Biomarker Identified for Novel Asthma Treatment
|
By LabMedica International staff writers Posted on 17 Sep 2018 |
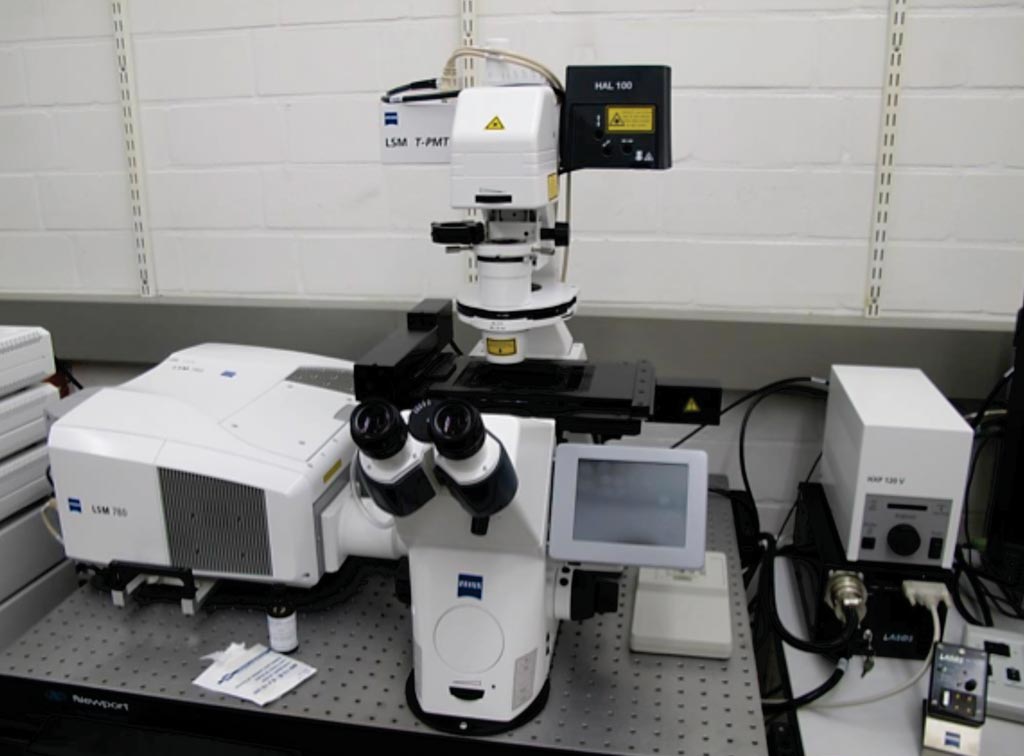

Image: The LSM 780 inverted laser scanning confocal microscope (Photo courtesy of Zeiss).
Asthma is a widespread chronic airway disease characterized by airway obstruction, inflammation, and hyperresponsiveness. Symptoms such as bronchoconstriction and cough range from mild intermittent to severe persistent.
In eosinophilic asthma, the most common form of asthma, eosinophils in the airway alter nerve function and exacerbate the disease. However, whether eosinophils also affect airway nerve structure is unclear. In type 2-high asthma, interleukin-5 (IL-5) promotes eosinophil maturation, recruitment, and survival.
An international team of scientists working with the Oregon Health and Science University (Portland, OR, USA) evaluated airway sensory innervation and eosinophilia in humans with and without asthma and to characterize the physiologic consequences of eosinophil and airway nerve interactions using transgenic mice. Patients over the age of 17 were recruited and medication use, pulmonary function testing, blood eosinophil counts, serum immunoglobulin E (IgE) levels, and smoking history were obtained.
Human bronchial biopsies (three to five per subject) were taken from the bifurcation of the right middle lobe and immediately fixed in formalin overnight. Tissues were immunostained at 4 °C on a shaker. Airway nerves were labeled with rabbit polyclonal antibody against pan-neuronal marker PGP9.5 (protein gene product 9.5), and other immunostaining was performed and images were acquired using a Zeiss LSM 780 confocal microscope.
The scientists reported that subjects with a type 2-high asthma phenotype, defined as blood eosinophils greater than 300 cells/μL, had longer airway nerves and increased nerve branch points compared to control airways. In contrast, nerves in type 2-low asthmatics with blood eosinophils less than 300 cells/μL were not significantly different from healthy subjects. The mean blood eosinophils counts were 182 ± 93 μL in the 19 controls; 277 ± 289/μL in the 13 intermittent asthma patients; and 301 ± 225/μL in the persistent asthma sufferers. Moderate persistent asthmatics had increased eosinophil peroxidase both above and below the epithelial basement membrane compared to mild intermittent asthmatics and control subjects.
The authors concluded that their data indicated that airway nerves contribute to asthma pathology. They have shown that moderate persistent asthmatics have increased airway sensory innervation that is especially marked in asthmatics with accompanying eosinophilia. Richard W. Costello, MB, MD, FRCPI, a professor and a senior author of the study, said, “We identified that inflammatory cells, in particular, eosinophils, promote airway nerve growth in patients with asthma. These observations provide a unique insight into a fundamental mechanism of how the inflammation caused by asthma causes people to experience the symptoms of asthma such as coughing and breathlessness. This means that we now know which markers to look for in a patient with severe asthma. A patient with markers which show they have this particular form of asthma is likely to respond well to these new treatments.” The study was published on September 5, 2018, in the journal Science Translational Medicine.
Related Links:
Oregon Health and Science University
In eosinophilic asthma, the most common form of asthma, eosinophils in the airway alter nerve function and exacerbate the disease. However, whether eosinophils also affect airway nerve structure is unclear. In type 2-high asthma, interleukin-5 (IL-5) promotes eosinophil maturation, recruitment, and survival.
An international team of scientists working with the Oregon Health and Science University (Portland, OR, USA) evaluated airway sensory innervation and eosinophilia in humans with and without asthma and to characterize the physiologic consequences of eosinophil and airway nerve interactions using transgenic mice. Patients over the age of 17 were recruited and medication use, pulmonary function testing, blood eosinophil counts, serum immunoglobulin E (IgE) levels, and smoking history were obtained.
Human bronchial biopsies (three to five per subject) were taken from the bifurcation of the right middle lobe and immediately fixed in formalin overnight. Tissues were immunostained at 4 °C on a shaker. Airway nerves were labeled with rabbit polyclonal antibody against pan-neuronal marker PGP9.5 (protein gene product 9.5), and other immunostaining was performed and images were acquired using a Zeiss LSM 780 confocal microscope.
The scientists reported that subjects with a type 2-high asthma phenotype, defined as blood eosinophils greater than 300 cells/μL, had longer airway nerves and increased nerve branch points compared to control airways. In contrast, nerves in type 2-low asthmatics with blood eosinophils less than 300 cells/μL were not significantly different from healthy subjects. The mean blood eosinophils counts were 182 ± 93 μL in the 19 controls; 277 ± 289/μL in the 13 intermittent asthma patients; and 301 ± 225/μL in the persistent asthma sufferers. Moderate persistent asthmatics had increased eosinophil peroxidase both above and below the epithelial basement membrane compared to mild intermittent asthmatics and control subjects.
The authors concluded that their data indicated that airway nerves contribute to asthma pathology. They have shown that moderate persistent asthmatics have increased airway sensory innervation that is especially marked in asthmatics with accompanying eosinophilia. Richard W. Costello, MB, MD, FRCPI, a professor and a senior author of the study, said, “We identified that inflammatory cells, in particular, eosinophils, promote airway nerve growth in patients with asthma. These observations provide a unique insight into a fundamental mechanism of how the inflammation caused by asthma causes people to experience the symptoms of asthma such as coughing and breathlessness. This means that we now know which markers to look for in a patient with severe asthma. A patient with markers which show they have this particular form of asthma is likely to respond well to these new treatments.” The study was published on September 5, 2018, in the journal Science Translational Medicine.
Related Links:
Oregon Health and Science University
Latest Immunology News
- Blood Test Identifies Lung Cancer Patients Who Can Benefit from Immunotherapy Drug
- Whole-Genome Sequencing Approach Identifies Cancer Patients Benefitting From PARP-Inhibitor Treatment
- Ultrasensitive Liquid Biopsy Demonstrates Efficacy in Predicting Immunotherapy Response
- Blood Test Could Identify Colon Cancer Patients to Benefit from NSAIDs
- Blood Test Could Detect Adverse Immunotherapy Effects
- Routine Blood Test Can Predict Who Benefits Most from CAR T-Cell Therapy
- New Test Distinguishes Vaccine-Induced False Positives from Active HIV Infection
- Gene Signature Test Predicts Response to Key Breast Cancer Treatment
- Chip Captures Cancer Cells from Blood to Help Select Right Breast Cancer Treatment
- Blood-Based Liquid Biopsy Model Analyzes Immunotherapy Effectiveness
- Signature Genes Predict T-Cell Expansion in Cancer Immunotherapy
- Molecular Microscope Diagnostic System Assesses Lung Transplant Rejection
- Blood Test Tracks Treatment Resistance in High-Grade Serous Ovarian Cancer
- Luminescent Probe Measures Immune Cell Activity in Real Time
- Blood-Based Immune Cell Signatures Could Guide Treatment Decisions for Critically Ill Patients
- Novel Tool Predicts Most Effective Multiple Sclerosis Medication for Patients
Channels
Clinical Chemistry
view channel
Rapid Blood Testing Method Aids Safer Decision-Making in Drug-Related Emergencies
Acute recreational drug toxicity is a frequent reason for emergency department visits, yet clinicians rarely have access to confirmatory toxicology results in real time. Instead, treatment decisions are... Read more
New PSA-Based Prognostic Model Improves Prostate Cancer Risk Assessment
Prostate cancer is the second-leading cause of cancer death among American men, and about one in eight will be diagnosed in their lifetime. Screening relies on blood levels of prostate-specific antigen... Read moreMolecular Diagnostics
view channel
Genetic Test Could Improve Early Detection of Prostate Cancer
Prostate cancer is the second-leading cause of cancer deaths among men in the United States and remains a major health burden. Current screening with prostate-specific antigen (PSA) blood tests can sometimes... Read more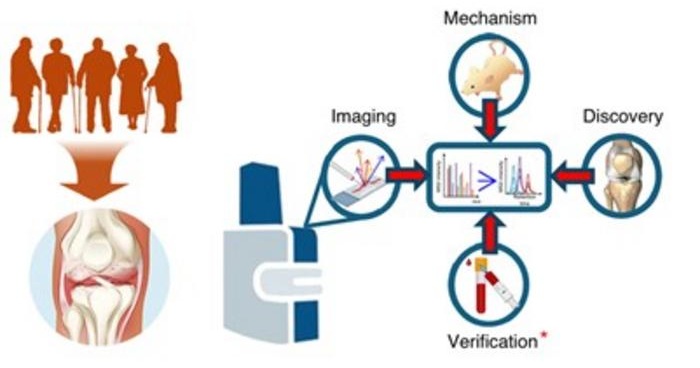
Bone Molecular Maps to Transform Early Osteoarthritis Detection
Osteoarthritis affects more than 500 million people worldwide and is a major cause of pain, disability, and reduced quality of life. By the time it is diagnosed through symptoms and visible cartilage loss,... Read moreImmunology
view channelBlood Test Identifies Lung Cancer Patients Who Can Benefit from Immunotherapy Drug
Small cell lung cancer (SCLC) is an aggressive disease with limited treatment options, and even newly approved immunotherapies do not benefit all patients. While immunotherapy can extend survival for some,... Read more
Whole-Genome Sequencing Approach Identifies Cancer Patients Benefitting From PARP-Inhibitor Treatment
Targeted cancer therapies such as PARP inhibitors can be highly effective, but only for patients whose tumors carry specific DNA repair defects. Identifying these patients accurately remains challenging,... Read more
Ultrasensitive Liquid Biopsy Demonstrates Efficacy in Predicting Immunotherapy Response
Immunotherapy has transformed cancer treatment, but only a small proportion of patients experience lasting benefit, with response rates often remaining between 10% and 20%. Clinicians currently lack reliable... Read moreMicrobiology
view channel
CRISPR-Based Technology Neutralizes Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria
Antibiotic resistance has accelerated into a global health crisis, with projections estimating more than 10 million deaths per year by 2050 as drug-resistant “superbugs” continue to spread.... Read more
Comprehensive Review Identifies Gut Microbiome Signatures Associated With Alzheimer’s Disease
Alzheimer’s disease affects approximately 6.7 million people in the United States and nearly 50 million worldwide, yet early cognitive decline remains difficult to characterize. Increasing evidence suggests... Read morePathology
view channel
AI-Powered Microscope Diagnoses Malaria in Blood Smears Within Minutes
Malaria remains one of the world’s deadliest infectious diseases, killing hundreds of thousands each year, mostly in under-resourced regions where laboratory infrastructure is limited. Diagnosis still... Read more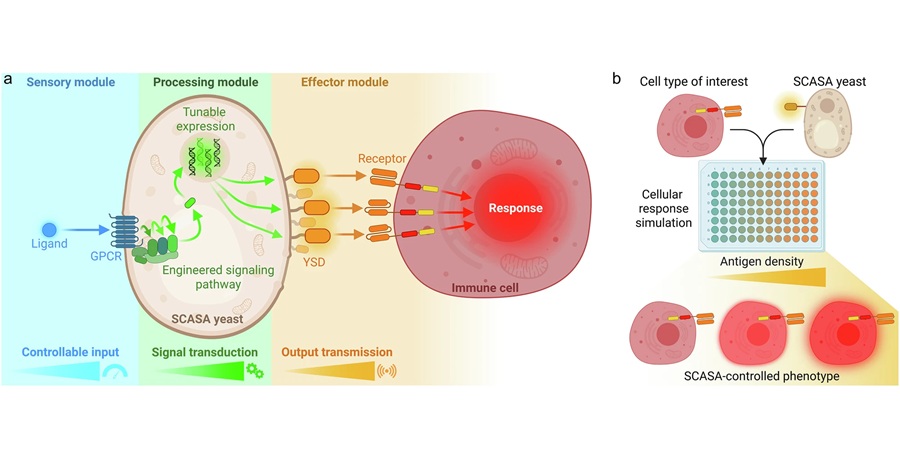
Engineered Yeast Cells Enable Rapid Testing of Cancer Immunotherapy
Developing new cancer immunotherapies is a slow, costly, and high-risk process, particularly for CAR T cell treatments that must precisely recognize cancer-specific antigens. Small differences in tumor... Read moreTechnology
view channel
Robotic Technology Unveiled for Automated Diagnostic Blood Draws
Routine diagnostic blood collection is a high‑volume task that can strain staffing and introduce human‑dependent variability, with downstream implications for sample quality and patient experience.... Read more
ADLM Launches First-of-Its-Kind Data Science Program for Laboratory Medicine Professionals
Clinical laboratories generate billions of test results each year, creating a treasure trove of data with the potential to support more personalized testing, improve operational efficiency, and enhance patient care.... Read moreAptamer Biosensor Technology to Transform Virus Detection
Rapid and reliable virus detection is essential for controlling outbreaks, from seasonal influenza to global pandemics such as COVID-19. Conventional diagnostic methods, including cell culture, antigen... Read more
AI Models Could Predict Pre-Eclampsia and Anemia Earlier Using Routine Blood Tests
Pre-eclampsia and anemia are major contributors to maternal and child mortality worldwide, together accounting for more than half a million deaths each year and leaving millions with long-term health complications.... Read moreIndustry
view channel
WHX Labs in Dubai spotlights leadership skills shaping next-generation laboratories
WHX Labs in Dubai (formerly Medlab Middle East), held at Dubai World Trade Centre (DWTC) from 10–13 February, brings together international experts to discuss the factors redefining laboratory leadership,... Read moreNew Collaboration Brings Automated Mass Spectrometry to Routine Laboratory Testing
Mass spectrometry is a powerful analytical technique that identifies and quantifies molecules based on their mass and electrical charge. Its high selectivity, sensitivity, and accuracy make it indispensable... Read more
AI-Powered Cervical Cancer Test Set for Major Rollout in Latin America
Noul Co., a Korean company specializing in AI-based blood and cancer diagnostics, announced it will supply its intelligence (AI)-based miLab CER cervical cancer diagnostic solution to Mexico under a multi‑year... Read more