Graphene-Based Sensor Helps Predict Asthma Attacks
|
By LabMedica International staff writers Posted on 05 Jun 2017 |
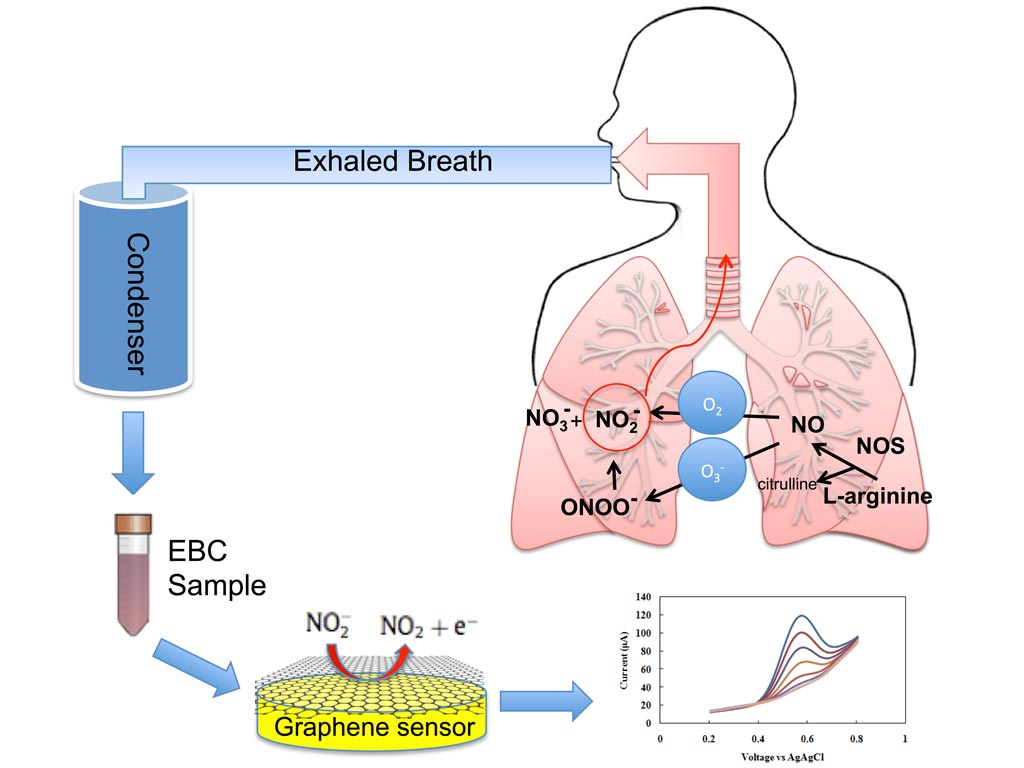
Image: Exhaled breath condensate is rapidly analyzed by a new graphene-based nanoelectronic sensor that detects nitrite, a key inflammatory marker in the inner lining of the respiratory airway (Photo courtesy of Azam Gholizadeh, Rutgers University).
Researchers have developed a prototype graphene-based device that detects inflammation in lungs, which could lead to earlier detection of asthma attacks and improve the management of asthma and other respiratory diseases, preventing hospitalizations and deaths. The invention helps pave the way for developing small wearable devices that could indicate when and at what dosage to take medication.
A diverse team of experts at Rutgers University-New Brunswick (New Brunswick, NJ, USA) created the sensor in response to the need for improved, minimally invasive methods for the molecular diagnosis and monitoring of asthma. Today’s non-invasive methods are limited in characterizing the nature and degree of airway inflammation, and require costly, bulky equipment that patients cannot easily keep with them. The methods include spirometry, which measures breathing capacity, and testing for exhaled nitric oxide, an indicator of airway inflammation.
Asthma causes inflammation of the airway and obstructs airflow. Other serious lung ailments include chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), which encompasses emphysema and chronic bronchitis.
“Our vision is to develop a device that someone with asthma or another respiratory disease can wear around their neck or on their wrist and blow into it periodically to predict the onset of an asthma attack or other problems,” said Mehdi Javanmard, assistant professor at Rutgers, “It advances the field of personalized and precision medicine.” Measuring biomarkers in exhaled breath condensate (tiny liquid droplets discharged during breathing) can also contribute to understanding asthma at the molecular level and lead to targeted treatment and better disease management.
Graphene is a thin layer of the graphite used in pencils. The new miniaturized electrochemical sensor accurately measures nitrite in exhaled breath condensate using reduced graphene oxide, which resists corrosion, has superior electrical properties, and is very accurate in detecting biomarkers.
“Nitrite level in breath condensate is a promising biomarker for inflammation in the respiratory tract. Having a rapid, easy method to measure it can help an asthmatic determine if air pollutants are affecting them so they can better manage use of medication and physical activity,” said Clifford Weisel, study co-author and professor at Rutgers, “It could also be used in a physician’s office and emergency departments to monitor the effectiveness of various anti-inflammatory drugs to optimize treatment.”
“Increases in airway inflammation may be an early warning sign of increased risk of an asthma attack or exacerbation of COPD, allowing for earlier and more-effective preventive measures or treatment,” said Robert Laumbach, study co-author and an occupational and environmental medicine physician at Rutgers.
“Just looking at coughing, wheezing, and other outward symptoms, diagnosis accuracy is often poor,” said Prof. Javanmard, “The ability to perform label-free quantification of nitrite content in exhaled breath condensate in a single step without any sample pre-treatment resolves a key bottleneck to enabling portable asthma management.” The next step is to develop a portable, wearable system. The researchers also envision expanding the number of inflammation biomarkers a device could detect and measure.
The study, by Gholizadeh A et al, was published May 22, 2017, in the journal Microsystems & Nanoengineering.
Related Links
Rutgers University-New Brunswick
A diverse team of experts at Rutgers University-New Brunswick (New Brunswick, NJ, USA) created the sensor in response to the need for improved, minimally invasive methods for the molecular diagnosis and monitoring of asthma. Today’s non-invasive methods are limited in characterizing the nature and degree of airway inflammation, and require costly, bulky equipment that patients cannot easily keep with them. The methods include spirometry, which measures breathing capacity, and testing for exhaled nitric oxide, an indicator of airway inflammation.
Asthma causes inflammation of the airway and obstructs airflow. Other serious lung ailments include chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), which encompasses emphysema and chronic bronchitis.
“Our vision is to develop a device that someone with asthma or another respiratory disease can wear around their neck or on their wrist and blow into it periodically to predict the onset of an asthma attack or other problems,” said Mehdi Javanmard, assistant professor at Rutgers, “It advances the field of personalized and precision medicine.” Measuring biomarkers in exhaled breath condensate (tiny liquid droplets discharged during breathing) can also contribute to understanding asthma at the molecular level and lead to targeted treatment and better disease management.
Graphene is a thin layer of the graphite used in pencils. The new miniaturized electrochemical sensor accurately measures nitrite in exhaled breath condensate using reduced graphene oxide, which resists corrosion, has superior electrical properties, and is very accurate in detecting biomarkers.
“Nitrite level in breath condensate is a promising biomarker for inflammation in the respiratory tract. Having a rapid, easy method to measure it can help an asthmatic determine if air pollutants are affecting them so they can better manage use of medication and physical activity,” said Clifford Weisel, study co-author and professor at Rutgers, “It could also be used in a physician’s office and emergency departments to monitor the effectiveness of various anti-inflammatory drugs to optimize treatment.”
“Increases in airway inflammation may be an early warning sign of increased risk of an asthma attack or exacerbation of COPD, allowing for earlier and more-effective preventive measures or treatment,” said Robert Laumbach, study co-author and an occupational and environmental medicine physician at Rutgers.
“Just looking at coughing, wheezing, and other outward symptoms, diagnosis accuracy is often poor,” said Prof. Javanmard, “The ability to perform label-free quantification of nitrite content in exhaled breath condensate in a single step without any sample pre-treatment resolves a key bottleneck to enabling portable asthma management.” The next step is to develop a portable, wearable system. The researchers also envision expanding the number of inflammation biomarkers a device could detect and measure.
The study, by Gholizadeh A et al, was published May 22, 2017, in the journal Microsystems & Nanoengineering.
Related Links
Rutgers University-New Brunswick
Latest Immunology News
- Blood Test Identifies Lung Cancer Patients Who Can Benefit from Immunotherapy Drug
- Whole-Genome Sequencing Approach Identifies Cancer Patients Benefitting From PARP-Inhibitor Treatment
- Ultrasensitive Liquid Biopsy Demonstrates Efficacy in Predicting Immunotherapy Response
- Blood Test Could Identify Colon Cancer Patients to Benefit from NSAIDs
- Blood Test Could Detect Adverse Immunotherapy Effects
- Routine Blood Test Can Predict Who Benefits Most from CAR T-Cell Therapy
- New Test Distinguishes Vaccine-Induced False Positives from Active HIV Infection
- Gene Signature Test Predicts Response to Key Breast Cancer Treatment
- Chip Captures Cancer Cells from Blood to Help Select Right Breast Cancer Treatment
- Blood-Based Liquid Biopsy Model Analyzes Immunotherapy Effectiveness
- Signature Genes Predict T-Cell Expansion in Cancer Immunotherapy
- Molecular Microscope Diagnostic System Assesses Lung Transplant Rejection
- Blood Test Tracks Treatment Resistance in High-Grade Serous Ovarian Cancer
- Luminescent Probe Measures Immune Cell Activity in Real Time
- Blood-Based Immune Cell Signatures Could Guide Treatment Decisions for Critically Ill Patients
- Novel Tool Predicts Most Effective Multiple Sclerosis Medication for Patients
Channels
Clinical Chemistry
view channel
Rapid Blood Testing Method Aids Safer Decision-Making in Drug-Related Emergencies
Acute recreational drug toxicity is a frequent reason for emergency department visits, yet clinicians rarely have access to confirmatory toxicology results in real time. Instead, treatment decisions are... Read more
New PSA-Based Prognostic Model Improves Prostate Cancer Risk Assessment
Prostate cancer is the second-leading cause of cancer death among American men, and about one in eight will be diagnosed in their lifetime. Screening relies on blood levels of prostate-specific antigen... Read moreMolecular Diagnostics
view channel
Group A Strep Molecular Test Delivers Definitive Results at POC in 15 Minutes
Strep throat is a bacterial infection caused by Group A Streptococcus (GAS). It is a leading bacterial cause of acute pharyngitis, particularly in children and adolescents, and one of the most common reasons... Read more
Rapid Molecular Test Identifies Sepsis Patients Most Likely to Have Positive Blood Cultures
Sepsis is caused by a patient’s overwhelming immune response to an infection. If undetected or left untreated, sepsis leads to tissue damage, organ failure, permanent disability, and often death.... Read moreHematology
view channel
Rapid Cartridge-Based Test Aims to Expand Access to Hemoglobin Disorder Diagnosis
Sickle cell disease and beta thalassemia are hemoglobin disorders that often require referral to specialized laboratories for definitive diagnosis, delaying results for patients and clinicians.... Read more
New Guidelines Aim to Improve AL Amyloidosis Diagnosis
Light chain (AL) amyloidosis is a rare, life-threatening bone marrow disorder in which abnormal amyloid proteins accumulate in organs. Approximately 3,260 people in the United States are diagnosed... Read moreImmunology
view channelBlood Test Identifies Lung Cancer Patients Who Can Benefit from Immunotherapy Drug
Small cell lung cancer (SCLC) is an aggressive disease with limited treatment options, and even newly approved immunotherapies do not benefit all patients. While immunotherapy can extend survival for some,... Read more
Whole-Genome Sequencing Approach Identifies Cancer Patients Benefitting From PARP-Inhibitor Treatment
Targeted cancer therapies such as PARP inhibitors can be highly effective, but only for patients whose tumors carry specific DNA repair defects. Identifying these patients accurately remains challenging,... Read more
Ultrasensitive Liquid Biopsy Demonstrates Efficacy in Predicting Immunotherapy Response
Immunotherapy has transformed cancer treatment, but only a small proportion of patients experience lasting benefit, with response rates often remaining between 10% and 20%. Clinicians currently lack reliable... Read moreMicrobiology
view channel
CRISPR-Based Technology Neutralizes Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria
Antibiotic resistance has accelerated into a global health crisis, with projections estimating more than 10 million deaths per year by 2050 as drug-resistant “superbugs” continue to spread.... Read more
Comprehensive Review Identifies Gut Microbiome Signatures Associated With Alzheimer’s Disease
Alzheimer’s disease affects approximately 6.7 million people in the United States and nearly 50 million worldwide, yet early cognitive decline remains difficult to characterize. Increasing evidence suggests... Read morePathology
view channel
AI Tool Uses Blood Biomarkers to Predict Transplant Complications Before Symptoms Appear
Stem cell and bone marrow transplants can be lifesaving, but serious complications may arise months after patients leave the hospital. One of the most dangerous is chronic graft-versus-host disease, in... Read more
Research Consortium Harnesses AI and Spatial Biology to Advance Cancer Discovery
AI has the potential to transform cancer care, yet progress remains constrained by fragmented, inaccessible data that hinder advances in early diagnosis and precision therapy. Unlocking patterns missed... Read moreIndustry
view channel
QuidelOrtho Collaborates with Lifotronic to Expand Global Immunoassay Portfolio
QuidelOrtho (San Diego, CA, USA) has entered a long-term strategic supply agreement with Lifotronic Technology (Shenzhen, China) to expand its global immunoassay portfolio and accelerate customer access... Read more