Link Identified between Inflammation and Depression
|
By LabMedica International staff writers Posted on 20 Jun 2018 |
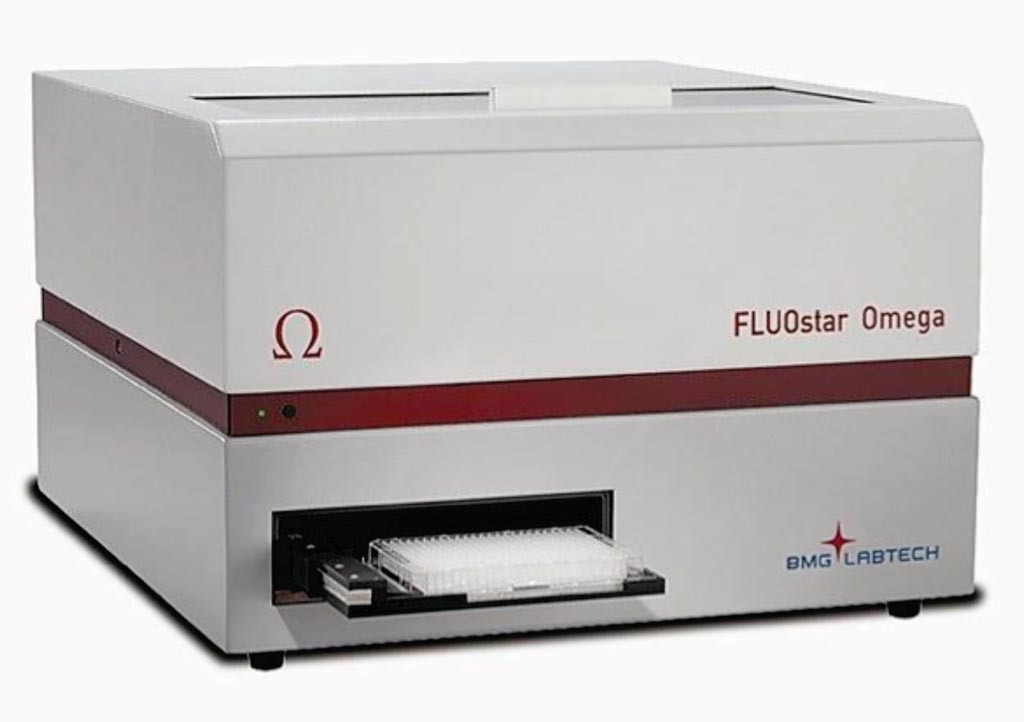

Image: The FLOUstar optima plate reader (Photo courtesy of BMG Labtech).
It is well established that people with both type-1 and type-2 diabetes have an increased risk of developing depression, a debilitating mental health disorder with potentially serious consequences, but the causes remain poorly understood.
Depression in type-1 diabetes patients is associated with higher levels of the inflammatory protein galectin-3, which is a key protein involved in promoting inflammatory immune system responses that are needed to repair tissue damage throughout the body, in response to injury or disease.
Scientists at Lund University (Lund, Sweden) and their colleagues carried out a cross-sectional study that included 283 type-1 diabetes (T1D) patients (56% men, age 18-59 years, diabetes duration ≥1 year). Depression was assessed by Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale depression subscale. Blood samples, anthropometrics and blood pressure were collected, supplemented with data from medical records and the Swedish National Diabetes Registry.
Galectin-3 was analyzed using a commercial human DuoSet enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) and supplementary ancillary kit. The ELISA analysis was performed and absorbance was measured at 450-580 nm in a FLOUstar optima plate reader. Concentrations of unknown samples were calculated using a four parameter logistic regression curve. The intra-assay coefficient of variation for the analysis was 4.3%. Galectin-3 levels equal to or greater than. 2.562 µg/L, corresponding to the 85th percentile, was defined as high galectin-3.
The scientists found that the median (quartile1, quartile3) galectin-3 was 1.3 µg/L (0.8, 2.9) for the 30 depressed patients, and 0.9 µg/L (0.5, 1.6) for the 253 non-depressed. Depression was associated with high galectin-3 in all the 283 patients (Adjusted odds ratio (AOR) 3.5), in the 161 men (AOR 3.4), and in the 122 women (AOR 3.9). HbA1c, serum-lipids, serum-creatinine, blood pressure, obesity, smoking, physical inactivity, cardiovascular complications, and drugs (antihypertensive, lipid lowering, oral anti-diabetic drugs, and antidepressants) were not associated with high galectin-3.
The authors concluded that their study was the first to show an association between depression and galectin-3. Depression was the only explored parameter associated with high circulating galectin-3 levels in 283 T1D patients. High galectin-3 levels might contribute to the increased risk for Alzheimer’s disease, cardiovascular and all-cause mortality observed in persons with depression. Potentially, in the future, treatment targeting galactin-3 might improve the prognosis for patients with high galectin-3 levels. The study was published on May 14, 2018, in the journal Endocrine Connections.
Related Links:
Lund University
Depression in type-1 diabetes patients is associated with higher levels of the inflammatory protein galectin-3, which is a key protein involved in promoting inflammatory immune system responses that are needed to repair tissue damage throughout the body, in response to injury or disease.
Scientists at Lund University (Lund, Sweden) and their colleagues carried out a cross-sectional study that included 283 type-1 diabetes (T1D) patients (56% men, age 18-59 years, diabetes duration ≥1 year). Depression was assessed by Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale depression subscale. Blood samples, anthropometrics and blood pressure were collected, supplemented with data from medical records and the Swedish National Diabetes Registry.
Galectin-3 was analyzed using a commercial human DuoSet enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) and supplementary ancillary kit. The ELISA analysis was performed and absorbance was measured at 450-580 nm in a FLOUstar optima plate reader. Concentrations of unknown samples were calculated using a four parameter logistic regression curve. The intra-assay coefficient of variation for the analysis was 4.3%. Galectin-3 levels equal to or greater than. 2.562 µg/L, corresponding to the 85th percentile, was defined as high galectin-3.
The scientists found that the median (quartile1, quartile3) galectin-3 was 1.3 µg/L (0.8, 2.9) for the 30 depressed patients, and 0.9 µg/L (0.5, 1.6) for the 253 non-depressed. Depression was associated with high galectin-3 in all the 283 patients (Adjusted odds ratio (AOR) 3.5), in the 161 men (AOR 3.4), and in the 122 women (AOR 3.9). HbA1c, serum-lipids, serum-creatinine, blood pressure, obesity, smoking, physical inactivity, cardiovascular complications, and drugs (antihypertensive, lipid lowering, oral anti-diabetic drugs, and antidepressants) were not associated with high galectin-3.
The authors concluded that their study was the first to show an association between depression and galectin-3. Depression was the only explored parameter associated with high circulating galectin-3 levels in 283 T1D patients. High galectin-3 levels might contribute to the increased risk for Alzheimer’s disease, cardiovascular and all-cause mortality observed in persons with depression. Potentially, in the future, treatment targeting galactin-3 might improve the prognosis for patients with high galectin-3 levels. The study was published on May 14, 2018, in the journal Endocrine Connections.
Related Links:
Lund University
Latest Clinical Chem. News
- Rapid Blood Testing Method Aids Safer Decision-Making in Drug-Related Emergencies
- New PSA-Based Prognostic Model Improves Prostate Cancer Risk Assessment
- Extracellular Vesicles Linked to Heart Failure Risk in CKD Patients
- Study Compares Analytical Performance of Quantitative Hepatitis B Surface Antigen Assays
- Blood Test Could Predict and Identify Early Relapses in Myeloma Patients
- Compact Raman Imaging System Detects Subtle Tumor Signals
- Noninvasive Blood-Glucose Monitoring to Replace Finger Pricks for Diabetics
- POC Breath Diagnostic System to Detect Pneumonia-Causing Pathogens
- Online Tool Detects Drug Exposure Directly from Patient Samples
- Chemical Imaging Probe Could Track and Treat Prostate Cancer
- Mismatch Between Two Common Kidney Function Tests Indicates Serious Health Problems
- VOCs Show Promise for Early Multi-Cancer Detection
- Portable Raman Spectroscopy Offers Cost-Effective Kidney Disease Diagnosis at POC
- Gold Nanoparticles to Improve Accuracy of Ovarian Cancer Diagnosis
- Simultaneous Cell Isolation Technology Improves Cancer Diagnostic Accuracy
- Simple Non-Invasive Hair-Based Test Could Speed ALS Diagnosis
Channels
Molecular Diagnostics
view channel
AI-Powered Liquid Biopsy Classifies Pediatric Brain Tumors with High Accuracy
Liquid biopsies offer a noninvasive way to study cancer by analyzing circulating tumor DNA in body fluids. However, in pediatric brain tumors, the small amount of ctDNA in cerebrospinal fluid has limited... Read more
New CSF Liquid Biopsy Assay Reveals Genomic Insights for CNS Tumors
Central nervous system (CNS) malignancies pose distinctive diagnostic challenges because tissue-based testing is often infeasible and the blood–brain barrier limits the usefulness of plasma liquid biopsy.... Read more
Group A Strep Molecular Test Delivers Definitive Results at POC in 15 Minutes
Strep throat is a bacterial infection caused by Group A Streptococcus (GAS). It is a leading bacterial cause of acute pharyngitis, particularly in children and adolescents, and one of the most common reasons... Read more
Rapid Molecular Test Identifies Sepsis Patients Most Likely to Have Positive Blood Cultures
Sepsis is caused by a patient’s overwhelming immune response to an infection. If undetected or left untreated, sepsis leads to tissue damage, organ failure, permanent disability, and often death.... Read moreHematology
view channel
Rapid Cartridge-Based Test Aims to Expand Access to Hemoglobin Disorder Diagnosis
Sickle cell disease and beta thalassemia are hemoglobin disorders that often require referral to specialized laboratories for definitive diagnosis, delaying results for patients and clinicians.... Read more
New Guidelines Aim to Improve AL Amyloidosis Diagnosis
Light chain (AL) amyloidosis is a rare, life-threatening bone marrow disorder in which abnormal amyloid proteins accumulate in organs. Approximately 3,260 people in the United States are diagnosed... Read moreImmunology
view channel
New Biomarker Predicts Chemotherapy Response in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
Triple-negative breast cancer is an aggressive form of breast cancer in which patients often show widely varying responses to chemotherapy. Predicting who will benefit from treatment remains challenging,... Read moreBlood Test Identifies Lung Cancer Patients Who Can Benefit from Immunotherapy Drug
Small cell lung cancer (SCLC) is an aggressive disease with limited treatment options, and even newly approved immunotherapies do not benefit all patients. While immunotherapy can extend survival for some,... Read more
Whole-Genome Sequencing Approach Identifies Cancer Patients Benefitting From PARP-Inhibitor Treatment
Targeted cancer therapies such as PARP inhibitors can be highly effective, but only for patients whose tumors carry specific DNA repair defects. Identifying these patients accurately remains challenging,... Read more
Ultrasensitive Liquid Biopsy Demonstrates Efficacy in Predicting Immunotherapy Response
Immunotherapy has transformed cancer treatment, but only a small proportion of patients experience lasting benefit, with response rates often remaining between 10% and 20%. Clinicians currently lack reliable... Read moreMicrobiology
view channel
Rapid Test Promises Faster Answers for Drug-Resistant Infections
Drug-resistant pathogens continue to pose a growing threat in healthcare facilities, where delayed detection can impede outbreak control and increase mortality. Candida auris is notoriously difficult to... Read more
CRISPR-Based Technology Neutralizes Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria
Antibiotic resistance has accelerated into a global health crisis, with projections estimating more than 10 million deaths per year by 2050 as drug-resistant “superbugs” continue to spread.... Read more
Comprehensive Review Identifies Gut Microbiome Signatures Associated With Alzheimer’s Disease
Alzheimer’s disease affects approximately 6.7 million people in the United States and nearly 50 million worldwide, yet early cognitive decline remains difficult to characterize. Increasing evidence suggests... Read morePathology
view channel
AI Tool Uses Blood Biomarkers to Predict Transplant Complications Before Symptoms Appear
Stem cell and bone marrow transplants can be lifesaving, but serious complications may arise months after patients leave the hospital. One of the most dangerous is chronic graft-versus-host disease, in... Read more
Research Consortium Harnesses AI and Spatial Biology to Advance Cancer Discovery
AI has the potential to transform cancer care, yet progress remains constrained by fragmented, inaccessible data that hinder advances in early diagnosis and precision therapy. Unlocking patterns missed... Read moreTechnology
view channel
AI-Powered Biomarker Predicts Liver Cancer Risk
Liver cancer, or hepatocellular carcinoma, causes more than 800,000 deaths worldwide each year and often goes undetected until late stages. Even after treatment, recurrence rates reach 70% to 80%, contributing... Read more
Robotic Technology Unveiled for Automated Diagnostic Blood Draws
Routine diagnostic blood collection is a high‑volume task that can strain staffing and introduce human‑dependent variability, with downstream implications for sample quality and patient experience.... Read more
ADLM Launches First-of-Its-Kind Data Science Program for Laboratory Medicine Professionals
Clinical laboratories generate billions of test results each year, creating a treasure trove of data with the potential to support more personalized testing, improve operational efficiency, and enhance patient care.... Read moreIndustry
view channel
QuidelOrtho Collaborates with Lifotronic to Expand Global Immunoassay Portfolio
QuidelOrtho (San Diego, CA, USA) has entered a long-term strategic supply agreement with Lifotronic Technology (Shenzhen, China) to expand its global immunoassay portfolio and accelerate customer access... Read more