HPV Testing Detects More Precancerous Lesions
|
By LabMedica International staff writers Posted on 03 Oct 2017 |
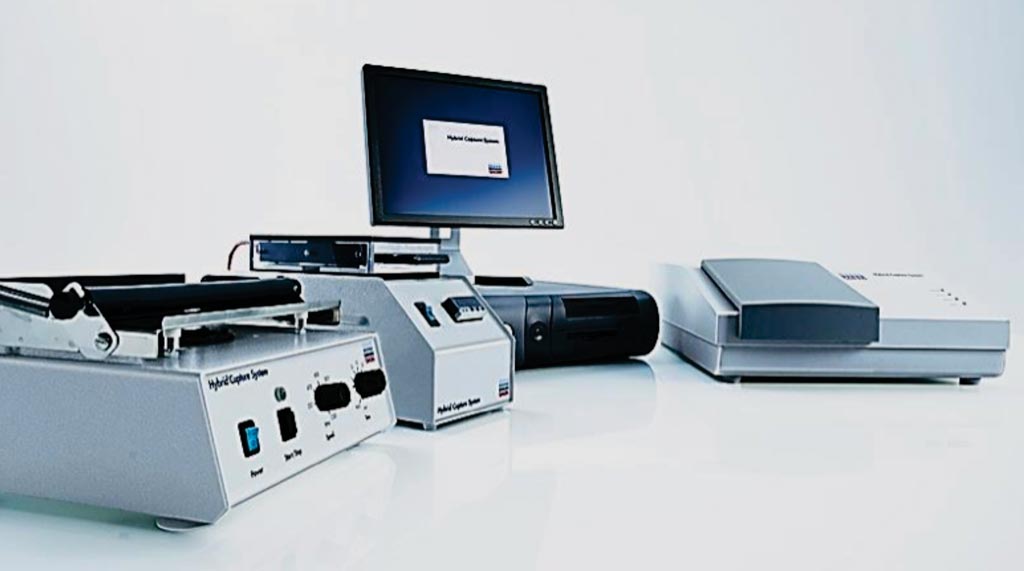

Image: The Hybrid Capture 2 modular system used for processing the digene HC2 HPV DNA Test of human papillomavirus infections (Photo courtesy of Qiagen).
Human papillomavirus (HPV) testing detects a higher number of precancerous cervical lesions than cytology-based Papanicolaou (Pap) smears in a female population including a proportion offered HPV vaccination according to a new study.
Many countries are currently considering switching from classic Pap tests to primary HPV tests for cervical cancer screening, based on the strong evidence linking cervical abnormalities and infection with certain HPV types, and data suggesting that HPV tests detect more high-grade precancerous lesions.
Scientists collaborating with those at the Victorian Cytology Service, Melbourne, Australia) randomized cervical samples from 4,995 women aged 25-64 in Australia, in a 1:2:2 ratio, to be analyzed by either cytology (with HPV testing of low-grade abnormalities), HPV testing with partial genotyping of the virus for the highest risk types HPV16 and 18, and cytology (for participants with other high-risk HPV genotypes), or HPV testing with partial genotyping and dual-stained cytology. In the first screening round of the trial, the scientists assessed the rates of women being referred for further testing and of detection of high-grade cervical intraepithelial neoplasia precancerous lesions (CIN2+).
For liquid-based cytology (LBC) screening and triage testing, ThinPrep was used. For HPV screening and triage testing, both the digene Hybrid Capture 2 (HC2) and Cobas 4800 technologies were used since the objectives of the study included laboratory evaluation of different HPV test technologies. The Cobas 4800 was used for the initial 3,104 (78%) of the total 4,003 HPV-screened women, and HC2 was used for the remainder.
The investigators found that for the cytology group, the overall referral and detected CIN2+ rates were 27/995 (2.7%) and 1/995 (0.1%) respectively; for the HPV testing and cytology group these were 75/1992 (3.8%)and 20/1992 (1.0%) and for the HPV and dual-stained cytology group these were 79/2008 (3.9%) and 24/2008 (1.2%). The team found that, in the first round of screening, detection of CIN2+ was significantly increased with HPV testing as compared with cytology, while referral was non-significantly increased. Adverse events were rare, and the one case of early-stage cervical cancer in the HPV testing plus cytology group was detected as appropriate by screening.
Karen Canfell, D.Phil, a professor of cancer epidemiology and lead author of the study, said, “These findings provide initial confirmation of an improved performance of primary HPV screening compared to cytology screening in settings with HPV-vaccinated populations. These findings support the planned imminent introduction of cervical screening by HPV testing in Australia which will occur at the end of 2017.” The study was published on September 19, 2017, in the journal Public Library of Science Medicine.
Related Links:
Victorian Cytology Service
Many countries are currently considering switching from classic Pap tests to primary HPV tests for cervical cancer screening, based on the strong evidence linking cervical abnormalities and infection with certain HPV types, and data suggesting that HPV tests detect more high-grade precancerous lesions.
Scientists collaborating with those at the Victorian Cytology Service, Melbourne, Australia) randomized cervical samples from 4,995 women aged 25-64 in Australia, in a 1:2:2 ratio, to be analyzed by either cytology (with HPV testing of low-grade abnormalities), HPV testing with partial genotyping of the virus for the highest risk types HPV16 and 18, and cytology (for participants with other high-risk HPV genotypes), or HPV testing with partial genotyping and dual-stained cytology. In the first screening round of the trial, the scientists assessed the rates of women being referred for further testing and of detection of high-grade cervical intraepithelial neoplasia precancerous lesions (CIN2+).
For liquid-based cytology (LBC) screening and triage testing, ThinPrep was used. For HPV screening and triage testing, both the digene Hybrid Capture 2 (HC2) and Cobas 4800 technologies were used since the objectives of the study included laboratory evaluation of different HPV test technologies. The Cobas 4800 was used for the initial 3,104 (78%) of the total 4,003 HPV-screened women, and HC2 was used for the remainder.
The investigators found that for the cytology group, the overall referral and detected CIN2+ rates were 27/995 (2.7%) and 1/995 (0.1%) respectively; for the HPV testing and cytology group these were 75/1992 (3.8%)and 20/1992 (1.0%) and for the HPV and dual-stained cytology group these were 79/2008 (3.9%) and 24/2008 (1.2%). The team found that, in the first round of screening, detection of CIN2+ was significantly increased with HPV testing as compared with cytology, while referral was non-significantly increased. Adverse events were rare, and the one case of early-stage cervical cancer in the HPV testing plus cytology group was detected as appropriate by screening.
Karen Canfell, D.Phil, a professor of cancer epidemiology and lead author of the study, said, “These findings provide initial confirmation of an improved performance of primary HPV screening compared to cytology screening in settings with HPV-vaccinated populations. These findings support the planned imminent introduction of cervical screening by HPV testing in Australia which will occur at the end of 2017.” The study was published on September 19, 2017, in the journal Public Library of Science Medicine.
Related Links:
Victorian Cytology Service
Latest Pathology News
- AI Tool Predicts Chemotherapy Response from Biopsy Slides
- Sex Differences in Alzheimer’s Biomarkers Linked to Faster Cognitive Decline
- World’s First Optical Microneedle Device to Enable Blood-Sampling-Free Clinical Testing
- Novel mcPCR Technology to Transform Testing of Clinical Samples
- Pathogen-Agnostic Testing Reveals Hidden Respiratory Threats in Negative Samples
- Molecular Imaging to Reduce Need for Melanoma Biopsies
- Urine Specimen Collection System Improves Diagnostic Accuracy and Efficiency
- AI-Powered 3D Scanning System Speeds Cancer Screening
- Single Sample Classifier Predicts Cancer-Associated Fibroblast Subtypes in Patient Samples
- New AI-Driven Platform Standardizes Tuberculosis Smear Microscopy Workflow
- AI Tool Uses Blood Biomarkers to Predict Transplant Complications Before Symptoms Appear
- High-Resolution Cancer Virus Imaging Uncovers Potential Therapeutic Targets
- Research Consortium Harnesses AI and Spatial Biology to Advance Cancer Discovery
- AI Tool Helps See How Cells Work Together Inside Diseased Tissue
- AI-Powered Microscope Diagnoses Malaria in Blood Smears Within Minutes
- Engineered Yeast Cells Enable Rapid Testing of Cancer Immunotherapy
Channels
Clinical Chemistry
view channel
AI Sensor Detects Neurological Disorders Using Single Saliva Drop
Neurological disorders such as Parkinson’s disease and Alzheimer’s disease often develop gradually and present subtle symptoms in their early stages. Because early signs are frequently vague or atypical,... Read moreNew Blood Test Index Offers Earlier Detection of Liver Scarring
Metabolic fatty liver disease is highly prevalent and often silent, yet it can progress to fibrosis, cirrhosis, and liver failure. Current first-line blood test scores frequently return indeterminate results,... Read moreMolecular Diagnostics
view channel
AI-Powered Blood Test Detects Early Pancreatic Cancer with More Than 90% Accuracy
Pancreatic cancer is one of the most lethal cancers, often referred to as the “King of Cancers” because symptoms usually appear only at advanced stages. As a result, most patients are diagnosed late, and... Read more
AI-Powered Blood Test Flags Relapse Risk Earlier After Transplant
Relapse after allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplant is a major cause of mortality in acute myeloid leukemia (AML) and myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS), and standard monitoring can miss early warning signals.... Read more
World’s First Portable POC Test Simultaneously Detects Four Common STIs in One Hour
Sexually transmitted infections (STIs) often present with similar symptoms, making accurate diagnosis challenging without laboratory testing. Delays in identifying the exact infection can lead to inappropriate... Read moreHematology
view channel
Rapid Cartridge-Based Test Aims to Expand Access to Hemoglobin Disorder Diagnosis
Sickle cell disease and beta thalassemia are hemoglobin disorders that often require referral to specialized laboratories for definitive diagnosis, delaying results for patients and clinicians.... Read more
New Guidelines Aim to Improve AL Amyloidosis Diagnosis
Light chain (AL) amyloidosis is a rare, life-threatening bone marrow disorder in which abnormal amyloid proteins accumulate in organs. Approximately 3,260 people in the United States are diagnosed... Read moreImmunology
view channel
Cancer Mutation ‘Fingerprints’ to Improve Prediction of Immunotherapy Response
Cancer cells accumulate thousands of genetic mutations, but not all mutations affect tumors in the same way. Some make cancer cells more visible to the immune system, while others allow tumors to evade... Read more
Immune Signature Identified in Treatment-Resistant Myasthenia Gravis
Myasthenia gravis is a rare autoimmune disorder in which immune attack at the neuromuscular junction causes fluctuating weakness that can impair vision, movement, speech, swallowing, and breathing.... Read more
New Biomarker Predicts Chemotherapy Response in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
Triple-negative breast cancer is an aggressive form of breast cancer in which patients often show widely varying responses to chemotherapy. Predicting who will benefit from treatment remains challenging,... Read moreBlood Test Identifies Lung Cancer Patients Who Can Benefit from Immunotherapy Drug
Small cell lung cancer (SCLC) is an aggressive disease with limited treatment options, and even newly approved immunotherapies do not benefit all patients. While immunotherapy can extend survival for some,... Read morePathology
view channel
Novel mcPCR Technology to Transform Testing of Clinical Samples
DNA methylation is an important biological marker used in the diagnosis and monitoring of many diseases, including cancer. These chemical modifications to DNA influence gene activity and can reveal early... Read more
Sex Differences in Alzheimer’s Biomarkers Linked to Faster Cognitive Decline
Sex differences in Alzheimer’s disease present ongoing diagnostic challenges, with women often experiencing a disproportionate disease burden even when preclinical amyloid-beta levels are similar to men.... Read moreTechnology
view channel
AI Model Outperforms Clinicians in Rare Disease Detection
Rare diseases affect an estimated 300 million people worldwide, yet diagnosis is often protracted and error-prone. Many conditions present with heterogeneous signs that overlap with common disorders, leading... Read more
AI-Driven Diagnostic Demonstrates High Accuracy in Detecting Periprosthetic Joint Infection
Periprosthetic joint infection (PJI) is a rare but serious complication affecting 1% to 2% of primary joint replacement surgeries. The condition occurs when bacteria or fungi infect tissues around an implanted... Read moreIndustry
view channel
Agilent Technologies Acquires Pathology Diagnostics Company Biocare Medical
Agilent Technologies (Santa Clara, CA, USA) has entered into a definitive agreement to acquire Biocare Medical (Pacheco, CA, USA), expanding its pathology portfolio through the addition of highly complementary... Read more
Cepheid Joins CDC Initiative to Strengthen U.S. Pandemic Testing Preparednesss
Cepheid (Sunnyvale, CA, USA) has been selected by the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) as one of four national collaborators in a federal initiative to speed rapid diagnostic technologies... Read more
QuidelOrtho Collaborates with Lifotronic to Expand Global Immunoassay Portfolio
QuidelOrtho (San Diego, CA, USA) has entered a long-term strategic supply agreement with Lifotronic Technology (Shenzhen, China) to expand its global immunoassay portfolio and accelerate customer access... Read more




















