Mycobacterium Infection Found in Gastric Patients’ Stomachs
|
By LabMedica International staff writers Posted on 26 Nov 2019 |
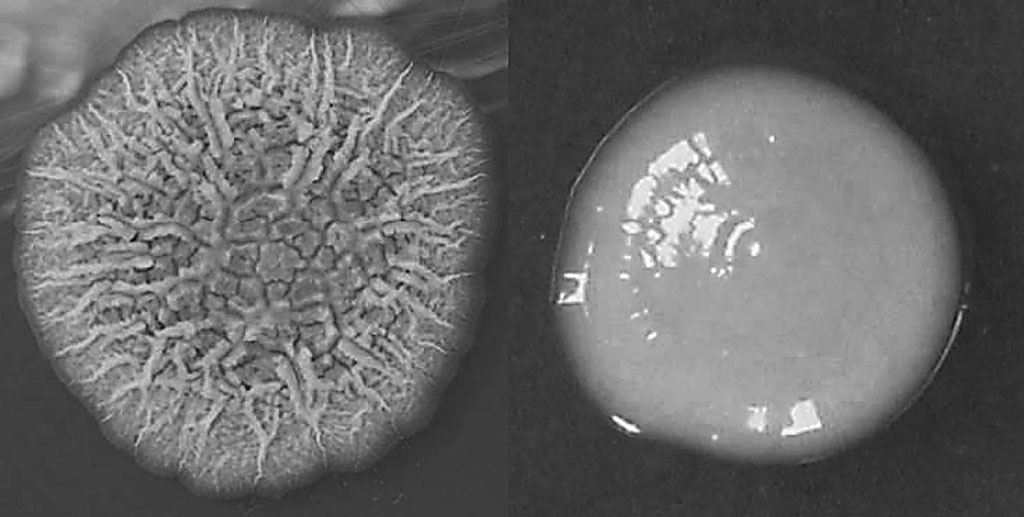
Image: Growth characteristics of rough and smooth phenotypes of Mycobacterium abscessus on 7H11 agar cultured at 37 °C: representative single rough (left) and smooth (right) colonies (Photo courtesy of Hannover Medical School)
Development of gastric diseases such as gastritis, peptic ulcer and gastric cancer is often associated with several biotic and abiotic factors. Helicobacter pylori infection is such a well-known biotic factor. However, not all H. pylori-infected individuals develop gastric diseases and not all individuals with gastric diseases are infected with H. pylori.
H. pylori is not the only bacterium that can colonize human stomach. Culture independent metagenomic sequence analyses have shown that human stomach carries a unique microbiota. The dominant phyla that are present in human stomach are Proteobacteria, Firmicutes, Actinobacteria and Fusobacterium. Interestingly, however, most of these bacteria cannot be cultured using traditional techniques.
Microbiologists at the Rajiv Gandhi Centre for Biotechnology (Thiruvananthapuram, India) recruited patients aged between 20 and 70 with various gastric and esophageal symptoms ranging from mild dyspepsia, gastro-esophageal reflux disorder to severe gastric diseases like gastric cancer and who were recommended to have upper gastrointestinal endoscopy. Three gastric biopsy specimens were collected from each patient for this study. The aim of this study was to isolate prevalent gastric bacteria under microaerobic condition and identify them by 16S rRNA gene sequence analysis.
The team employed various technologies including gastric bacteria culture, bacterial DNA isolation, extraction of intracellular bacterial DNA from biopsy tissues, molecular characterization of the bacteria isolated from stomach. The purified DNA fragments were sequenced by a 3730XL DNA analyzer (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, Massachusetts, USA). The team also performed Hematoxylin and Eosin (H&E) and Ziehl-Neelsen Acid-fast staining on tissue biopsies, and immunohistochemistry.
Analysis of gastric biopsies showed infection of Mycobacterium abscessus (phylum Actinobacteria) to be highly prevalent in the stomachs of subjects included. The data showed that of 129 (67 male and 62 female) patients with gastric symptoms, 96 (51 male and 45 female) showed the presence of M. abscessus in stomach tissues. Infection of M. abscessus in gastric epithelium was further confirmed by imaging with acid fast staining, immunohistochemistry and immunofluorescence. Surprisingly, the subjects studied, the prevalence of M. abscessus infection in stomach is even higher than the prevalence of H. pylori infection.
The authors concluded that their study on 129 individuals with gastric diseases shows that the prevalence of gastric M. abscessus is higher in the local population as compared to the prevalence of H. pylori. The route of transmission is not known at present, but water could be a source. Significance of this infection is also presently unknown, but it may have a significant role in the formation or progression of gastric disease. The study was published on November 4, 2019 in the journal PLOS Neglected Tropical Diseases.
Related Links:
Rajiv Gandhi Centre for Biotechnology
Thermo Fisher Scientific
H. pylori is not the only bacterium that can colonize human stomach. Culture independent metagenomic sequence analyses have shown that human stomach carries a unique microbiota. The dominant phyla that are present in human stomach are Proteobacteria, Firmicutes, Actinobacteria and Fusobacterium. Interestingly, however, most of these bacteria cannot be cultured using traditional techniques.
Microbiologists at the Rajiv Gandhi Centre for Biotechnology (Thiruvananthapuram, India) recruited patients aged between 20 and 70 with various gastric and esophageal symptoms ranging from mild dyspepsia, gastro-esophageal reflux disorder to severe gastric diseases like gastric cancer and who were recommended to have upper gastrointestinal endoscopy. Three gastric biopsy specimens were collected from each patient for this study. The aim of this study was to isolate prevalent gastric bacteria under microaerobic condition and identify them by 16S rRNA gene sequence analysis.
The team employed various technologies including gastric bacteria culture, bacterial DNA isolation, extraction of intracellular bacterial DNA from biopsy tissues, molecular characterization of the bacteria isolated from stomach. The purified DNA fragments were sequenced by a 3730XL DNA analyzer (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, Massachusetts, USA). The team also performed Hematoxylin and Eosin (H&E) and Ziehl-Neelsen Acid-fast staining on tissue biopsies, and immunohistochemistry.
Analysis of gastric biopsies showed infection of Mycobacterium abscessus (phylum Actinobacteria) to be highly prevalent in the stomachs of subjects included. The data showed that of 129 (67 male and 62 female) patients with gastric symptoms, 96 (51 male and 45 female) showed the presence of M. abscessus in stomach tissues. Infection of M. abscessus in gastric epithelium was further confirmed by imaging with acid fast staining, immunohistochemistry and immunofluorescence. Surprisingly, the subjects studied, the prevalence of M. abscessus infection in stomach is even higher than the prevalence of H. pylori infection.
The authors concluded that their study on 129 individuals with gastric diseases shows that the prevalence of gastric M. abscessus is higher in the local population as compared to the prevalence of H. pylori. The route of transmission is not known at present, but water could be a source. Significance of this infection is also presently unknown, but it may have a significant role in the formation or progression of gastric disease. The study was published on November 4, 2019 in the journal PLOS Neglected Tropical Diseases.
Related Links:
Rajiv Gandhi Centre for Biotechnology
Thermo Fisher Scientific
Latest Molecular Diagnostics News
- Study Uses Blood Samples to Identify Diseases Years Before They Start
- MicroRNA-Based Method Predicts CKD and Cardiovascular Risk
- Swab Test Helps Transplant Patients Receive Right Anti-Rejection Medication Dose
- Blood Test Predicts Which Bladder Cancer Patients May Safely Skip Surgery
- Ultra-Sensitive DNA Test Identifies Relapse Risk in Aggressive Leukemia
- Blood Test Could Help Detect Gallbladder Cancer Earlier
- New Blood Test Score Detects Hidden Alcohol-Related Liver Disease
- New Blood Test Predicts Who Will Most Likely Live Longer
- Genetic Test Predicts Radiation Therapy Risk for Prostate Cancer Patients
- Genetic Test Aids Early Detection and Improved Treatment for Cancers
- New Genome Sequencing Technique Measures Epstein-Barr Virus in Blood
- Blood Test Boosts Early Detection of Brain Cancer
- Molecular Monitoring Approach Helps Bladder Cancer Patients Avoid Surgery
- Genetic Tests to Speed Diagnosis of Lymphatic Disorders
- Changes In Lymphatic Vessels Can Aid Early Identification of Aggressive Oral Cancer
- New Extraction Kit Enables Consistent, Scalable cfDNA Isolation from Multiple Biofluids
Channels
Clinical Chemistry
view channelNew Blood Test Index Offers Earlier Detection of Liver Scarring
Metabolic fatty liver disease is highly prevalent and often silent, yet it can progress to fibrosis, cirrhosis, and liver failure. Current first-line blood test scores frequently return indeterminate results,... Read more
Electronic Nose Smells Early Signs of Ovarian Cancer in Blood
Ovarian cancer is often diagnosed at a late stage because its symptoms are vague and resemble those of more common conditions. Unlike breast cancer, there is currently no reliable screening method, and... Read moreMolecular Diagnostics
view channel
Study Uses Blood Samples to Identify Diseases Years Before They Start
Chronic diseases such as lupus, rheumatoid arthritis, Crohn’s disease, colon cancer, and heart failure often develop silently for years before symptoms appear. By the time they are diagnosed, significant... Read more
MicroRNA-Based Method Predicts CKD and Cardiovascular Risk
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) affects more than 850 million people worldwide and is a rapidly growing public health threat. Although it progressively damages kidney function, many patients die prematurely... Read moreHematology
view channel
Rapid Cartridge-Based Test Aims to Expand Access to Hemoglobin Disorder Diagnosis
Sickle cell disease and beta thalassemia are hemoglobin disorders that often require referral to specialized laboratories for definitive diagnosis, delaying results for patients and clinicians.... Read more
New Guidelines Aim to Improve AL Amyloidosis Diagnosis
Light chain (AL) amyloidosis is a rare, life-threatening bone marrow disorder in which abnormal amyloid proteins accumulate in organs. Approximately 3,260 people in the United States are diagnosed... Read moreImmunology
view channel
Immune Signature Identified in Treatment-Resistant Myasthenia Gravis
Myasthenia gravis is a rare autoimmune disorder in which immune attack at the neuromuscular junction causes fluctuating weakness that can impair vision, movement, speech, swallowing, and breathing.... Read more
New Biomarker Predicts Chemotherapy Response in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
Triple-negative breast cancer is an aggressive form of breast cancer in which patients often show widely varying responses to chemotherapy. Predicting who will benefit from treatment remains challenging,... Read moreBlood Test Identifies Lung Cancer Patients Who Can Benefit from Immunotherapy Drug
Small cell lung cancer (SCLC) is an aggressive disease with limited treatment options, and even newly approved immunotherapies do not benefit all patients. While immunotherapy can extend survival for some,... Read more
Whole-Genome Sequencing Approach Identifies Cancer Patients Benefitting From PARP-Inhibitor Treatment
Targeted cancer therapies such as PARP inhibitors can be highly effective, but only for patients whose tumors carry specific DNA repair defects. Identifying these patients accurately remains challenging,... Read morePathology
view channel
Molecular Imaging to Reduce Need for Melanoma Biopsies
Melanoma is the deadliest form of skin cancer and accounts for the vast majority of skin cancer-related deaths. Because early melanomas can closely resemble benign moles, clinicians often rely on visual... Read more
Urine Specimen Collection System Improves Diagnostic Accuracy and Efficiency
Urine testing is a critical, non-invasive diagnostic tool used to detect conditions such as pregnancy, urinary tract infections, metabolic disorders, cancer, and kidney disease. However, contaminated or... Read moreTechnology
view channel
AI-Driven Diagnostic Demonstrates High Accuracy in Detecting Periprosthetic Joint Infection
Periprosthetic joint infection (PJI) is a rare but serious complication affecting 1% to 2% of primary joint replacement surgeries. The condition occurs when bacteria or fungi infect tissues around an implanted... Read more
Blood Test “Clocks” Predict Start of Alzheimer’s Symptoms
More than 7 million Americans live with Alzheimer’s disease, and related health and long-term care costs are projected to reach nearly USD 400 billion in 2025. The disease has no cure, and symptoms often... Read moreIndustry
view channel
Cepheid Joins CDC Initiative to Strengthen U.S. Pandemic Testing Preparednesss
Cepheid (Sunnyvale, CA, USA) has been selected by the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) as one of four national collaborators in a federal initiative to speed rapid diagnostic technologies... Read more
QuidelOrtho Collaborates with Lifotronic to Expand Global Immunoassay Portfolio
QuidelOrtho (San Diego, CA, USA) has entered a long-term strategic supply agreement with Lifotronic Technology (Shenzhen, China) to expand its global immunoassay portfolio and accelerate customer access... Read more




















