Высокочувствительный иммуноанализ обнаруживает малярийный белок, богатый гистидином 2
|
By LabMedica International staff writers Posted on 21 Nov 2018 |
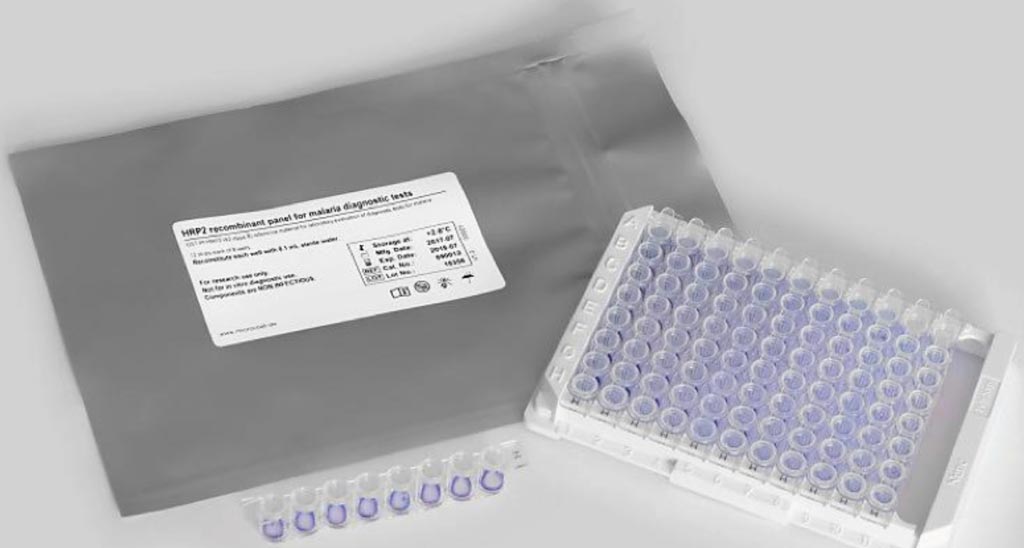
Рекомбинантная панель белка, богатого гистидином 2 (HRP2), для диагностики малярии (фото любезно предоставлено Microcoat Biotechnologie).
Малярия - это распространяемая посредством укусов насекомых болезнь, являющаяся актуальной проблемой для общественного здравоохранения во всем мире. Обнаружение субмикроскопических инфекций в условиях низкой распространенности становится все более важной задачей для стратегий ликвидации малярии.
Современные быстрые диагностические тесты на малярию Plasmodium falciparum, предназначенные для использования во внелабораторных условиях, не в состоянии выявить инфекции с низкой плотностью паразитов. По этой причине возникла необходимость разработать более чувствительные полевые диагностические инструменты. Параллельно для оценки новых диагностических инструментов потребуется очень чувствительный лабораторный анализ для референсных значений.
Группа международных ученых, в основном связанных с PATH (Сиэтл, штат Вашингтон, США), собрала образцы цельной крови у участников исследования из Карен Виллэдж, (Мьянма) и Нагонгеры (Уганда). Присутствие или отсутствие белка P. falciparum, богатого гистидином 2 (Histidine-Rich Protein 2 - HRP2), выявлялось с помощью ИФA Alere Malaria Ag P.f (HRP2). Аналитические и клинические показатели HS ELISA определялись с использованием рекомбинантных P. falciparum HRP2, паразитов нативной культуры P. falciparum и архивированных высокоспецифических образцов цельной крови.
Ученые сообщили, что HS ELISA имеет аналитическую чувствительность менее 25 пг/мл и проявляет сильную специфичность для P. falciparum HRP2 при тестировании на штаммы нативной культуры P. falciparum с делециями генов pfhrp2 и pfhrp3. В сравнении с клиническими образцами цельной крови с согласованными результатами микроскопии и полимеразной цепной реакцией (ПЦР), HS ELISA показал 100% диагностическую чувствительность и 97,9% диагностическую специфичность. Для положительных образцов P. falciparum с концентрацией HRP2 ниже 400 пг/мл чувствительность и специфичность составляли 100% и 88,9% соответственно. Общая чувствительность и специфичность для всех 352 образцов составляла 100% и 97,3%.
Авторы пришли к выводу, что анализ ELISA HS продемонстрировал приемлемую чувствительность и специфичность для обнаружения P. falciparum HRP2, включая рекомбинантный белок, паразитов нативной культуры P. falciparum и клинические образцы цельной крови. Новый анализ будет полезен при оценке новых диагностических инструментов и, возможно, других исследований воздействия малярии из-за его более низкого предела обнаружения P. falciparum HRP2. Исследование было опубликовано 1 ноября 2018 года в “Журнале малярии” (Malaria Journal).
Ссылки по теме:
PATH
Современные быстрые диагностические тесты на малярию Plasmodium falciparum, предназначенные для использования во внелабораторных условиях, не в состоянии выявить инфекции с низкой плотностью паразитов. По этой причине возникла необходимость разработать более чувствительные полевые диагностические инструменты. Параллельно для оценки новых диагностических инструментов потребуется очень чувствительный лабораторный анализ для референсных значений.
Группа международных ученых, в основном связанных с PATH (Сиэтл, штат Вашингтон, США), собрала образцы цельной крови у участников исследования из Карен Виллэдж, (Мьянма) и Нагонгеры (Уганда). Присутствие или отсутствие белка P. falciparum, богатого гистидином 2 (Histidine-Rich Protein 2 - HRP2), выявлялось с помощью ИФA Alere Malaria Ag P.f (HRP2). Аналитические и клинические показатели HS ELISA определялись с использованием рекомбинантных P. falciparum HRP2, паразитов нативной культуры P. falciparum и архивированных высокоспецифических образцов цельной крови.
Ученые сообщили, что HS ELISA имеет аналитическую чувствительность менее 25 пг/мл и проявляет сильную специфичность для P. falciparum HRP2 при тестировании на штаммы нативной культуры P. falciparum с делециями генов pfhrp2 и pfhrp3. В сравнении с клиническими образцами цельной крови с согласованными результатами микроскопии и полимеразной цепной реакцией (ПЦР), HS ELISA показал 100% диагностическую чувствительность и 97,9% диагностическую специфичность. Для положительных образцов P. falciparum с концентрацией HRP2 ниже 400 пг/мл чувствительность и специфичность составляли 100% и 88,9% соответственно. Общая чувствительность и специфичность для всех 352 образцов составляла 100% и 97,3%.
Авторы пришли к выводу, что анализ ELISA HS продемонстрировал приемлемую чувствительность и специфичность для обнаружения P. falciparum HRP2, включая рекомбинантный белок, паразитов нативной культуры P. falciparum и клинические образцы цельной крови. Новый анализ будет полезен при оценке новых диагностических инструментов и, возможно, других исследований воздействия малярии из-за его более низкого предела обнаружения P. falciparum HRP2. Исследование было опубликовано 1 ноября 2018 года в “Журнале малярии” (Malaria Journal).
Ссылки по теме:
PATH
Latest Иммунология News
Channels
Clinical Chemistry
view channel
New PSA-Based Prognostic Model Improves Prostate Cancer Risk Assessment
Prostate cancer is the second-leading cause of cancer death among American men, and about one in eight will be diagnosed in their lifetime. Screening relies on blood levels of prostate-specific antigen... Read more
Extracellular Vesicles Linked to Heart Failure Risk in CKD Patients
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) affects more than 1 in 7 Americans and is strongly associated with cardiovascular complications, which account for more than half of deaths among people with CKD.... Read moreMolecular Diagnostics
view channel
POC Test Uses Fingerstick Blood, Serum, Or Plasma Sample to Detect Typhoid Fever
Typhoid fever is an acute febrile illness caused by Salmonella enterica serovar Typhi (S. Typhi) and affects an estimated 11–21 million people globally each year, resulting in approximately 128,000–161,000... Read more
Rapid Testing Panel Simultaneously Detects 15 Drugs of Abuse in Urine Within 21 Minutes
Illicit drug use and excessive use of prescription medicine is growing across the US amid a severe opioid crisis. Although overdose fatalities were reported to have declined by nearly 27% in 2024, many... Read moreHematology
view channel
New Guidelines Aim to Improve AL Amyloidosis Diagnosis
Light chain (AL) amyloidosis is a rare, life-threatening bone marrow disorder in which abnormal amyloid proteins accumulate in organs. Approximately 3,260 people in the United States are diagnosed... Read more
Fast and Easy Test Could Revolutionize Blood Transfusions
Blood transfusions are a cornerstone of modern medicine, yet red blood cells can deteriorate quietly while sitting in cold storage for weeks. Although blood units have a fixed expiration date, cells from... Read more
Automated Hemostasis System Helps Labs of All Sizes Optimize Workflow
High-volume hemostasis sections must sustain rapid turnaround while managing reruns and reflex testing. Manual tube handling and preanalytical checks can strain staff time and increase opportunities for error.... Read more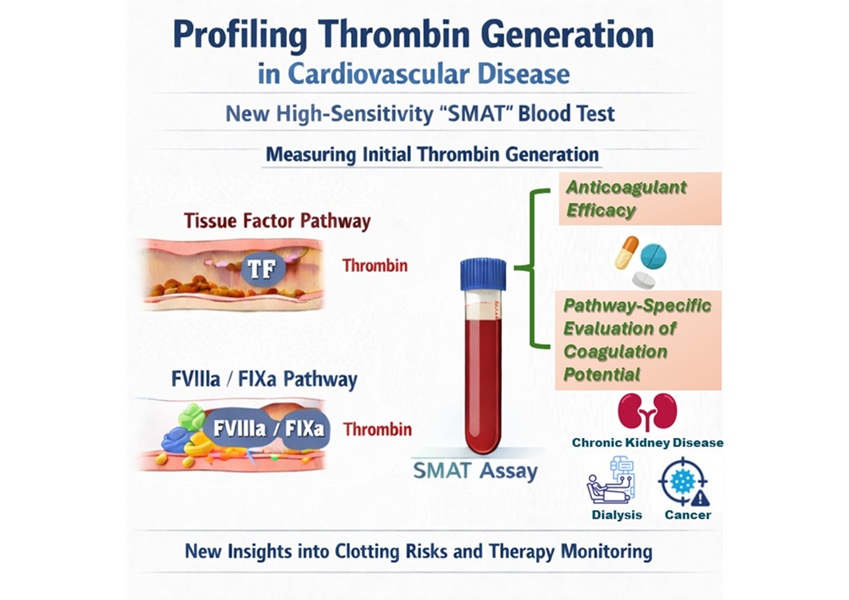
High-Sensitivity Blood Test Improves Assessment of Clotting Risk in Heart Disease Patients
Blood clotting is essential for preventing bleeding, but even small imbalances can lead to serious conditions such as thrombosis or dangerous hemorrhage. In cardiovascular disease, clinicians often struggle... Read moreImmunology
view channelBlood Test Identifies Lung Cancer Patients Who Can Benefit from Immunotherapy Drug
Small cell lung cancer (SCLC) is an aggressive disease with limited treatment options, and even newly approved immunotherapies do not benefit all patients. While immunotherapy can extend survival for some,... Read more
Whole-Genome Sequencing Approach Identifies Cancer Patients Benefitting From PARP-Inhibitor Treatment
Targeted cancer therapies such as PARP inhibitors can be highly effective, but only for patients whose tumors carry specific DNA repair defects. Identifying these patients accurately remains challenging,... Read more
Ultrasensitive Liquid Biopsy Demonstrates Efficacy in Predicting Immunotherapy Response
Immunotherapy has transformed cancer treatment, but only a small proportion of patients experience lasting benefit, with response rates often remaining between 10% and 20%. Clinicians currently lack reliable... Read moreMicrobiology
view channel
Comprehensive Review Identifies Gut Microbiome Signatures Associated With Alzheimer’s Disease
Alzheimer’s disease affects approximately 6.7 million people in the United States and nearly 50 million worldwide, yet early cognitive decline remains difficult to characterize. Increasing evidence suggests... Read moreAI-Powered Platform Enables Rapid Detection of Drug-Resistant C. Auris Pathogens
Infections caused by the pathogenic yeast Candida auris pose a significant threat to hospitalized patients, particularly those with weakened immune systems or those who have invasive medical devices.... Read morePathology
view channel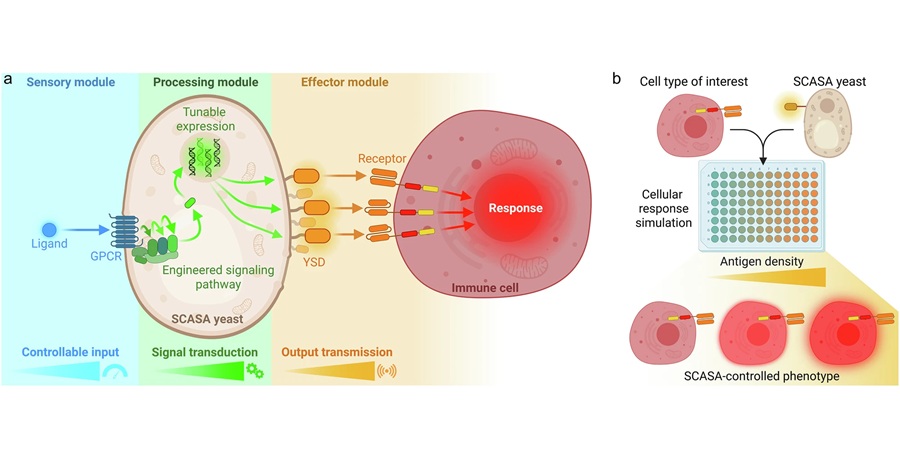
Engineered Yeast Cells Enable Rapid Testing of Cancer Immunotherapy
Developing new cancer immunotherapies is a slow, costly, and high-risk process, particularly for CAR T cell treatments that must precisely recognize cancer-specific antigens. Small differences in tumor... Read more
First-Of-Its-Kind Test Identifies Autism Risk at Birth
Autism spectrum disorder is treatable, and extensive research shows that early intervention can significantly improve cognitive, social, and behavioral outcomes. Yet in the United States, the average age... Read moreTechnology
view channel
Robotic Technology Unveiled for Automated Diagnostic Blood Draws
Routine diagnostic blood collection is a high‑volume task that can strain staffing and introduce human‑dependent variability, with downstream implications for sample quality and patient experience.... Read more
ADLM Launches First-of-Its-Kind Data Science Program for Laboratory Medicine Professionals
Clinical laboratories generate billions of test results each year, creating a treasure trove of data with the potential to support more personalized testing, improve operational efficiency, and enhance patient care.... Read moreAptamer Biosensor Technology to Transform Virus Detection
Rapid and reliable virus detection is essential for controlling outbreaks, from seasonal influenza to global pandemics such as COVID-19. Conventional diagnostic methods, including cell culture, antigen... Read more
AI Models Could Predict Pre-Eclampsia and Anemia Earlier Using Routine Blood Tests
Pre-eclampsia and anemia are major contributors to maternal and child mortality worldwide, together accounting for more than half a million deaths each year and leaving millions with long-term health complications.... Read moreIndustry
view channel
WHX Labs in Dubai spotlights leadership skills shaping next-generation laboratories
WHX Labs in Dubai (formerly Medlab Middle East), held at Dubai World Trade Centre (DWTC) from 10–13 February, brings together international experts to discuss the factors redefining laboratory leadership,... Read moreNew Collaboration Brings Automated Mass Spectrometry to Routine Laboratory Testing
Mass spectrometry is a powerful analytical technique that identifies and quantifies molecules based on their mass and electrical charge. Its high selectivity, sensitivity, and accuracy make it indispensable... Read more
AI-Powered Cervical Cancer Test Set for Major Rollout in Latin America
Noul Co., a Korean company specializing in AI-based blood and cancer diagnostics, announced it will supply its intelligence (AI)-based miLab CER cervical cancer diagnostic solution to Mexico under a multi‑year... Read more