Potential Noninvasive Biomarker of EoE Disease Activity Identified
|
By LabMedica International staff writers Posted on 24 May 2016 |
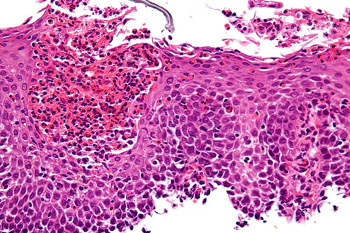
Image: A micrograph of eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE), H&E stain. Characteristic features are present: Abundant eosinophils – criteria vary; one common definition is: > 20 eosinophils/0.24 mm2; Papillae are elongated; papillae reach into the top 1/3 of the epithelial layer; Basal cell hyperplasia; > 3 cells thick or >15% of epithelial thickness; Spongiosis (Photo courtesy of Michael Bonert / Wikimedia).
Researchers have identified a potential blood-based marker of disease activity for the severe and often painful food allergic disease eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE) – possibly leading to a blood test, which could spare EoE patients, often children, the discomfort and risk of the currently used invasive endoscopic monitoring procedures.
Researchers at the Cincinnati Center for Eosinophilic Disorders (CCED) of Cincinnati Children’s Hospital Medical Center (Cincinnati, OH, USA) led the study. “Adults and children with EoE can be on highly restricted diets of formula alone or only a few foods,” said Patricia C. Fulkerson, MD, PhD, senior study author, “One of the major obstacles to families participating in studies to introduce foods back into the child’s diet is the need for endoscopy after each food is tried to see whether or not it triggers disease activity.”
The disease activity of EoE is currently monitored using peak esophageal eosinophil count, which requires endoscopy to collect esophageal tissue biopsies. People with EoE, a lifelong disease, must continue monitoring disease activity, even after effective treatment with restricted diets or steroids. Treatment changes, such as reintroducing a single food, require additional endoscopic exams to assess for disease flare-ups.
Prior research has demonstrated that testing blood of EoE patients is not a clinically useful indication of active disease because eosinophil levels in blood do not correlate well with levels in the esophagus. This led the team to investigate a precursor cell to eosinophils, a lineage-committed eosinophil progenitor (EoP), as a potential marker. They found elevated EoP levels in the blood of pediatric patients with active EoE disease, suggesting a promising, blood-based marker.
The authors emphasize that additional research is needed to validate the marker before routine clinical use. “This clinical study is the first to investigate EoP levels in patients with EoE and identifies a potential new noninvasive biomarker,” said study author Vincent A. Mukkada, MD, physician at Cincinnati Children’s and CCED member, “This work is an essential step toward improving outcomes for patients with EoE. It will be followed by repeated testing of more patients and with sequential measurements of EoP levels in the same patient during different disease states.”
Allergic diseases have been on the rise over the past 20 years. The CCED team has previously reported that incidence of EoE is estimated at 1 of 1,000 people. Their research has also shown that EoE is caused by a combination of genetic and environmental factors, and is primarily mediated by an immunologic response to foods. The hallmark of EoE is swelling and inflammation in the esophagus, accompanied by high levels of eosinophils.
The study, by Morris DW et al, was published May 16, 2016, in the Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology.
Related Links:
Cincinnati Children’s Hospital Medical Center
Researchers at the Cincinnati Center for Eosinophilic Disorders (CCED) of Cincinnati Children’s Hospital Medical Center (Cincinnati, OH, USA) led the study. “Adults and children with EoE can be on highly restricted diets of formula alone or only a few foods,” said Patricia C. Fulkerson, MD, PhD, senior study author, “One of the major obstacles to families participating in studies to introduce foods back into the child’s diet is the need for endoscopy after each food is tried to see whether or not it triggers disease activity.”
The disease activity of EoE is currently monitored using peak esophageal eosinophil count, which requires endoscopy to collect esophageal tissue biopsies. People with EoE, a lifelong disease, must continue monitoring disease activity, even after effective treatment with restricted diets or steroids. Treatment changes, such as reintroducing a single food, require additional endoscopic exams to assess for disease flare-ups.
Prior research has demonstrated that testing blood of EoE patients is not a clinically useful indication of active disease because eosinophil levels in blood do not correlate well with levels in the esophagus. This led the team to investigate a precursor cell to eosinophils, a lineage-committed eosinophil progenitor (EoP), as a potential marker. They found elevated EoP levels in the blood of pediatric patients with active EoE disease, suggesting a promising, blood-based marker.
The authors emphasize that additional research is needed to validate the marker before routine clinical use. “This clinical study is the first to investigate EoP levels in patients with EoE and identifies a potential new noninvasive biomarker,” said study author Vincent A. Mukkada, MD, physician at Cincinnati Children’s and CCED member, “This work is an essential step toward improving outcomes for patients with EoE. It will be followed by repeated testing of more patients and with sequential measurements of EoP levels in the same patient during different disease states.”
Allergic diseases have been on the rise over the past 20 years. The CCED team has previously reported that incidence of EoE is estimated at 1 of 1,000 people. Their research has also shown that EoE is caused by a combination of genetic and environmental factors, and is primarily mediated by an immunologic response to foods. The hallmark of EoE is swelling and inflammation in the esophagus, accompanied by high levels of eosinophils.
The study, by Morris DW et al, was published May 16, 2016, in the Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology.
Related Links:
Cincinnati Children’s Hospital Medical Center
Latest Pathology News
- Molecular Imaging to Reduce Need for Melanoma Biopsies
- Urine Specimen Collection System Improves Diagnostic Accuracy and Efficiency
- AI-Powered 3D Scanning System Speeds Cancer Screening
- Single Sample Classifier Predicts Cancer-Associated Fibroblast Subtypes in Patient Samples
- New AI-Driven Platform Standardizes Tuberculosis Smear Microscopy Workflow
- AI Tool Uses Blood Biomarkers to Predict Transplant Complications Before Symptoms Appear
- High-Resolution Cancer Virus Imaging Uncovers Potential Therapeutic Targets
- Research Consortium Harnesses AI and Spatial Biology to Advance Cancer Discovery
- AI Tool Helps See How Cells Work Together Inside Diseased Tissue
- AI-Powered Microscope Diagnoses Malaria in Blood Smears Within Minutes
- Engineered Yeast Cells Enable Rapid Testing of Cancer Immunotherapy
- First-Of-Its-Kind Test Identifies Autism Risk at Birth
- AI Algorithms Improve Genetic Mutation Detection in Cancer Diagnostics
- Skin Biopsy Offers New Diagnostic Method for Neurodegenerative Diseases
- Fast Label-Free Method Identifies Aggressive Cancer Cells
- New X-Ray Method Promises Advances in Histology
Channels
Clinical Chemistry
view channelNew Blood Test Index Offers Earlier Detection of Liver Scarring
Metabolic fatty liver disease is highly prevalent and often silent, yet it can progress to fibrosis, cirrhosis, and liver failure. Current first-line blood test scores frequently return indeterminate results,... Read more
Electronic Nose Smells Early Signs of Ovarian Cancer in Blood
Ovarian cancer is often diagnosed at a late stage because its symptoms are vague and resemble those of more common conditions. Unlike breast cancer, there is currently no reliable screening method, and... Read moreMolecular Diagnostics
view channel
New Test Detects Alzheimer’s by Analyzing Altered Protein Shapes in Blood
Alzheimer’s disease begins developing years before memory loss or other symptoms become visible. Misfolded proteins gradually accumulate in the brain, disrupting normal cellular processes.... Read more
New Diagnostic Markers for Multiple Sclerosis Discovered in Cerebrospinal Fluid
Multiple sclerosis (MS) affects nearly three million people worldwide and can cause symptoms such as numbness, visual disturbances, fatigue, and neurological disability. Diagnosing the disease can be challenging... Read moreHematology
view channel
Rapid Cartridge-Based Test Aims to Expand Access to Hemoglobin Disorder Diagnosis
Sickle cell disease and beta thalassemia are hemoglobin disorders that often require referral to specialized laboratories for definitive diagnosis, delaying results for patients and clinicians.... Read more
New Guidelines Aim to Improve AL Amyloidosis Diagnosis
Light chain (AL) amyloidosis is a rare, life-threatening bone marrow disorder in which abnormal amyloid proteins accumulate in organs. Approximately 3,260 people in the United States are diagnosed... Read moreMicrobiology
view channel
Rapid Sequencing Could Transform Tuberculosis Care
Tuberculosis remains the world’s leading cause of death from a single infectious agent, responsible for more than one million deaths each year. Diagnosing and monitoring the disease can be slow because... Read more
Blood-Based Viral Signature Identified in Crohn’s Disease
Crohn’s disease is a chronic inflammatory intestinal disorder affecting approximately 0.4% of the European population, with symptoms and progression that vary widely. Although viral components of the microbiome... Read morePathology
view channel
Molecular Imaging to Reduce Need for Melanoma Biopsies
Melanoma is the deadliest form of skin cancer and accounts for the vast majority of skin cancer-related deaths. Because early melanomas can closely resemble benign moles, clinicians often rely on visual... Read more
Urine Specimen Collection System Improves Diagnostic Accuracy and Efficiency
Urine testing is a critical, non-invasive diagnostic tool used to detect conditions such as pregnancy, urinary tract infections, metabolic disorders, cancer, and kidney disease. However, contaminated or... Read moreTechnology
view channel
AI Model Outperforms Clinicians in Rare Disease Detection
Rare diseases affect an estimated 300 million people worldwide, yet diagnosis is often protracted and error-prone. Many conditions present with heterogeneous signs that overlap with common disorders, leading... Read more
AI-Driven Diagnostic Demonstrates High Accuracy in Detecting Periprosthetic Joint Infection
Periprosthetic joint infection (PJI) is a rare but serious complication affecting 1% to 2% of primary joint replacement surgeries. The condition occurs when bacteria or fungi infect tissues around an implanted... Read moreIndustry
view channel
Cepheid Joins CDC Initiative to Strengthen U.S. Pandemic Testing Preparednesss
Cepheid (Sunnyvale, CA, USA) has been selected by the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) as one of four national collaborators in a federal initiative to speed rapid diagnostic technologies... Read more
QuidelOrtho Collaborates with Lifotronic to Expand Global Immunoassay Portfolio
QuidelOrtho (San Diego, CA, USA) has entered a long-term strategic supply agreement with Lifotronic Technology (Shenzhen, China) to expand its global immunoassay portfolio and accelerate customer access... Read more







 Analyzer.jpg)














