diagnostic Technology Could Make On-The-Spot Testing Widely Accessible
Home testing gained significant importance during the COVID-19 pandemic, yet the availability of rapid tests is limited, and most of them can only drive one liquid across the strip, leading to continued... Read moreIndustry
view channel_1.jpg)
Thermo Fisher and Bio-Techne Enter Into Strategic Distribution Agreement for Europe
Thermo Fisher Scientific (Waltham, MA USA) has entered into a strategic distribution agreement with Bio-Techne Corporation (Minneapolis, MN, USA), resulting in a significant collaboration between two industry... Read more
ECCMID Congress Name Changes to ESCMID Global
Over the last few years, the European Society of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases (ESCMID, Basel, Switzerland) has evolved remarkably. The society is now stronger and broader than ever before... Read more