Genetic Alterations Associated with Sporadic Congenital Hydrocephalus
|
By LabMedica International staff writers Posted on 02 Nov 2020 |
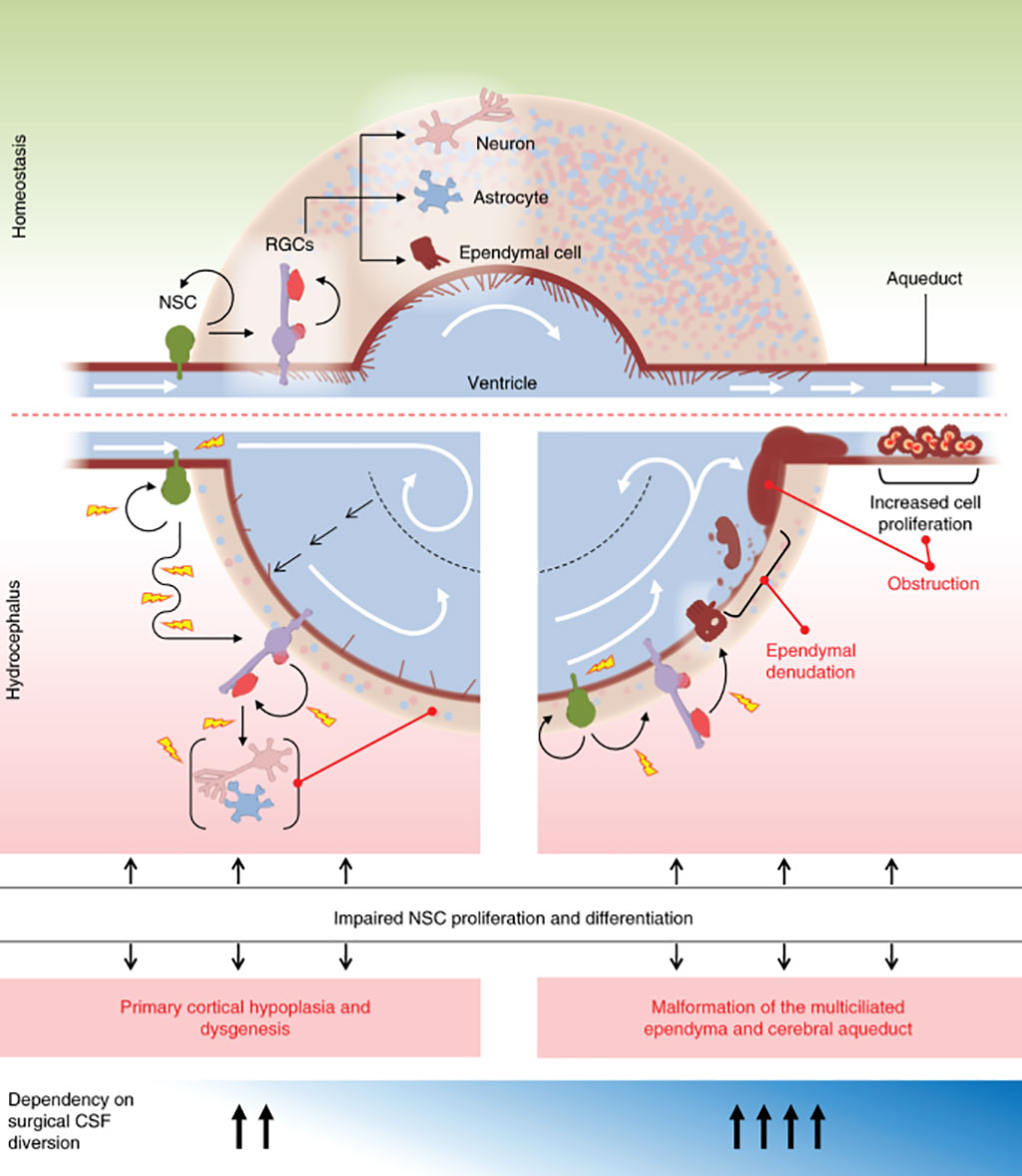
Image: A neural stem cell model of sporadic congenital hydrocephalus (Photo courtesy of Yale University School of Medicine).
Congenital hydrocephalus (CH), characterized by enlarged brain ventricles, is considered a disease of excessive cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) accumulation and thereby treated with neurosurgical CSF diversion with high morbidity and failure rates.
Congenital hydrocephalus is present in the infant prior to birth, meaning the fetus developed hydrocephalus in utero during fetal development. The most common cause of congenital hydrocephalus is aqueductal stenosis, which occurs when the narrow passage between the third and fourth ventricles in the brain is blocked or too narrow to allow sufficient CSF to drain.
A multidisciplinary team at Yale University School of Medicine (New Haven, CT, USA) performed whole-exome sequencing of 381 individuals with sporadic congenital hydrocephalus who were treated with neurosurgery, a cohort that included 232 parent-offspring trios. Another 1,798 trios of unaffected siblings and parents of individuals with autism spectrum disorder were analyzed in parallel as a control group.
The team uncovered 12 genes with two or more de novo mutations each that were predicted to be protein damaging. Five of these genes: TRIM71, SMARCC1, PTEN, PIK3CA, and FOXJ1, had significantly more mutations than expected. The investigators further estimated that about 22% of sporadic congenital hydrocephalus are due to rare, damaging mutations. The teams’ analysis additionally implicated a number of genes in the PI3K signaling pathway in congenital hydrocephalus. These genes regulate cell growth, proliferation, and differentiation in numerous tissues, including developing neural stem cells. In particular, they uncovered three de novo mutations in PI3KCA, three in PTEN, and two in MTOR.
Individuals with mutations in TRIM71, which maintains stem cell pluripotency, are more likely to have cranial nerve defect, non-obstructive inter-hemispheric cysts, and hearing loss. Meanwhile, individuals with mutations in SMARCC1, which regulates gene expression needed for neural stem cell proliferation, differentiation, and survival during telencephalon development, are more likely to have aqueductal stenosis and cardiac and skeletal abnormalities.
All together, the known, high-confidence, and probable risk genes for congenital hydrocephalus converge in gene co-expression networks of the mid-gestational human cortex, In particular, the congenital hydrocephalus risk genes converge on a network previously linked to autism spectrum disorder that is enriched for neuronal differentiation and RNA processing gene ontology terms.
Kristopher T. Kahle, MD, PhD, an assistant professor of neurosurgery and a senior author of the study, said, “It is possible that some of the neurological problems that many of these congenital hydrocephalus patients have may not be due to inadequately working shunts, but are in fact neurodevelopmental sequelae of a genetic condition that alters neuronal function.”
The authors concluded that that genetic disruptions affecting early brain development may drive sporadic congenital hydrocephalus. Their data implicate genetically encoded neural stem cell dysregulation and an associated impairment of fetal neurogliogenesis as primary pathophysiological events in a significant number of congenital hydrocephalus cases. The study was published on October 19, 2020 in the journal Nature Medicine.
Related Links:
Yale University School of Medicine
Congenital hydrocephalus is present in the infant prior to birth, meaning the fetus developed hydrocephalus in utero during fetal development. The most common cause of congenital hydrocephalus is aqueductal stenosis, which occurs when the narrow passage between the third and fourth ventricles in the brain is blocked or too narrow to allow sufficient CSF to drain.
A multidisciplinary team at Yale University School of Medicine (New Haven, CT, USA) performed whole-exome sequencing of 381 individuals with sporadic congenital hydrocephalus who were treated with neurosurgery, a cohort that included 232 parent-offspring trios. Another 1,798 trios of unaffected siblings and parents of individuals with autism spectrum disorder were analyzed in parallel as a control group.
The team uncovered 12 genes with two or more de novo mutations each that were predicted to be protein damaging. Five of these genes: TRIM71, SMARCC1, PTEN, PIK3CA, and FOXJ1, had significantly more mutations than expected. The investigators further estimated that about 22% of sporadic congenital hydrocephalus are due to rare, damaging mutations. The teams’ analysis additionally implicated a number of genes in the PI3K signaling pathway in congenital hydrocephalus. These genes regulate cell growth, proliferation, and differentiation in numerous tissues, including developing neural stem cells. In particular, they uncovered three de novo mutations in PI3KCA, three in PTEN, and two in MTOR.
Individuals with mutations in TRIM71, which maintains stem cell pluripotency, are more likely to have cranial nerve defect, non-obstructive inter-hemispheric cysts, and hearing loss. Meanwhile, individuals with mutations in SMARCC1, which regulates gene expression needed for neural stem cell proliferation, differentiation, and survival during telencephalon development, are more likely to have aqueductal stenosis and cardiac and skeletal abnormalities.
All together, the known, high-confidence, and probable risk genes for congenital hydrocephalus converge in gene co-expression networks of the mid-gestational human cortex, In particular, the congenital hydrocephalus risk genes converge on a network previously linked to autism spectrum disorder that is enriched for neuronal differentiation and RNA processing gene ontology terms.
Kristopher T. Kahle, MD, PhD, an assistant professor of neurosurgery and a senior author of the study, said, “It is possible that some of the neurological problems that many of these congenital hydrocephalus patients have may not be due to inadequately working shunts, but are in fact neurodevelopmental sequelae of a genetic condition that alters neuronal function.”
The authors concluded that that genetic disruptions affecting early brain development may drive sporadic congenital hydrocephalus. Their data implicate genetically encoded neural stem cell dysregulation and an associated impairment of fetal neurogliogenesis as primary pathophysiological events in a significant number of congenital hydrocephalus cases. The study was published on October 19, 2020 in the journal Nature Medicine.
Related Links:
Yale University School of Medicine
Latest Pathology News
- AI Tool Predicts Chemotherapy Response from Biopsy Slides
- Sex Differences in Alzheimer’s Biomarkers Linked to Faster Cognitive Decline
- World’s First Optical Microneedle Device to Enable Blood-Sampling-Free Clinical Testing
- Novel mcPCR Technology to Transform Testing of Clinical Samples
- Pathogen-Agnostic Testing Reveals Hidden Respiratory Threats in Negative Samples
- Molecular Imaging to Reduce Need for Melanoma Biopsies
- Urine Specimen Collection System Improves Diagnostic Accuracy and Efficiency
- AI-Powered 3D Scanning System Speeds Cancer Screening
- Single Sample Classifier Predicts Cancer-Associated Fibroblast Subtypes in Patient Samples
- New AI-Driven Platform Standardizes Tuberculosis Smear Microscopy Workflow
- AI Tool Uses Blood Biomarkers to Predict Transplant Complications Before Symptoms Appear
- High-Resolution Cancer Virus Imaging Uncovers Potential Therapeutic Targets
- Research Consortium Harnesses AI and Spatial Biology to Advance Cancer Discovery
- AI Tool Helps See How Cells Work Together Inside Diseased Tissue
- AI-Powered Microscope Diagnoses Malaria in Blood Smears Within Minutes
- Engineered Yeast Cells Enable Rapid Testing of Cancer Immunotherapy
Channels
Clinical Chemistry
view channel
AI Sensor Detects Neurological Disorders Using Single Saliva Drop
Neurological disorders such as Parkinson’s disease and Alzheimer’s disease often develop gradually and present subtle symptoms in their early stages. Because early signs are frequently vague or atypical,... Read moreNew Blood Test Index Offers Earlier Detection of Liver Scarring
Metabolic fatty liver disease is highly prevalent and often silent, yet it can progress to fibrosis, cirrhosis, and liver failure. Current first-line blood test scores frequently return indeterminate results,... Read moreHematology
view channel
Rapid Cartridge-Based Test Aims to Expand Access to Hemoglobin Disorder Diagnosis
Sickle cell disease and beta thalassemia are hemoglobin disorders that often require referral to specialized laboratories for definitive diagnosis, delaying results for patients and clinicians.... Read more
New Guidelines Aim to Improve AL Amyloidosis Diagnosis
Light chain (AL) amyloidosis is a rare, life-threatening bone marrow disorder in which abnormal amyloid proteins accumulate in organs. Approximately 3,260 people in the United States are diagnosed... Read moreImmunology
view channel
Cancer Mutation ‘Fingerprints’ to Improve Prediction of Immunotherapy Response
Cancer cells accumulate thousands of genetic mutations, but not all mutations affect tumors in the same way. Some make cancer cells more visible to the immune system, while others allow tumors to evade... Read more
Immune Signature Identified in Treatment-Resistant Myasthenia Gravis
Myasthenia gravis is a rare autoimmune disorder in which immune attack at the neuromuscular junction causes fluctuating weakness that can impair vision, movement, speech, swallowing, and breathing.... Read more
New Biomarker Predicts Chemotherapy Response in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
Triple-negative breast cancer is an aggressive form of breast cancer in which patients often show widely varying responses to chemotherapy. Predicting who will benefit from treatment remains challenging,... Read moreBlood Test Identifies Lung Cancer Patients Who Can Benefit from Immunotherapy Drug
Small cell lung cancer (SCLC) is an aggressive disease with limited treatment options, and even newly approved immunotherapies do not benefit all patients. While immunotherapy can extend survival for some,... Read moreMicrobiology
view channel
New Imaging Approach Could Help Predict Dangerous Gut Infection
Clostridioides difficile infections affect roughly half a million people in the United States each year and are a leading cause of infectious diarrhea in healthcare settings. The bacterium can trigger... Read more
Rapid Sequencing Could Transform Tuberculosis Care
Tuberculosis remains the world’s leading cause of death from a single infectious agent, responsible for more than one million deaths each year. Diagnosing and monitoring the disease can be slow because... Read morePathology
view channel
Novel mcPCR Technology to Transform Testing of Clinical Samples
DNA methylation is an important biological marker used in the diagnosis and monitoring of many diseases, including cancer. These chemical modifications to DNA influence gene activity and can reveal early... Read more
Sex Differences in Alzheimer’s Biomarkers Linked to Faster Cognitive Decline
Sex differences in Alzheimer’s disease present ongoing diagnostic challenges, with women often experiencing a disproportionate disease burden even when preclinical amyloid-beta levels are similar to men.... Read moreTechnology
view channel
AI Model Outperforms Clinicians in Rare Disease Detection
Rare diseases affect an estimated 300 million people worldwide, yet diagnosis is often protracted and error-prone. Many conditions present with heterogeneous signs that overlap with common disorders, leading... Read more
AI-Driven Diagnostic Demonstrates High Accuracy in Detecting Periprosthetic Joint Infection
Periprosthetic joint infection (PJI) is a rare but serious complication affecting 1% to 2% of primary joint replacement surgeries. The condition occurs when bacteria or fungi infect tissues around an implanted... Read moreIndustry
view channel
Cepheid Joins CDC Initiative to Strengthen U.S. Pandemic Testing Preparednesss
Cepheid (Sunnyvale, CA, USA) has been selected by the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) as one of four national collaborators in a federal initiative to speed rapid diagnostic technologies... Read more
QuidelOrtho Collaborates with Lifotronic to Expand Global Immunoassay Portfolio
QuidelOrtho (San Diego, CA, USA) has entered a long-term strategic supply agreement with Lifotronic Technology (Shenzhen, China) to expand its global immunoassay portfolio and accelerate customer access... Read more




















