Rapid Metagenomics Diagnoses Antibiotic Resistant Bloodstream Infections 18-42 Hours Faster Than Conventional Tests
|
By LabMedica International staff writers Posted on 20 Apr 2023 |

Bloodstream infections can quickly progress to sepsis, multiple organ failure, and even death. Timely and appropriate antibiotic therapy is crucial for managing the infection. Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) poses a significant challenge in treating bloodstream infections. Current clinical methods for identifying the causative pathogen are lengthy and labor-intensive, involving two culture and sensitivity tests that take at least 1 to 3 days to complete—first isolating and identifying the pathogen and then performing antimicrobial susceptibility testing. Now, new research presented at ECCMID 2023 demonstrates that metagenomic sequencing can offer rapid and actionable AMR predictions for treating bloodstream infections much faster than traditional laboratory tests, potentially saving lives and improving antibiotic management.
The study conducted by researchers at the University of Oxford (Oxford, UK) reveals that rapid metagenomics can provide accurate results within just six hours of detecting bacterial growth in a blood sample. Clinical metagenomics sequences all genetic material, including infectious pathogens, in a sample simultaneously, reducing the time spent on running tests, waiting for results, and conducting additional tests. For their study, the Oxford researchers randomly selected 210 positive and 61 negative blood culture specimens for metagenomic sequencing, using the Oxford Nanopore GridION platform to sequence DNA. The sequences were utilized to identify the pathogen species causing infections and to detect common species that can contaminate blood cultures.
Sequencing successfully identified 99% of infecting pathogens, including polymicrobial infections and contaminants, and yielded negative results in 100% of culture-negative samples. In some cases, sequencing detected probable infection causes that routine cultures missed, while in others, it identified uncultivable species when a result could not be determined. Sequencing could also detect antibiotic resistance in the 10 most common infection causes. A total of 741 resistant and 4047 sensitive antibiotic-pathogen combinations were examined, with traditional culture-based testing and sequencing results agreeing 92% of the time. Comparable performance could be achieved using raw reads after just two hours of sequencing, with an overall agreement of 90%. The average time from sample extraction to sequencing was four hours, with complete AMR prediction achieved two hours later, providing actionable AMR results 18-42 hours sooner than conventional laboratory methods.
“Antibiotic resistant bloodstream infections are a leading killer in hospitals, and rapidly starting the right antibiotic saves lives,” said Dr. Kumeren Govender from the John Radcliffe Hospital, University of Oxford, who led the study. “Our results suggests that metagenomics is a powerful tool for the rapid and accurate diagnosis of pathogenic organisms and antimicrobial resistance, allowing for effective treatment 18 to 42 hours earlier than would be possible using standard culture techniques.”
“This is a really exciting breakthrough that means we will be able to diagnose the cause of patients’ infections faster and more completely than has been possible before,” added David Eyre, Professor of Infectious Diseases at the University of Oxford, who co-led the study. “We are working hard to continue to overcome some of the remaining barriers to metagenomic sequencing being used more widely, which include its current high cost, further improving accuracy, and creating improved laboratory expertise in these new technologies and simpler workflows for interpreting results.”
Related Links:
University of Oxford
Latest Microbiology News
- Blood-Based Viral Signature Identified in Crohn’s Disease
- Hidden Gut Viruses Linked to Colorectal Cancer Risk
- Three-Test Panel Launched for Detection of Liver Fluke Infections
- Rapid Test Promises Faster Answers for Drug-Resistant Infections
- CRISPR-Based Technology Neutralizes Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria
- Comprehensive Review Identifies Gut Microbiome Signatures Associated With Alzheimer’s Disease
- AI-Powered Platform Enables Rapid Detection of Drug-Resistant C. Auris Pathogens
- New Test Measures How Effectively Antibiotics Kill Bacteria
- New Antimicrobial Stewardship Standards for TB Care to Optimize Diagnostics
- New UTI Diagnosis Method Delivers Antibiotic Resistance Results 24 Hours Earlier
- Breakthroughs in Microbial Analysis to Enhance Disease Prediction
- Blood-Based Diagnostic Method Could Identify Pediatric LRTIs
- Rapid Diagnostic Test Matches Gold Standard for Sepsis Detection
- Rapid POC Tuberculosis Test Provides Results Within 15 Minutes
- Rapid Assay Identifies Bloodstream Infection Pathogens Directly from Patient Samples
- Blood-Based Molecular Signatures to Enable Rapid EPTB Diagnosis
Channels
Clinical Chemistry
view channelNew Blood Test Index Offers Earlier Detection of Liver Scarring
Metabolic fatty liver disease is highly prevalent and often silent, yet it can progress to fibrosis, cirrhosis, and liver failure. Current first-line blood test scores frequently return indeterminate results,... Read more
Electronic Nose Smells Early Signs of Ovarian Cancer in Blood
Ovarian cancer is often diagnosed at a late stage because its symptoms are vague and resemble those of more common conditions. Unlike breast cancer, there is currently no reliable screening method, and... Read moreMolecular Diagnostics
view channel
Study Uses Blood Samples to Identify Diseases Years Before They Start
Chronic diseases such as lupus, rheumatoid arthritis, Crohn’s disease, colon cancer, and heart failure often develop silently for years before symptoms appear. By the time they are diagnosed, significant... Read more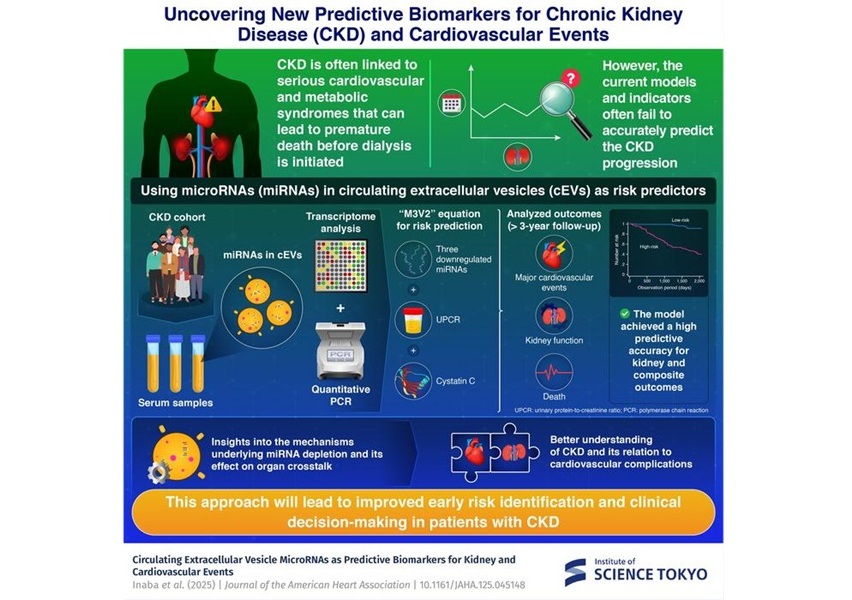
MicroRNA-Based Method Predicts CKD and Cardiovascular Risk
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) affects more than 850 million people worldwide and is a rapidly growing public health threat. Although it progressively damages kidney function, many patients die prematurely... Read moreHematology
view channel
Rapid Cartridge-Based Test Aims to Expand Access to Hemoglobin Disorder Diagnosis
Sickle cell disease and beta thalassemia are hemoglobin disorders that often require referral to specialized laboratories for definitive diagnosis, delaying results for patients and clinicians.... Read more
New Guidelines Aim to Improve AL Amyloidosis Diagnosis
Light chain (AL) amyloidosis is a rare, life-threatening bone marrow disorder in which abnormal amyloid proteins accumulate in organs. Approximately 3,260 people in the United States are diagnosed... Read moreImmunology
view channel
Immune Signature Identified in Treatment-Resistant Myasthenia Gravis
Myasthenia gravis is a rare autoimmune disorder in which immune attack at the neuromuscular junction causes fluctuating weakness that can impair vision, movement, speech, swallowing, and breathing.... Read more
New Biomarker Predicts Chemotherapy Response in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
Triple-negative breast cancer is an aggressive form of breast cancer in which patients often show widely varying responses to chemotherapy. Predicting who will benefit from treatment remains challenging,... Read moreBlood Test Identifies Lung Cancer Patients Who Can Benefit from Immunotherapy Drug
Small cell lung cancer (SCLC) is an aggressive disease with limited treatment options, and even newly approved immunotherapies do not benefit all patients. While immunotherapy can extend survival for some,... Read more
Whole-Genome Sequencing Approach Identifies Cancer Patients Benefitting From PARP-Inhibitor Treatment
Targeted cancer therapies such as PARP inhibitors can be highly effective, but only for patients whose tumors carry specific DNA repair defects. Identifying these patients accurately remains challenging,... Read morePathology
view channel
Molecular Imaging to Reduce Need for Melanoma Biopsies
Melanoma is the deadliest form of skin cancer and accounts for the vast majority of skin cancer-related deaths. Because early melanomas can closely resemble benign moles, clinicians often rely on visual... Read more
Urine Specimen Collection System Improves Diagnostic Accuracy and Efficiency
Urine testing is a critical, non-invasive diagnostic tool used to detect conditions such as pregnancy, urinary tract infections, metabolic disorders, cancer, and kidney disease. However, contaminated or... Read moreTechnology
view channel
AI-Driven Diagnostic Demonstrates High Accuracy in Detecting Periprosthetic Joint Infection
Periprosthetic joint infection (PJI) is a rare but serious complication affecting 1% to 2% of primary joint replacement surgeries. The condition occurs when bacteria or fungi infect tissues around an implanted... Read more
Blood Test “Clocks” Predict Start of Alzheimer’s Symptoms
More than 7 million Americans live with Alzheimer’s disease, and related health and long-term care costs are projected to reach nearly USD 400 billion in 2025. The disease has no cure, and symptoms often... Read moreIndustry
view channel
Cepheid Joins CDC Initiative to Strengthen U.S. Pandemic Testing Preparednesss
Cepheid (Sunnyvale, CA, USA) has been selected by the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) as one of four national collaborators in a federal initiative to speed rapid diagnostic technologies... Read more
QuidelOrtho Collaborates with Lifotronic to Expand Global Immunoassay Portfolio
QuidelOrtho (San Diego, CA, USA) has entered a long-term strategic supply agreement with Lifotronic Technology (Shenzhen, China) to expand its global immunoassay portfolio and accelerate customer access... Read more




















