Next-Gen POC Whole Blood Hemostasis System Recognizes Specific Needs of EDs and ORs 
|
By LabMedica International staff writers Posted on 01 Nov 2022 |
Current hemostatic tests provide only a subset of needed information, or take too long to be useful in critical bleeding situations, forcing clinicians to use iterative transfusion protocols that do not account for the patient’s actual coagulation status. This approach leads to over-transfusion and transfusion of inappropriate products. Up to 60% of red blood cell (RBC) transfusions lack clinical justification. Further, blood products are costly, making up about 1-2% of a hospital’s budget. Hospitals around the world are thus seeking ways to reduce their transfusion rates to improve outcomes and reduce costs.
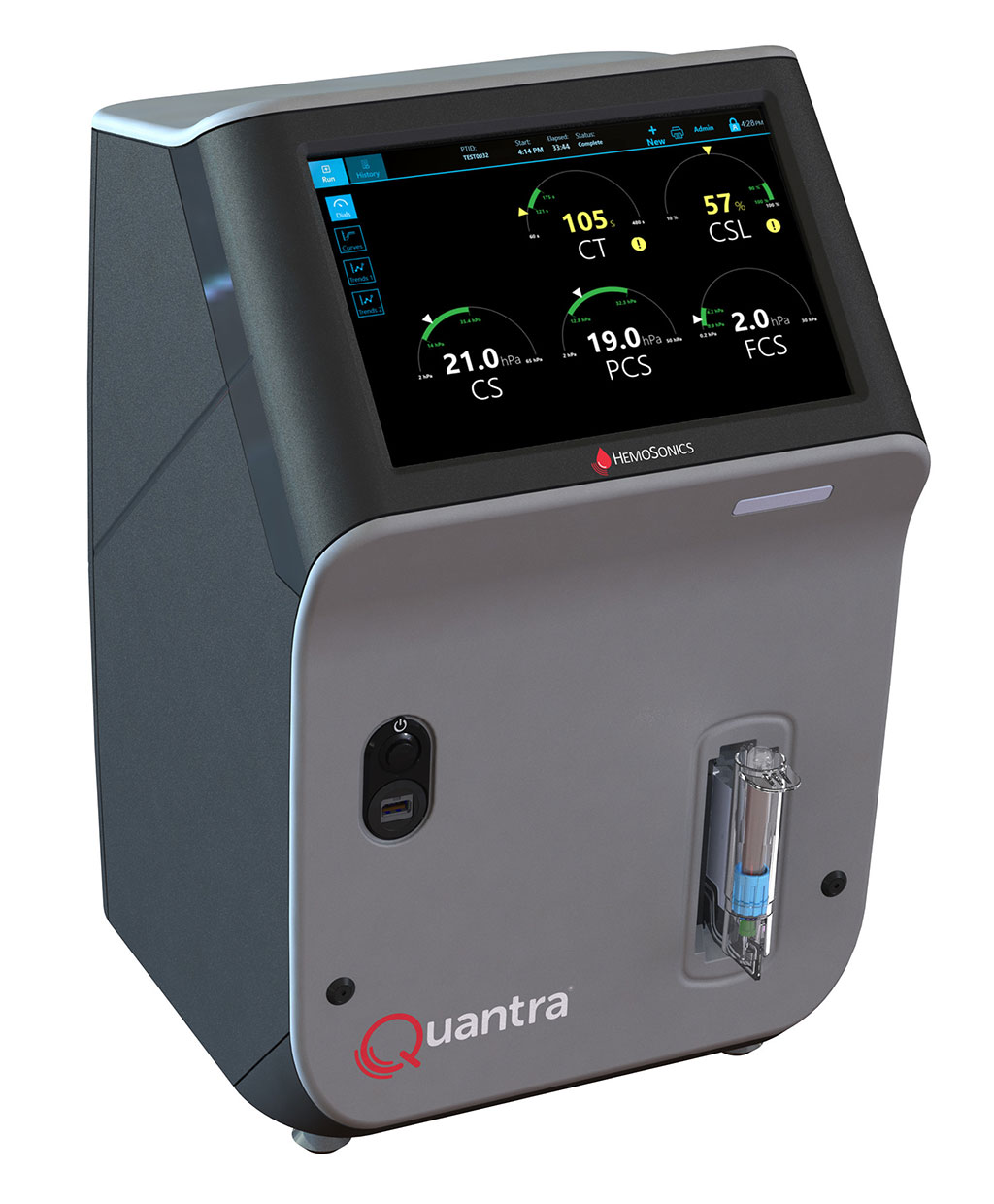
Now, a next-generation point-of-care (POC) hemostasis system leverages innovative medical-grade ultrasound technology to measure the coagulation properties of a whole blood sample. The system enables clinicians to deliver patient-centered coagulation therapy that improves care and optimizes blood product usage. With its rapid results, ease of operation, and dials screen for straightforward interpretation, it is the only whole blood hemostasis testing system specifically cleared for use in POC settings, such as operating rooms, emergency departments, and intensive care units.
HemoSonics, LLC’s (Durham, NC, USA) innovative Quantra hemostasis analyzer platform, based on patented SEER sonorheometry, enables fully automated, rapid point-of-care viscoelastic testing and gives physicians the results they need at the POC to make more informed decisions. SEER uses state-of-the-art ultrasound technology to measure clot stiffness (shear modulus of elasticity) over time using ultrasound-induced resonance. The Quantra system’s innovative closed-cartridge design requires no open-tube blood manipulation after sample collection and it automatically runs internal QC every eight hours and with every test. The Quantra system’s innovative ultrasound technology, proprietary closed-cartridge design, unparalleled ease of use, and ease of interpretation make it uniquely suited for use in critical or emergency care settings.
HemoSonics has now received 510(k) market clearance from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for the Quantra Hemostasis System with QStat Cartridge. The FDA clearance of the QStat Cartridge expands the Quantra System's indications for use to include trauma, and liver transplantation procedures. The QStat Cartridge assay, in addition to the System's already established QPlus Cartridge assay, increases Quantra's overall diagnostic capabilities to now cover the broadest range of clinical indications of any point-of-care hemostasis analyzer available in the U.S. market today.
"The Quantra Hemostasis System with QStat Cartridge is breaking new ground and leading innovation in the point-of-care and laboratory-based whole blood hemostasis testing market. Today's clearance significantly expands the clinical indications of the Quantra System, creating the greatest opportunity to address the critical unmet clinical needs of our healthcare provider partners and the patients that we serve," said Robert Roda, President, and Chief Executive Officer of HemoSonics.
"Point-of-care data is the answer to PBM-guided patient decisions. It is a triple win; Patients get improved outcomes, public health is improved, and cost savings are achieved," said Dr. Bruce Spiess, Medical Director of HemoSonics. "The Quantra Hemostasis System with QStat and QPlus Cartridges will assist more clinicians in determining which specific blood products are needed to rapidly treat individual patients. It has the potential to positively impact patient outcomes for hundreds of thousands of trauma patients and thousands of liver transplant recipients each year by optimizing blood product usage and conserving critically low blood supplies."
Related Links:
HemoSonics, LLC
Latest Point of Care News
Channels
Clinical Chemistry
view channelNew Blood Test Index Offers Earlier Detection of Liver Scarring
Metabolic fatty liver disease is highly prevalent and often silent, yet it can progress to fibrosis, cirrhosis, and liver failure. Current first-line blood test scores frequently return indeterminate results,... Read more
Electronic Nose Smells Early Signs of Ovarian Cancer in Blood
Ovarian cancer is often diagnosed at a late stage because its symptoms are vague and resemble those of more common conditions. Unlike breast cancer, there is currently no reliable screening method, and... Read moreMolecular Diagnostics
view channel
Study Uses Blood Samples to Identify Diseases Years Before They Start
Chronic diseases such as lupus, rheumatoid arthritis, Crohn’s disease, colon cancer, and heart failure often develop silently for years before symptoms appear. By the time they are diagnosed, significant... Read more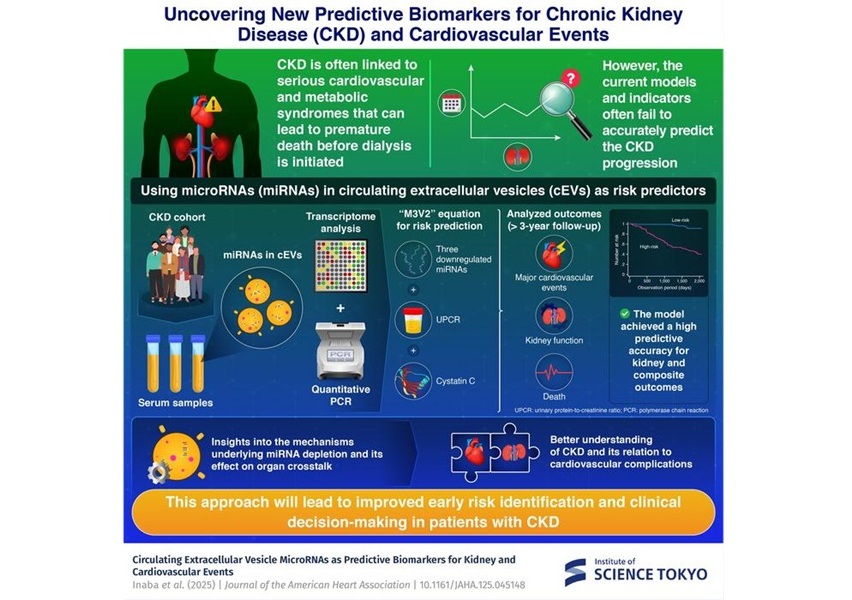
MicroRNA-Based Method Predicts CKD and Cardiovascular Risk
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) affects more than 850 million people worldwide and is a rapidly growing public health threat. Although it progressively damages kidney function, many patients die prematurely... Read moreHematology
view channel
Rapid Cartridge-Based Test Aims to Expand Access to Hemoglobin Disorder Diagnosis
Sickle cell disease and beta thalassemia are hemoglobin disorders that often require referral to specialized laboratories for definitive diagnosis, delaying results for patients and clinicians.... Read more
New Guidelines Aim to Improve AL Amyloidosis Diagnosis
Light chain (AL) amyloidosis is a rare, life-threatening bone marrow disorder in which abnormal amyloid proteins accumulate in organs. Approximately 3,260 people in the United States are diagnosed... Read moreImmunology
view channel
Immune Signature Identified in Treatment-Resistant Myasthenia Gravis
Myasthenia gravis is a rare autoimmune disorder in which immune attack at the neuromuscular junction causes fluctuating weakness that can impair vision, movement, speech, swallowing, and breathing.... Read more
New Biomarker Predicts Chemotherapy Response in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
Triple-negative breast cancer is an aggressive form of breast cancer in which patients often show widely varying responses to chemotherapy. Predicting who will benefit from treatment remains challenging,... Read moreBlood Test Identifies Lung Cancer Patients Who Can Benefit from Immunotherapy Drug
Small cell lung cancer (SCLC) is an aggressive disease with limited treatment options, and even newly approved immunotherapies do not benefit all patients. While immunotherapy can extend survival for some,... Read more
Whole-Genome Sequencing Approach Identifies Cancer Patients Benefitting From PARP-Inhibitor Treatment
Targeted cancer therapies such as PARP inhibitors can be highly effective, but only for patients whose tumors carry specific DNA repair defects. Identifying these patients accurately remains challenging,... Read moreMicrobiology
view channel
Blood-Based Viral Signature Identified in Crohn’s Disease
Crohn’s disease is a chronic inflammatory intestinal disorder affecting approximately 0.4% of the European population, with symptoms and progression that vary widely. Although viral components of the microbiome... Read more
Hidden Gut Viruses Linked to Colorectal Cancer Risk
Colorectal cancer (CRC) remains a leading cause of cancer mortality in many Western countries, and existing risk-stratification approaches leave substantial room for improvement. Although age, diet, and... Read morePathology
view channel
Molecular Imaging to Reduce Need for Melanoma Biopsies
Melanoma is the deadliest form of skin cancer and accounts for the vast majority of skin cancer-related deaths. Because early melanomas can closely resemble benign moles, clinicians often rely on visual... Read more
Urine Specimen Collection System Improves Diagnostic Accuracy and Efficiency
Urine testing is a critical, non-invasive diagnostic tool used to detect conditions such as pregnancy, urinary tract infections, metabolic disorders, cancer, and kidney disease. However, contaminated or... Read moreTechnology
view channel
AI-Driven Diagnostic Demonstrates High Accuracy in Detecting Periprosthetic Joint Infection
Periprosthetic joint infection (PJI) is a rare but serious complication affecting 1% to 2% of primary joint replacement surgeries. The condition occurs when bacteria or fungi infect tissues around an implanted... Read more
Blood Test “Clocks” Predict Start of Alzheimer’s Symptoms
More than 7 million Americans live with Alzheimer’s disease, and related health and long-term care costs are projected to reach nearly USD 400 billion in 2025. The disease has no cure, and symptoms often... Read moreIndustry
view channel
Cepheid Joins CDC Initiative to Strengthen U.S. Pandemic Testing Preparednesss
Cepheid (Sunnyvale, CA, USA) has been selected by the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) as one of four national collaborators in a federal initiative to speed rapid diagnostic technologies... Read more
QuidelOrtho Collaborates with Lifotronic to Expand Global Immunoassay Portfolio
QuidelOrtho (San Diego, CA, USA) has entered a long-term strategic supply agreement with Lifotronic Technology (Shenzhen, China) to expand its global immunoassay portfolio and accelerate customer access... Read more










 (3) (1).png)











