Microbiology
Coronavirus Linked to Neurological Disease in Humans
A case-study of fatal encephalitis has, for the first time, led researchers to discover a direct association with strain OC 43 of the human coronavirus (HCoV), providing confirmatory evidence for the hypothesis that this respiratory virus can cause certain neurological diseases of unknown origin such as multiple sclerosis, Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, and encephalitis. More...11 Oct 2016

Quantitative Molecular Diagnostic Methods Identify Causes of Childhood Diarrhea
The number of cases of childhood diarrhea attributed to pathogens such as bacteria, parasites, viruses or other infections has been substantially underestimated and may be nearly twice as high as previous analysis suggests. More...06 Oct 2016
New Technology Quickly Diagnoses Malaria
The gold standard for malaria diagnosis is manual microscopic evaluation of Giemsa stained blood smears; however, the utility of this approach is limited by the skill of an expert microscopist. Further, both the staining process and microscopic examination can be time consuming. More...06 Oct 2016

Extended Multilocus Sequence Typing Developed for Leptospirosis
Leptospirosis is a zoonotic disease caused by pathogenic species of Leptospira that can be carried naturally by most mammalian species and transmission to humans most commonly occurs via direct animal contact or via water contaminated with animal urine. More...05 Oct 2016
Screening for Latent Tuberculosis Infection Recommended
Tuberculosis remains an important preventable disease, including active tuberculosis infection, which may be infectious and latent infection (LTBI), which is asymptomatic and not infectious, but can later reactivate and progress to active disease. More...29 Sep 2016
Field Performance for Rapid Detection of Influenza Virus Analyzed
Clinical differentiation of influenza A virus from infections caused by influenza B virus and the other viruses is unreliable, however effective antiviral treatment is only available for influenza A virus infections and must be administered early in the course of disease to be effective. More...27 Sep 2016
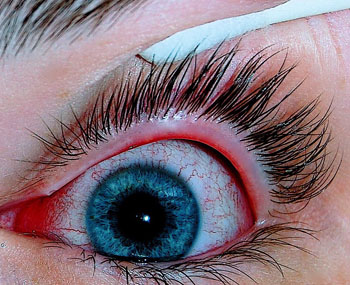
Zika Virus Detected in Conjunctival Fluid
Researchers have found that Zika virus (ZIKV) can be detected in samples of conjunctival fluid from patients with ZIKV infection, suggesting the possibility for a simpler and safer noninvasive test for diagnosis and/or screening than blood testing. The results also add evidence about the cause of conjunctivitis in ZIKV-infected infants with microcephaly. More...26 Sep 2016
In Other News
Test Developed for Healthcare-Acquired Infections Validated
Performance of Field Evaluated Malaria Rapid Diagnostic Tests
Biomarker Outperforms Current Gold Standard to Detect Brain Shunt Infections
Rapid Molecular Diagnostic Test Detects Zika Virus
Urinary Tract Infection Tracked by Routine and Automated Urinalysis
Clostridium Difficile Diagnostic Guidelines Updated
Fatal Fungal Infection Has Unique Growth Patterns
Miniaturized Clinical Test Rapidly Detects Antibiotic Resistance
New Types of African Salmonella Associated with Lethal Infection
Prognostic Biomarkers Predict Dengue Shock and Organ Failure
Two-Gene Panel Differentiates between Pediatric Bacterial and Viral Infections
Innate Immune Sensor of Microbial Proteolysis Revealed
Rapid Diagnostic Test Performance Assessed for Placental Malaria
Latent Toxoplasmosis Prevalence Analyzed Retrospectively
Molecular Testing Accuracy for Clostridium difficile Scrutinized
Simple Test Could Improve TB Diagnosis in Developing Countries
Cell-Free DNA Sequencing Confirms Myelodysplastic Syndrome Diagnosis
Alternative Methods Compared for Urine Culture Collection and Transport
Lateral Flow-Based Antibody Test Developed for Trachoma
Rapid Method Developed for Direct Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing
Rapid Bacterial Infection Test Reduces Antibiotic Use
Increased Risk of HIV Associated with Parasitic Worm Infections
Neutrophil CD64 Index Helps Diagnose Spontaneous Bacterial Peritonitis
The LabMedica Microbiology channel provides the latest news in the fields of epidemiology, bacteriology, virology, and parasitology, all viewed from the unique perspective of Laboratory Medicine.










