Pathology
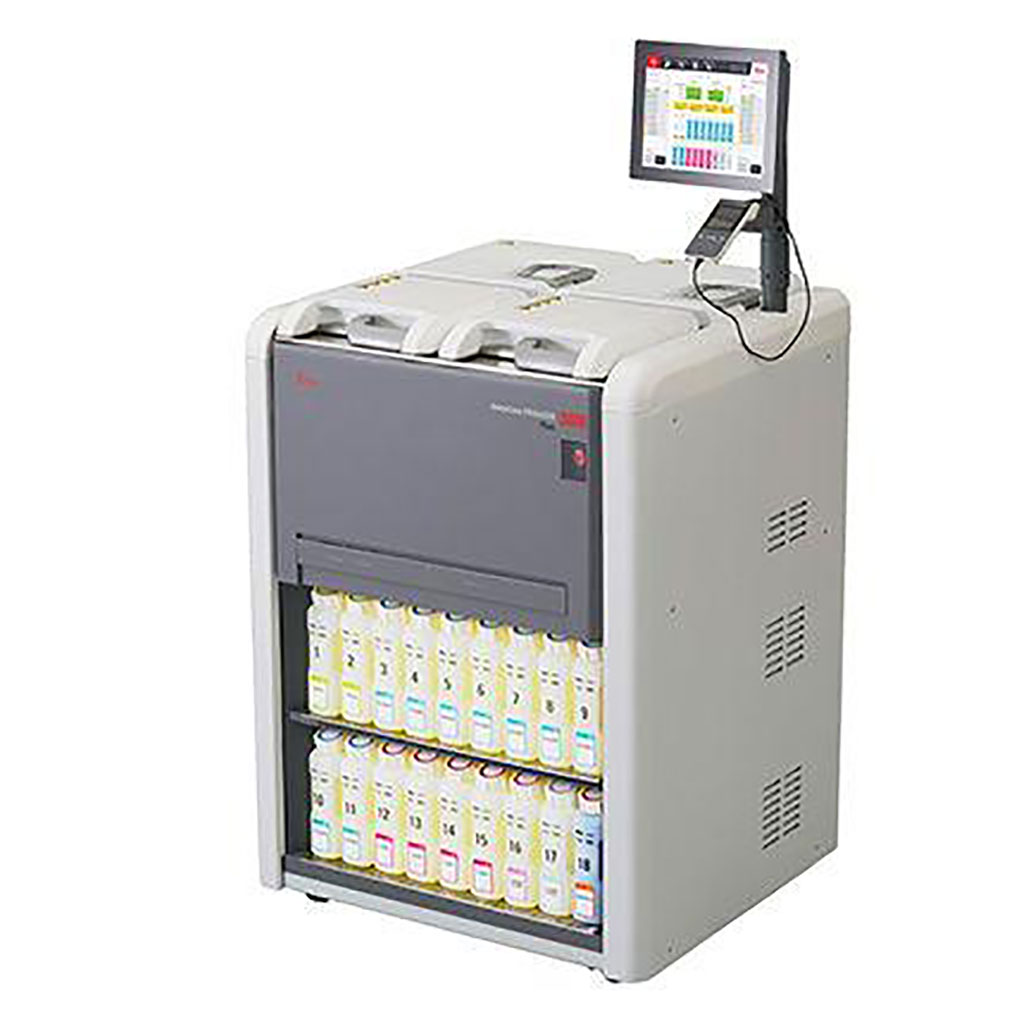

Leica Biosystems Launches HistoCore PEGASUS Plus Dual-Retort Tissue Processor in Europe
Leica Biosystems (Nussloch, Germany) has launched a compact, dual-retort tissue processor, the HistoCore PEGASUS Plus. For the first time, the technology will now be available to medium-sized laboratories, enabling them to optimize histopathology workflows. More...04 May 2022
Urinary Microbiome Linked to Prostate Cancer Risk
Prostate cancer is the most common non-skin malignancy in men in developed countries, with over 250,000 deaths annually worldwide. The clinical course of prostate cancer is highly heterogeneous, and critical decisions are made about the likelihood of aggressive disease based on information obtained at presentation. More...02 May 2022
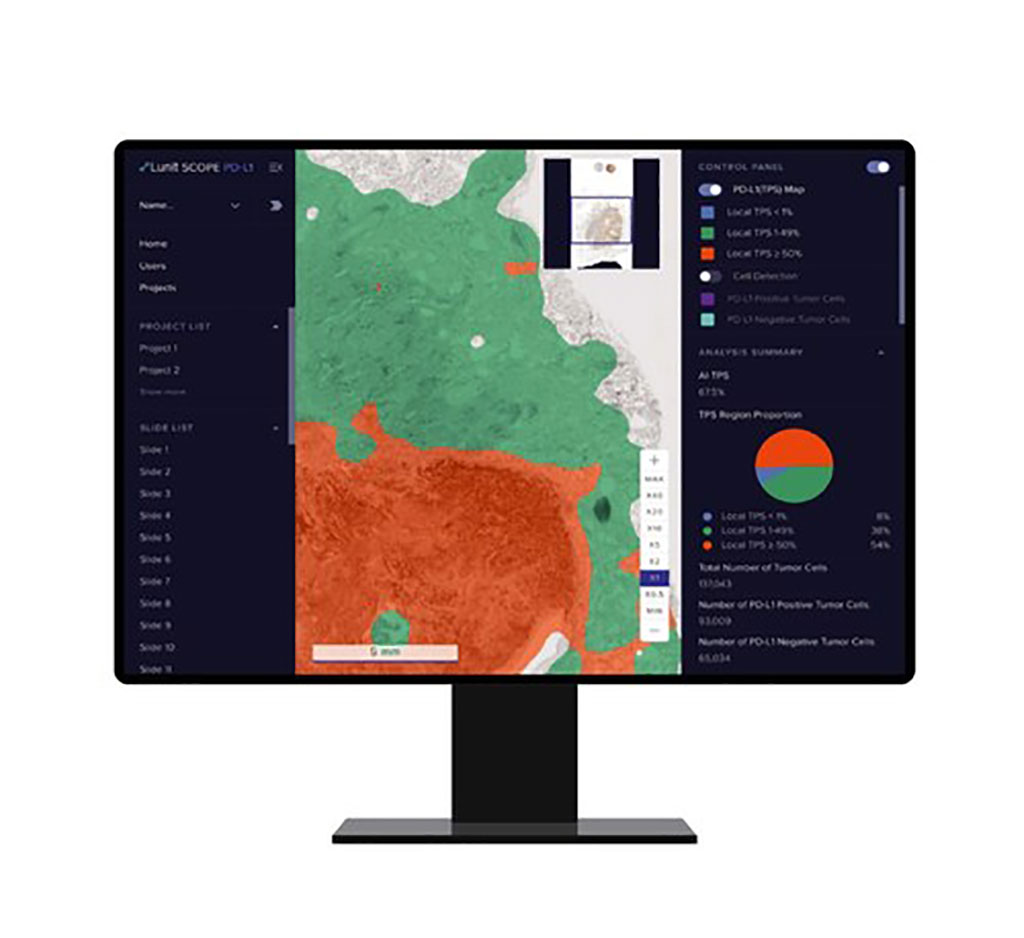
Lunit AI-Powered Pathology Solution Aids Highly Accurate Cancer Diagnosis
Programmed death ligand 1 (PD-L1) expression is the standard biomarker in advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). However, manual evaluation of PD-L1 tumor proportion score (TPS) by pathologists has practical limitations of interobserver bias, variation in subjectivity on the area of interest, and intensive labor. Now, a new artificial intelligence (AI)-powered TPS analyzer could reduce the human discrepancy. More...28 Apr 2022

Immunohistochemistry-Guided Sequencing Finds Mutations in Most Cortisol-Producing Adenomas
Cushing syndrome (CS) represents a constellation of signs and symptoms associated with chronic and excessive exposure to glucocorticoids, from either endogenous endocrinopathies or, more commonly, from exogenous pharmacologic sources. More...27 Apr 2022

Single-Cell Proteomics of Localized Prostate Cancer Defines Disease Heterogeneity
Prostate cancer affects about 12.6% of men over the course of their lives, and while most individuals with localized disease can be cured, disease does recur in a small number of patients. The treatment of localized prostate cancer is based on clinicopathological information including Gleason score, prostate-specific antigen (PSA) levels, stage, and patient age. More...26 Apr 2022
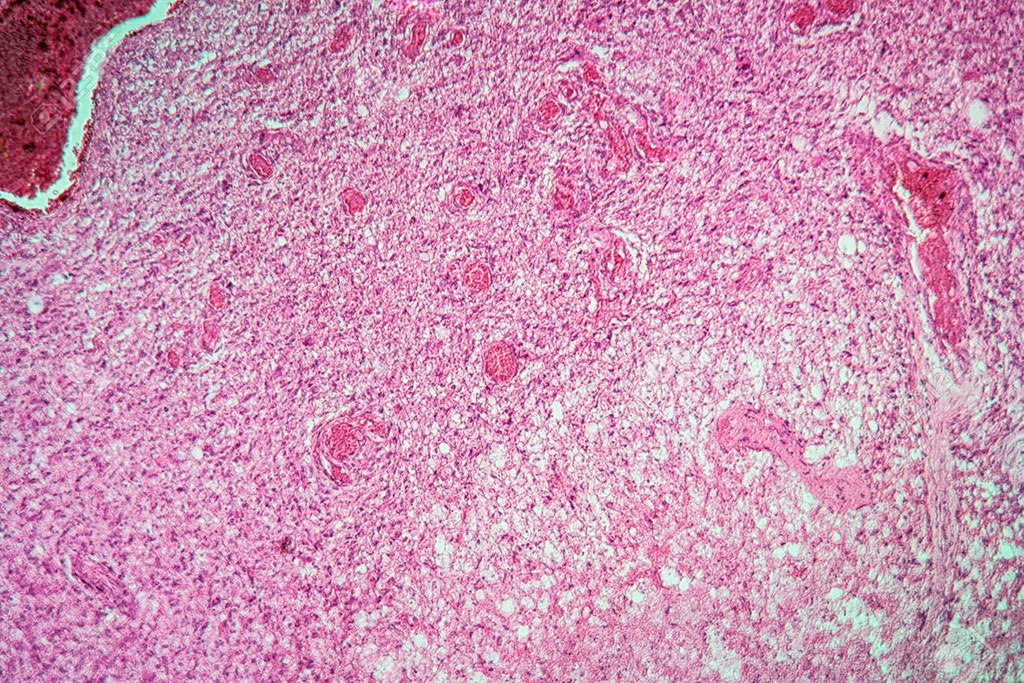
Two Simple Serum Biomarkers Differentiate Lymphoma from Glioma
Two simple serum biomarkers, absolute lymphocyte count and prognostic nutritional index, which are easily derived from routine pre-treatment blood tests, have fair correlation and acceptable diagnostic accuracy for differentiating primary central nervous system lymphoma (PCNSL) from high-grade glioma (HGG) in patients with similar morphology on MRI. More...22 Apr 2022

Neurofilament Light Biomarker Linked With Parkinson's Disease
Parkinson's disease is caused by a loss of nerve cells in part of the brain called the substantia nigra. This leads to a reduction in a chemical called dopamine in the brain. Blood biomarkers may allow earlier identification of Parkinson’s disease (PD), Parkinsonism, and poor PD-related outcomes, such as physical functioning. More...19 Apr 2022
In Other News
Epigenomic Biomarker Predict CAR T-Cell Therapy Resistance in Pediatric Leukemia
Broad Gene Panel Diagnoses Patients With Kidney Disease
First-of-Its-Kind AI-Enabled Service Digitizes Glass Slides to Help Labs Create Digital Pathology Repositories
Genetic Overlap Found for Ovarian Cancer Subtypes and Endometriosis (Cell Reports Medicine: University of Queensland)
Single Cell Characterization Acral Melanoma Identifies Novel Targets for Immunotherapy
New Fluorescent DNA Label Reveals Nanoscopic Cancer Features
AI Platform Identifies 99% of Positive Cancer Cases in Pathology Reports
Inherited Cancer Risk Detected in Significant Subset of Wilms Tumor Cases
Immunohistochemistry Evaluated for Tissue-Invasive Cytomegalovirus in Gastrointestinal Mucosal Biopsies
TTMV-HPV DNA Biomarker Predicts Recurrence of Oropharynx Cancer
Two Important Cardiovascular Disease Risk Factors Operate Independently
Immunoassay Detects Pancreatic Cancer in People at High Risk
First-of-Its-Kind Clinical Blood Test Predicts Cancer Patient’s Response to ICI Immunotherapy
Tintin-Truncating Variant Associated With Late-Onset Dilated Cardiomyopathy
Histological Criteria Predicts Lymphoma Transformation in Bone Marrow Biopsies
Multi-Cancer Early Detection Test Could Become a Game-Changing Screening Tool
Early-Stage Prostate Cancer Detection Blood Test Granted FDA Breakthrough Designation
Cytosponge Biomarker Panel Prioritizes Endoscopic Barrett's Esophagus Surveillance
AI-Powered Diagnostic Platform Improves Early Detection of Esophageal Cancer in Patients with Barrett’s Esophagus
Novel Urinary miRNA Biomarker for Early Detection of Colorectal Cancer
New Method Determines Optimal Number of Pathologists Needed for Correct Disease Diagnosis
Diagnostic Value of Serum CHI3L1 in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Explored
Proteomic Noninvasive Biomarkers Associated with Sport-Related Concussions
The Pathology channel details advances in the field of Surgical Pathology and all its subspecialties, including Cytopathology and its subspecialties.










