Novel Nanosensing Technologies Developed for Exosome Detection and Profiling
|
By LabMedica International staff writers Posted on 20 Nov 2019 |
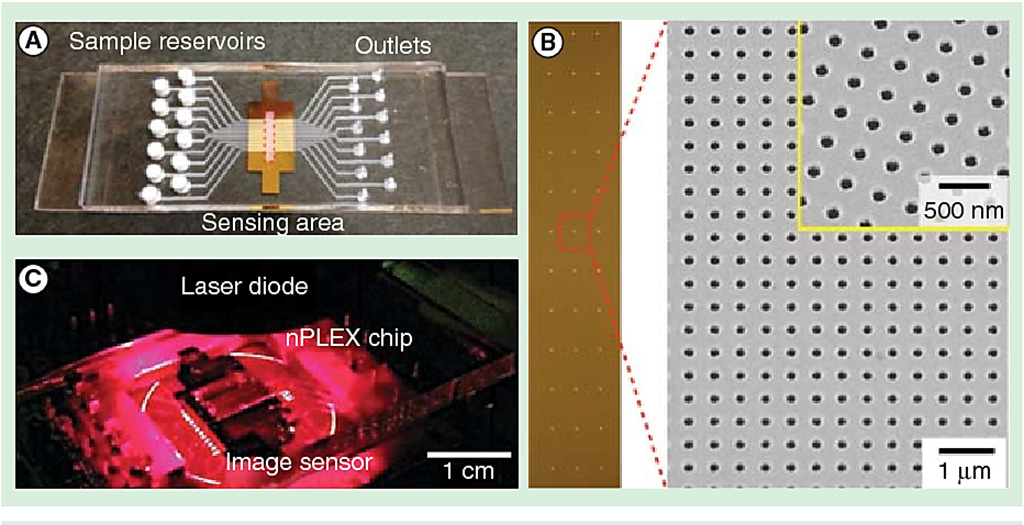
Image: The nano-plasmonic exosome (nPLEX) sensor (Photo courtesy of Massachusetts General Hospital).
Exosomes are extracellular vesicles (EVs) that are produced in the endosomal compartment of most eukaryotic cells. Liquid biopsy technologies have been developed to do high-throughput exosome protein profiling and point-of-care (POC) exosome analysis.
The aim is to develop multiplexed assay systems to streamline the analysis of exosomes and evaluate their clinical utility for cancer management, both as diagnostic tools and to predict disease recurrence. Nanoplasmonic sensors are fabricated to accommodate at most one exosome and individually imaged in real time, enabling the label-free recording of digital responses in a highly multiplexed geometry.
Scientists at the Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH, Boston, MA, USA) and their colleagues developed the nano-plasmonic exosome (nPLEX) sensor, in routine use at MGH, which detects exosome protein levels based on “spectral shifts” (intensity changes) of light through thousands of optimally spaced 200-nanometer (nm) holes. Antibodies against cancer biomarkers get immobilized on the nanopores for capture.
Nanoholes on the sensor are gold and exosomes are labeled by gold nanoparticles for signal amplification. Gold has proven to have the best chemical stability for this type of assay. The device is being manufactured on a glass-based substrate, as silicon wafers proved to be too fragile. The iMEX (integrated magnetic-electrochemical exosome) device, meanwhile, integrates vesicle isolation and detection in a single platform. Target-specific exosomes first get enriched through immunomagnetic selection, for high detection sensitivity. The sensors can be miniaturized and expanded for parallel measurements.
The nPLEX has demonstrated good accuracy and 100 times greater sensitivity than the commonly used enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) and able to detect as few as 3,000 exosomes. The team has also come up with a protein signature for pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) that is powerful enough for diagnostic purposes, a combination of EGFR (epidermal growth factor receptor), EpCAM, MUC1, GPC1 and WNT2. As demonstrated in a prospective study involving more than 100 patients and age-matched controls, as the tumors shrink the biomarker combination gets lower and lower.
The scientists have also used nPLEX technology to show how exosome protein expression of cancer cells changes with drug treatment. Discovery of these unique, drug-dependent protein signatures suggests the exosome screening assay will be a potentially powerful molecular screening tool. Hyungsoon Im, PhD, an assistant professor of radiology and a senior author of the study, said, “The screening assay could be incorporated into point–of–care (POC) instruments for more rigorous testing of different drugs in different settings. The study was presented at the 2019 Next Generation Dx Summit held August 20-22, 2019 in Washington, DC, USA.
Related Links:
Massachusetts General Hospital
The aim is to develop multiplexed assay systems to streamline the analysis of exosomes and evaluate their clinical utility for cancer management, both as diagnostic tools and to predict disease recurrence. Nanoplasmonic sensors are fabricated to accommodate at most one exosome and individually imaged in real time, enabling the label-free recording of digital responses in a highly multiplexed geometry.
Scientists at the Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH, Boston, MA, USA) and their colleagues developed the nano-plasmonic exosome (nPLEX) sensor, in routine use at MGH, which detects exosome protein levels based on “spectral shifts” (intensity changes) of light through thousands of optimally spaced 200-nanometer (nm) holes. Antibodies against cancer biomarkers get immobilized on the nanopores for capture.
Nanoholes on the sensor are gold and exosomes are labeled by gold nanoparticles for signal amplification. Gold has proven to have the best chemical stability for this type of assay. The device is being manufactured on a glass-based substrate, as silicon wafers proved to be too fragile. The iMEX (integrated magnetic-electrochemical exosome) device, meanwhile, integrates vesicle isolation and detection in a single platform. Target-specific exosomes first get enriched through immunomagnetic selection, for high detection sensitivity. The sensors can be miniaturized and expanded for parallel measurements.
The nPLEX has demonstrated good accuracy and 100 times greater sensitivity than the commonly used enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) and able to detect as few as 3,000 exosomes. The team has also come up with a protein signature for pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) that is powerful enough for diagnostic purposes, a combination of EGFR (epidermal growth factor receptor), EpCAM, MUC1, GPC1 and WNT2. As demonstrated in a prospective study involving more than 100 patients and age-matched controls, as the tumors shrink the biomarker combination gets lower and lower.
The scientists have also used nPLEX technology to show how exosome protein expression of cancer cells changes with drug treatment. Discovery of these unique, drug-dependent protein signatures suggests the exosome screening assay will be a potentially powerful molecular screening tool. Hyungsoon Im, PhD, an assistant professor of radiology and a senior author of the study, said, “The screening assay could be incorporated into point–of–care (POC) instruments for more rigorous testing of different drugs in different settings. The study was presented at the 2019 Next Generation Dx Summit held August 20-22, 2019 in Washington, DC, USA.
Related Links:
Massachusetts General Hospital
Latest Molecular Diagnostics News
- World’s First Portable POC Test Simultaneously Detects Four Common STIs in One Hour
- Simple One-Hour Saliva Test Detects Common Cancers
- Blood Test Could Help Guide Treatment Decisions in Germ Cell Tumors
- Blood Test Could Spot Common Post-Surgery Condition Early
- New Blood Test Can Help Predict Testicular Cancer Recurrence
- New Test Detects Alzheimer’s by Analyzing Altered Protein Shapes in Blood
- New Diagnostic Markers for Multiple Sclerosis Discovered in Cerebrospinal Fluid
- Cell-Free DNA Predicts Bloodstream Infections in Children with Leukemia
- Study Uses Blood Samples to Identify Diseases Years Before They Start
- MicroRNA-Based Method Predicts CKD and Cardiovascular Risk
- Swab Test Helps Transplant Patients Receive Right Anti-Rejection Medication Dose
- Blood Test Predicts Which Bladder Cancer Patients May Safely Skip Surgery
- Ultra-Sensitive DNA Test Identifies Relapse Risk in Aggressive Leukemia
- Blood Test Could Help Detect Gallbladder Cancer Earlier
- New Blood Test Score Detects Hidden Alcohol-Related Liver Disease
- New Blood Test Predicts Who Will Most Likely Live Longer
Channels
Clinical Chemistry
view channel
AI Sensor Detects Neurological Disorders Using Single Saliva Drop
Neurological disorders such as Parkinson’s disease and Alzheimer’s disease often develop gradually and present subtle symptoms in their early stages. Because early signs are frequently vague or atypical,... Read moreNew Blood Test Index Offers Earlier Detection of Liver Scarring
Metabolic fatty liver disease is highly prevalent and often silent, yet it can progress to fibrosis, cirrhosis, and liver failure. Current first-line blood test scores frequently return indeterminate results,... Read moreMolecular Diagnostics
view channel
World’s First Portable POC Test Simultaneously Detects Four Common STIs in One Hour
Sexually transmitted infections (STIs) often present with similar symptoms, making accurate diagnosis challenging without laboratory testing. Delays in identifying the exact infection can lead to inappropriate... Read more
Simple One-Hour Saliva Test Detects Common Cancers
Early detection is critical for improving cancer outcomes, yet many diagnostic tests rely on invasive procedures such as blood draws or biopsies. Researchers are exploring simpler approaches that could... Read moreHematology
view channel
Rapid Cartridge-Based Test Aims to Expand Access to Hemoglobin Disorder Diagnosis
Sickle cell disease and beta thalassemia are hemoglobin disorders that often require referral to specialized laboratories for definitive diagnosis, delaying results for patients and clinicians.... Read more
New Guidelines Aim to Improve AL Amyloidosis Diagnosis
Light chain (AL) amyloidosis is a rare, life-threatening bone marrow disorder in which abnormal amyloid proteins accumulate in organs. Approximately 3,260 people in the United States are diagnosed... Read moreImmunology
view channel
Cancer Mutation ‘Fingerprints’ to Improve Prediction of Immunotherapy Response
Cancer cells accumulate thousands of genetic mutations, but not all mutations affect tumors in the same way. Some make cancer cells more visible to the immune system, while others allow tumors to evade... Read more
Immune Signature Identified in Treatment-Resistant Myasthenia Gravis
Myasthenia gravis is a rare autoimmune disorder in which immune attack at the neuromuscular junction causes fluctuating weakness that can impair vision, movement, speech, swallowing, and breathing.... Read more
New Biomarker Predicts Chemotherapy Response in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
Triple-negative breast cancer is an aggressive form of breast cancer in which patients often show widely varying responses to chemotherapy. Predicting who will benefit from treatment remains challenging,... Read moreBlood Test Identifies Lung Cancer Patients Who Can Benefit from Immunotherapy Drug
Small cell lung cancer (SCLC) is an aggressive disease with limited treatment options, and even newly approved immunotherapies do not benefit all patients. While immunotherapy can extend survival for some,... Read moreMicrobiology
view channel
WHO Recommends Near POC Tests, Tongue Swabs and Sputum Pooling for TB Diagnosis
Tuberculosis (TB) remains one of the world’s leading infectious disease killers, yet millions of cases go undiagnosed or are detected too late. Barriers such as reliance on sputum samples, limited laboratory... Read more
New Imaging Approach Could Help Predict Dangerous Gut Infection
Clostridioides difficile infections affect roughly half a million people in the United States each year and are a leading cause of infectious diarrhea in healthcare settings. The bacterium can trigger... Read morePathology
view channel
Novel mcPCR Technology to Transform Testing of Clinical Samples
DNA methylation is an important biological marker used in the diagnosis and monitoring of many diseases, including cancer. These chemical modifications to DNA influence gene activity and can reveal early... Read more
Sex Differences in Alzheimer’s Biomarkers Linked to Faster Cognitive Decline
Sex differences in Alzheimer’s disease present ongoing diagnostic challenges, with women often experiencing a disproportionate disease burden even when preclinical amyloid-beta levels are similar to men.... Read moreIndustry
view channel
Cepheid Joins CDC Initiative to Strengthen U.S. Pandemic Testing Preparednesss
Cepheid (Sunnyvale, CA, USA) has been selected by the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) as one of four national collaborators in a federal initiative to speed rapid diagnostic technologies... Read more
QuidelOrtho Collaborates with Lifotronic to Expand Global Immunoassay Portfolio
QuidelOrtho (San Diego, CA, USA) has entered a long-term strategic supply agreement with Lifotronic Technology (Shenzhen, China) to expand its global immunoassay portfolio and accelerate customer access... Read more





















