Next-Gen Sequencing Matches Blood Group Antigens for Transfusion
|
By LabMedica International staff writers Posted on 26 Sep 2019 |
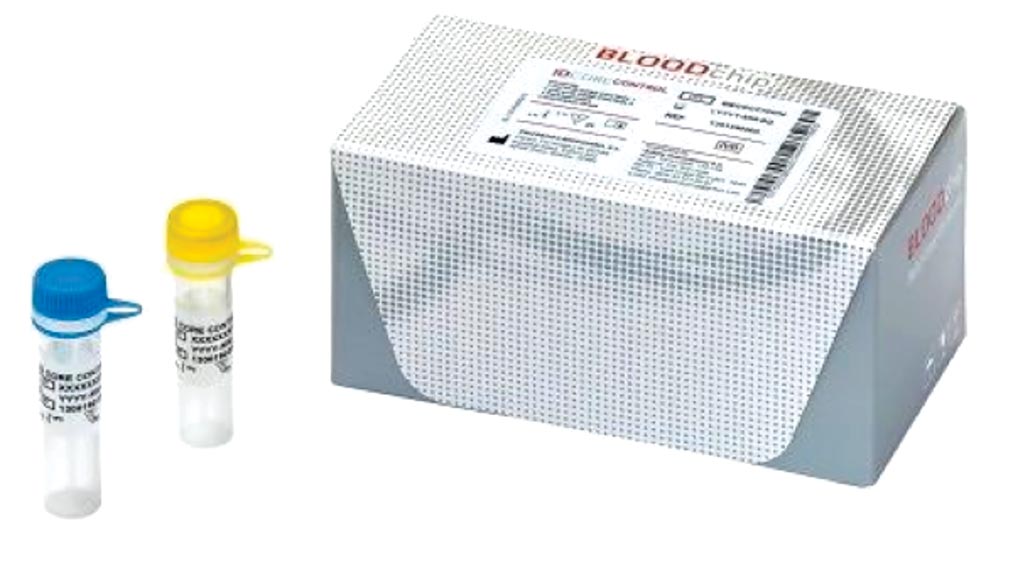

Image: The ID Core XT BLOODchip is a molecular-based assay used in blood transfusion medicine to help determine blood compatibility and could supplement the classical blood match methodology (Photo courtesy of Progenika Biopharma SA).
Transfusion is the procedure of introducing donor material with unknown blood cell antigens into the recipient’s circulatory system. The recipient’s immune system recognizes foreign antigens, produces specific antibodies and sensitization (alloimmunization) occurs.
To date, more than 300 red blood cell (RBC) and 33 human platelet antigens (HPA) have been described. Extended antigen typing is time-consuming, serological methods are costly and depend on the availability of reagents for antigen detection. The procedure is usually performed in reference laboratories, which complicates and delays the delivery of blood for transfusion.
Scientists at the Institute of Hematology and Transfusion Medicine (Warsaw, Poland) have reviewed the advances in applying next-generation sequencing (NGS) to transfusion medicine for the purpose of genotyping alleles encoding clinically important red blood cell and platelet antigens. The currently available technologies allow various levels of sequencing; either the whole genome (WGS), coding regions, exons (WES) or only selected genes or regions of interest. NGS technology significantly reduces the cost of testing. It has been successfully implemented in transplantation medicine for testing donors’ genotypes of HLA antigens in high-throughput mode. Over 9,000 HLA alleles for over 500 individuals can be identified per run.
NGS is particularly effective for finding unknown variations responsible for different phenotypes in patients with antibodies of unknown specificity because it enables screening of the whole genome, exome or particular genes and finding an unknown or rare variant. Recent studies have confirmed NGS effectiveness in resolving the molecular background of orphan antigens with an as yet unknown genetic basis. NGS is also effective in reducing the risk of post-transfusion alloimmunization since the huge capacity of one investigation enables the immediate and cost-effective determination of all RBC and platelet antigen genotypes. Study results support extended profiling of donors and patients for the best prophylactic antigen matching to prevent alloimmunization.
The application of NGS technology for blood typing contributes to the following aspects of patient care: Prevention of alloimmunization in sickle cell disease (SCD) and other transfusion-dependent patients; faster and cheaper diagnostics in the case of patients with unexplained, complex serological results; the huge capacity of the NGS investigations makes this technology an ideal tool for mass screening of blood donors for all clinically important antigens and also to detect individuals with rare blood group antigens in various ethnic groups; this facilitates access to compatible donors for alloimmunised patients.
The authors concluded that the future of NGS as a supplementary test used to provide highly compatible blood as well as to reduce the risk of patient’s alloimmunization and this is part of personalized medicine. The study was published on September 3, 2019, in the journal International Journal of Clinical Transfusion Medicine.
Related Links:
Institute of Hematology and Transfusion Medicine
To date, more than 300 red blood cell (RBC) and 33 human platelet antigens (HPA) have been described. Extended antigen typing is time-consuming, serological methods are costly and depend on the availability of reagents for antigen detection. The procedure is usually performed in reference laboratories, which complicates and delays the delivery of blood for transfusion.
Scientists at the Institute of Hematology and Transfusion Medicine (Warsaw, Poland) have reviewed the advances in applying next-generation sequencing (NGS) to transfusion medicine for the purpose of genotyping alleles encoding clinically important red blood cell and platelet antigens. The currently available technologies allow various levels of sequencing; either the whole genome (WGS), coding regions, exons (WES) or only selected genes or regions of interest. NGS technology significantly reduces the cost of testing. It has been successfully implemented in transplantation medicine for testing donors’ genotypes of HLA antigens in high-throughput mode. Over 9,000 HLA alleles for over 500 individuals can be identified per run.
NGS is particularly effective for finding unknown variations responsible for different phenotypes in patients with antibodies of unknown specificity because it enables screening of the whole genome, exome or particular genes and finding an unknown or rare variant. Recent studies have confirmed NGS effectiveness in resolving the molecular background of orphan antigens with an as yet unknown genetic basis. NGS is also effective in reducing the risk of post-transfusion alloimmunization since the huge capacity of one investigation enables the immediate and cost-effective determination of all RBC and platelet antigen genotypes. Study results support extended profiling of donors and patients for the best prophylactic antigen matching to prevent alloimmunization.
The application of NGS technology for blood typing contributes to the following aspects of patient care: Prevention of alloimmunization in sickle cell disease (SCD) and other transfusion-dependent patients; faster and cheaper diagnostics in the case of patients with unexplained, complex serological results; the huge capacity of the NGS investigations makes this technology an ideal tool for mass screening of blood donors for all clinically important antigens and also to detect individuals with rare blood group antigens in various ethnic groups; this facilitates access to compatible donors for alloimmunised patients.
The authors concluded that the future of NGS as a supplementary test used to provide highly compatible blood as well as to reduce the risk of patient’s alloimmunization and this is part of personalized medicine. The study was published on September 3, 2019, in the journal International Journal of Clinical Transfusion Medicine.
Related Links:
Institute of Hematology and Transfusion Medicine
Latest Hematology News
- Rapid Cartridge-Based Test Aims to Expand Access to Hemoglobin Disorder Diagnosis
- New Guidelines Aim to Improve AL Amyloidosis Diagnosis
- Automated Hemostasis System Helps Labs of All Sizes Optimize Workflow
- Fast and Easy Test Could Revolutionize Blood Transfusions
- High-Sensitivity Blood Test Improves Assessment of Clotting Risk in Heart Disease Patients
- AI Algorithm Effectively Distinguishes Alpha Thalassemia Subtypes
- MRD Tests Could Predict Survival in Leukemia Patients
- Platelet Activity Blood Test in Middle Age Could Identify Early Alzheimer’s Risk
- Microvesicles Measurement Could Detect Vascular Injury in Sickle Cell Disease Patients
- ADLM’s New Coagulation Testing Guidance to Improve Care for Patients on Blood Thinners
- Viscoelastic Testing Could Improve Treatment of Maternal Hemorrhage
- Pioneering Model Measures Radiation Exposure in Blood for Precise Cancer Treatments
- Platelets Could Improve Early and Minimally Invasive Detection of Cancer
- Portable and Disposable Device Obtains Platelet-Rich Plasma Without Complex Equipment
- Disposable Cartridge-Based Test Delivers Rapid and Accurate CBC Results
- First Point-of-Care Heparin Monitoring Test Provides Results in Under 15 Minutes

Channels
Clinical Chemistry
view channel
Electronic Nose Smells Early Signs of Ovarian Cancer in Blood
Ovarian cancer is often diagnosed at a late stage because its symptoms are vague and resemble those of more common conditions. Unlike breast cancer, there is currently no reliable screening method, and... Read more
Simple Blood Test Offers New Path to Alzheimer’s Assessment in Primary Care
Timely evaluation of cognitive symptoms in primary care is often limited by restricted access to specialized diagnostics and invasive confirmatory procedures. Clinicians need accessible tools to determine... Read moreMolecular Diagnostics
view channel
New Blood Test Score Detects Hidden Alcohol-Related Liver Disease
Fatty liver disease affects nearly one in three adults worldwide and can be driven by metabolic conditions such as obesity and diabetes or by excessive alcohol use. In routine care, it is often difficult... Read more
New Blood Test Predicts Who Will Most Likely Live Longer
As people age, it becomes increasingly difficult to determine who is likely to maintain stable health and who may face serious decline. Traditional indicators such as age, cholesterol, and physical activity... Read moreImmunology
view channel
New Biomarker Predicts Chemotherapy Response in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
Triple-negative breast cancer is an aggressive form of breast cancer in which patients often show widely varying responses to chemotherapy. Predicting who will benefit from treatment remains challenging,... Read moreBlood Test Identifies Lung Cancer Patients Who Can Benefit from Immunotherapy Drug
Small cell lung cancer (SCLC) is an aggressive disease with limited treatment options, and even newly approved immunotherapies do not benefit all patients. While immunotherapy can extend survival for some,... Read more
Whole-Genome Sequencing Approach Identifies Cancer Patients Benefitting From PARP-Inhibitor Treatment
Targeted cancer therapies such as PARP inhibitors can be highly effective, but only for patients whose tumors carry specific DNA repair defects. Identifying these patients accurately remains challenging,... Read more
Ultrasensitive Liquid Biopsy Demonstrates Efficacy in Predicting Immunotherapy Response
Immunotherapy has transformed cancer treatment, but only a small proportion of patients experience lasting benefit, with response rates often remaining between 10% and 20%. Clinicians currently lack reliable... Read moreMicrobiology
view channel
Hidden Gut Viruses Linked to Colorectal Cancer Risk
Colorectal cancer (CRC) remains a leading cause of cancer mortality in many Western countries, and existing risk-stratification approaches leave substantial room for improvement. Although age, diet, and... Read more
Three-Test Panel Launched for Detection of Liver Fluke Infections
Parasitic liver fluke infections remain endemic in parts of Asia, where transmission commonly occurs through consumption of raw freshwater fish or aquatic plants. Chronic infection is a well-established... Read morePathology
view channel
Urine Specimen Collection System Improves Diagnostic Accuracy and Efficiency
Urine testing is a critical, non-invasive diagnostic tool used to detect conditions such as pregnancy, urinary tract infections, metabolic disorders, cancer, and kidney disease. However, contaminated or... Read more
AI-Powered 3D Scanning System Speeds Cancer Screening
Cytology remains a cornerstone of cancer detection, requiring specialists to examine bodily fluids and cells under a microscope. This labor-intensive process involves inspecting up to one million cells... Read moreTechnology
view channel
Blood Test “Clocks” Predict Start of Alzheimer’s Symptoms
More than 7 million Americans live with Alzheimer’s disease, and related health and long-term care costs are projected to reach nearly USD 400 billion in 2025. The disease has no cure, and symptoms often... Read more
AI-Powered Biomarker Predicts Liver Cancer Risk
Liver cancer, or hepatocellular carcinoma, causes more than 800,000 deaths worldwide each year and often goes undetected until late stages. Even after treatment, recurrence rates reach 70% to 80%, contributing... Read more
Robotic Technology Unveiled for Automated Diagnostic Blood Draws
Routine diagnostic blood collection is a high‑volume task that can strain staffing and introduce human‑dependent variability, with downstream implications for sample quality and patient experience.... Read more
ADLM Launches First-of-Its-Kind Data Science Program for Laboratory Medicine Professionals
Clinical laboratories generate billions of test results each year, creating a treasure trove of data with the potential to support more personalized testing, improve operational efficiency, and enhance patient care.... Read moreIndustry
view channel
Cepheid Joins CDC Initiative to Strengthen U.S. Pandemic Testing Preparednesss
Cepheid (Sunnyvale, CA, USA) has been selected by the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) as one of four national collaborators in a federal initiative to speed rapid diagnostic technologies... Read more
QuidelOrtho Collaborates with Lifotronic to Expand Global Immunoassay Portfolio
QuidelOrtho (San Diego, CA, USA) has entered a long-term strategic supply agreement with Lifotronic Technology (Shenzhen, China) to expand its global immunoassay portfolio and accelerate customer access... Read more