Blood Type Linked to Severity of Diarrhea
|
By LabMedica International staff writers Posted on 29 May 2018 |
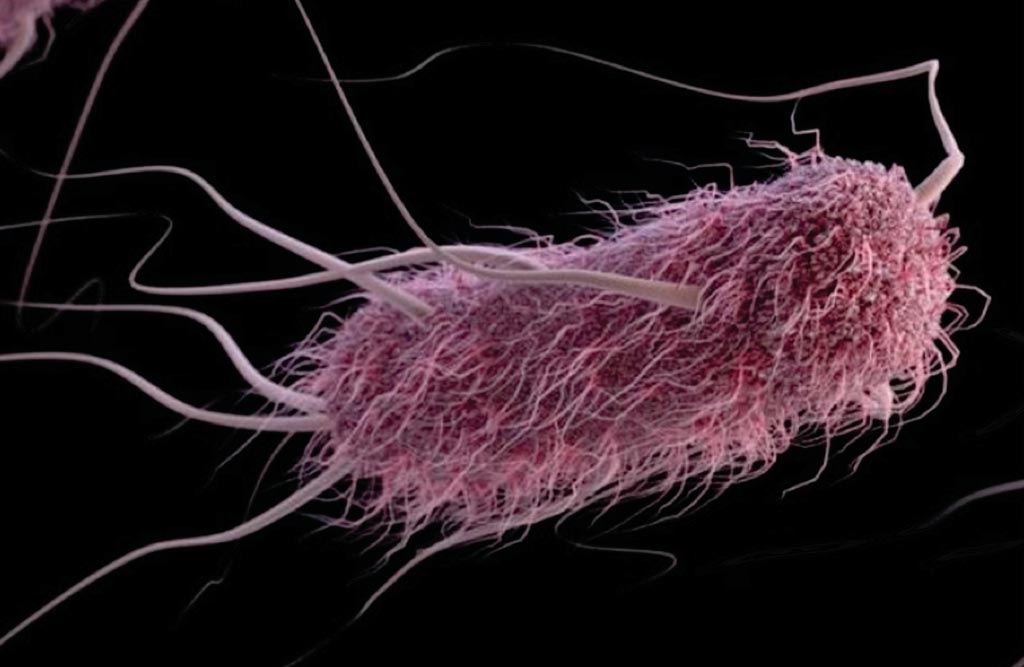
Image: A computer-generated image of E. coli (Photo courtesy of Alissa Eckert and Jennifer Oosthuizen / CDC).
Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli are responsible for millions of cases of diarrhea and hundreds of thousands of deaths every year, mainly of young children. It primarily infects people living in or visiting developing countries.
Some people infected with the bacterium develop severe, cholera-like, watery diarrhea that can be lethal. Others experience unpleasant symptoms but recover easily, while some do not get sick at all. A new study shows that a kind of E. coli most associated with "travelers' diarrhea" and children in underdeveloped areas of the world causes more severe disease in people with blood type A.
A team of scientists led by those at Washington University School of Medicine (St. Louis, MO, USA) carried out controlled human infection clinical trials, and gave healthy volunteers a dose of an E. coli strain originally isolated from a person in Bangladesh with severe, cholera-like diarrhea. Then, they observed the volunteers for five days. Those who developed moderate to severe diarrhea were treated with antibiotics. The disease comes on quickly, so anyone who was still healthy at the end of five days was unlikely to get sick later. Nonetheless, any remaining healthy participants also were given antibiotics to clear the bacteria before going home.
The investigators obtained data and blood samples from 106 people, each of whom participated in one of four such studies. They found that people with blood type A got sick sooner and more seriously than those of other blood types. More than eight out of 10 (81%) of blood group A people developed diarrhea that required treatment, as compared with about half of people with blood group B or O. They found that the bacteria produce a specific protein that sticks to A-type sugars, but not B- or O-type sugars, on intestinal cells. Since the protein also sticks to E. coli, it effectively fastens the bacteria to the intestinal wall, making it easy for them to deliver diarrhea-causing toxins to intestinal cells.
F. Matthew Kuhlmann, MD, a clinical investigator and a senior author of the study, said, “I don't want anyone to cancel their travel plans to Mexico because they have type A blood, Or the converse: I don't want anyone to think they're safe because their blood group is not A. There are a lot of different species of bacteria and viruses that can cause diarrhea, so even though this blood-group association is strong, it doesn't change your overall risk. You should continue taking the same precautions whatever your blood type.” The study was published on May 17, 2018, in The Journal of Clinical Investigation.
Related Links:
Washington University School of Medicine
Some people infected with the bacterium develop severe, cholera-like, watery diarrhea that can be lethal. Others experience unpleasant symptoms but recover easily, while some do not get sick at all. A new study shows that a kind of E. coli most associated with "travelers' diarrhea" and children in underdeveloped areas of the world causes more severe disease in people with blood type A.
A team of scientists led by those at Washington University School of Medicine (St. Louis, MO, USA) carried out controlled human infection clinical trials, and gave healthy volunteers a dose of an E. coli strain originally isolated from a person in Bangladesh with severe, cholera-like diarrhea. Then, they observed the volunteers for five days. Those who developed moderate to severe diarrhea were treated with antibiotics. The disease comes on quickly, so anyone who was still healthy at the end of five days was unlikely to get sick later. Nonetheless, any remaining healthy participants also were given antibiotics to clear the bacteria before going home.
The investigators obtained data and blood samples from 106 people, each of whom participated in one of four such studies. They found that people with blood type A got sick sooner and more seriously than those of other blood types. More than eight out of 10 (81%) of blood group A people developed diarrhea that required treatment, as compared with about half of people with blood group B or O. They found that the bacteria produce a specific protein that sticks to A-type sugars, but not B- or O-type sugars, on intestinal cells. Since the protein also sticks to E. coli, it effectively fastens the bacteria to the intestinal wall, making it easy for them to deliver diarrhea-causing toxins to intestinal cells.
F. Matthew Kuhlmann, MD, a clinical investigator and a senior author of the study, said, “I don't want anyone to cancel their travel plans to Mexico because they have type A blood, Or the converse: I don't want anyone to think they're safe because their blood group is not A. There are a lot of different species of bacteria and viruses that can cause diarrhea, so even though this blood-group association is strong, it doesn't change your overall risk. You should continue taking the same precautions whatever your blood type.” The study was published on May 17, 2018, in The Journal of Clinical Investigation.
Related Links:
Washington University School of Medicine
Latest Hematology News
- Rapid Cartridge-Based Test Aims to Expand Access to Hemoglobin Disorder Diagnosis
- New Guidelines Aim to Improve AL Amyloidosis Diagnosis
- Automated Hemostasis System Helps Labs of All Sizes Optimize Workflow
- Fast and Easy Test Could Revolutionize Blood Transfusions
- High-Sensitivity Blood Test Improves Assessment of Clotting Risk in Heart Disease Patients
- AI Algorithm Effectively Distinguishes Alpha Thalassemia Subtypes
- MRD Tests Could Predict Survival in Leukemia Patients
- Platelet Activity Blood Test in Middle Age Could Identify Early Alzheimer’s Risk
- Microvesicles Measurement Could Detect Vascular Injury in Sickle Cell Disease Patients
- ADLM’s New Coagulation Testing Guidance to Improve Care for Patients on Blood Thinners
- Viscoelastic Testing Could Improve Treatment of Maternal Hemorrhage
- Pioneering Model Measures Radiation Exposure in Blood for Precise Cancer Treatments
- Platelets Could Improve Early and Minimally Invasive Detection of Cancer
- Portable and Disposable Device Obtains Platelet-Rich Plasma Without Complex Equipment
- Disposable Cartridge-Based Test Delivers Rapid and Accurate CBC Results
- First Point-of-Care Heparin Monitoring Test Provides Results in Under 15 Minutes

Channels
Clinical Chemistry
view channel
Blood Test Tracks Transplant Health Using Donor DNA
Organ transplantation offers life-saving treatment for patients with end-stage disease, but complications such as rejection remain a constant risk. Monitoring transplanted organs typically relies on invasive... Read more
AI Sensor Detects Neurological Disorders Using Single Saliva Drop
Neurological disorders such as Parkinson’s disease and Alzheimer’s disease often develop gradually and present subtle symptoms in their early stages. Because early signs are frequently vague or atypical,... Read moreMolecular Diagnostics
view channel
Blood Test Predicts Dementia in Women 25 Years Before Symptoms Begin
Dementia and Alzheimer’s disease often develop silently over many years before symptoms appear. Detecting risk earlier could allow preventive strategies to begin long before memory problems interfere with... Read more
Serial Liquid Biopsies Reveal Therapy Resistance in Metastatic Prostate Cancer
Metastatic Prostate cancer can rapidly adapt under treatment, making it difficult to detect resistance before clinical progression. Genomic results from archival tumor tissue may no longer reflect the... Read moreHematology
view channel
Rapid Cartridge-Based Test Aims to Expand Access to Hemoglobin Disorder Diagnosis
Sickle cell disease and beta thalassemia are hemoglobin disorders that often require referral to specialized laboratories for definitive diagnosis, delaying results for patients and clinicians.... Read more
New Guidelines Aim to Improve AL Amyloidosis Diagnosis
Light chain (AL) amyloidosis is a rare, life-threatening bone marrow disorder in which abnormal amyloid proteins accumulate in organs. Approximately 3,260 people in the United States are diagnosed... Read moreImmunology
view channel
Cancer Mutation ‘Fingerprints’ to Improve Prediction of Immunotherapy Response
Cancer cells accumulate thousands of genetic mutations, but not all mutations affect tumors in the same way. Some make cancer cells more visible to the immune system, while others allow tumors to evade... Read more
Immune Signature Identified in Treatment-Resistant Myasthenia Gravis
Myasthenia gravis is a rare autoimmune disorder in which immune attack at the neuromuscular junction causes fluctuating weakness that can impair vision, movement, speech, swallowing, and breathing.... Read more
New Biomarker Predicts Chemotherapy Response in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
Triple-negative breast cancer is an aggressive form of breast cancer in which patients often show widely varying responses to chemotherapy. Predicting who will benefit from treatment remains challenging,... Read moreBlood Test Identifies Lung Cancer Patients Who Can Benefit from Immunotherapy Drug
Small cell lung cancer (SCLC) is an aggressive disease with limited treatment options, and even newly approved immunotherapies do not benefit all patients. While immunotherapy can extend survival for some,... Read morePathology
view channel
Novel mcPCR Technology to Transform Testing of Clinical Samples
DNA methylation is an important biological marker used in the diagnosis and monitoring of many diseases, including cancer. These chemical modifications to DNA influence gene activity and can reveal early... Read more
Sex Differences in Alzheimer’s Biomarkers Linked to Faster Cognitive Decline
Sex differences in Alzheimer’s disease present ongoing diagnostic challenges, with women often experiencing a disproportionate disease burden even when preclinical amyloid-beta levels are similar to men.... Read moreTechnology
view channel
AI Model Outperforms Clinicians in Rare Disease Detection
Rare diseases affect an estimated 300 million people worldwide, yet diagnosis is often protracted and error-prone. Many conditions present with heterogeneous signs that overlap with common disorders, leading... Read more
AI-Driven Diagnostic Demonstrates High Accuracy in Detecting Periprosthetic Joint Infection
Periprosthetic joint infection (PJI) is a rare but serious complication affecting 1% to 2% of primary joint replacement surgeries. The condition occurs when bacteria or fungi infect tissues around an implanted... Read moreIndustry
view channel
MGI Tech Strengthens Sequencing Portfolio with Dual Acquisition
MGI Tech Co., Ltd. (Shenzhen, China) announced the acquisition of STOmics and CycloneSEQ on March 3, 2026, as part of its “SEQALL+GLI+Omics” strategy. According to the company, the combined portfolio spans... Read more
Agilent Technologies Acquires Pathology Diagnostics Company Biocare Medical
Agilent Technologies (Santa Clara, CA, USA) has entered into a definitive agreement to acquire Biocare Medical (Pacheco, CA, USA), expanding its pathology portfolio through the addition of highly complementary... Read more