Microfluidic Device Rapidly Detects Urinary Tract Infections
|
By LabMedica International staff writers Posted on 23 Aug 2015 |
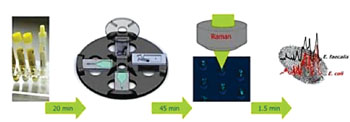
Image: The workflow of the Lab-on-a-Disc device for identifying bacteria in urine samples. From left to right (i) Urine sample from patient; (ii) Capturing bacteria in V-cup-structures on a Lab-on-a-Disk platform by centrifugation; (iii) Raman spectroscopic analysis of captured bacteria within the V-cups; (iv) Fingerprint-like spectroscopic information on the UTI pathogen (Photo courtesy of Ute Neugebauer).

Image: The alpha300 R Superior Confocal Raman Imaging System (Photo courtesy of WITec).
A polymeric centrifugal microfluidic platform has been developed for the rapid and sensitive identification of bacteria directly from urine, thus eliminating time-consuming cultivation steps.
Untreated urinary tract infections can quickly move to a life-threatening condition and cases may trigger sepsis, which occurs when the immune system, in an attempt to fight off the infection, inadvertently activates body-wide inflammation that can cause blood clots and leaky blood vessels.
Scientists at the Jena University Hospital (Germany) have created a Lab-on-a-Disc platform that combines microfluidics and Raman microscopy, a modern optical detection method. The platform utilizes the rotationally induced centrifugal field to efficiently capture bacteria directly from suspension within a glass-polymer hybrid chip. Once trapped in an array of small V-shaped structures, the bacteria are readily available for spectroscopic characterization, such as Raman spectroscopic fingerprinting, providing valuable information on the characteristics of the captured bacteria.
Anonymized urine samples were provided by the hospital’s Institute of Medical Microbiology. They originated from different patients with single pathogen urinary tract infections (UTIs) of Enterococcus faecalis and Escherichia coli. To remove bigger particles such as leukocytes or epithelial cells, the urine samples were run through membrane filters, centrifuged, the pellet washed twice with phosphate buffered saline (PBS), and is finally re-suspended in PBS before being loaded into the device. A CRM 300 micro-Raman setup (WITec, Ulm, Germany), equipped with a 600 lines/mm grating was used for micro-Raman measurements.
The whole procedure, including sample preparation, requires about one hour to obtain a valuable result, marking a significant reduction in diagnosis time when compared to the 24 hours and more, typically required for standard microbiological methods. Characterization of the captured bacteria by label-free conventional micro-Raman spectroscopy allows rapid identification of the pathogens with their characteristic features, which is valuable for first screening analysis. The device has been easily adapted for fluorescence measurements, paving the way for the development of microfluidics-based immunochemical assays, illustrating a high potential of the device for numerous applications in spectroscopy-based point-of-care diagnostics.
Ulrich-Christian Schröder, a doctoral student and lead author of the study said, “Our device works by loading a few microliters of a patient's urine sample into a tiny chip, which is then rotated with a high angular velocity so that any bacteria is guided by centrifugal force through microfluidic channels to a small chamber where 'V-cup capture units' collect it for optical investigation. We were able to identify Escherichia coli and Enterococcus faecalis within 70 minutes, directly from patients' urine samples.” The study was published on August 11, 2015, in the journal Biomicrofluidics.
Related Links:
Jena University Hospital
WITec
Untreated urinary tract infections can quickly move to a life-threatening condition and cases may trigger sepsis, which occurs when the immune system, in an attempt to fight off the infection, inadvertently activates body-wide inflammation that can cause blood clots and leaky blood vessels.
Scientists at the Jena University Hospital (Germany) have created a Lab-on-a-Disc platform that combines microfluidics and Raman microscopy, a modern optical detection method. The platform utilizes the rotationally induced centrifugal field to efficiently capture bacteria directly from suspension within a glass-polymer hybrid chip. Once trapped in an array of small V-shaped structures, the bacteria are readily available for spectroscopic characterization, such as Raman spectroscopic fingerprinting, providing valuable information on the characteristics of the captured bacteria.
Anonymized urine samples were provided by the hospital’s Institute of Medical Microbiology. They originated from different patients with single pathogen urinary tract infections (UTIs) of Enterococcus faecalis and Escherichia coli. To remove bigger particles such as leukocytes or epithelial cells, the urine samples were run through membrane filters, centrifuged, the pellet washed twice with phosphate buffered saline (PBS), and is finally re-suspended in PBS before being loaded into the device. A CRM 300 micro-Raman setup (WITec, Ulm, Germany), equipped with a 600 lines/mm grating was used for micro-Raman measurements.
The whole procedure, including sample preparation, requires about one hour to obtain a valuable result, marking a significant reduction in diagnosis time when compared to the 24 hours and more, typically required for standard microbiological methods. Characterization of the captured bacteria by label-free conventional micro-Raman spectroscopy allows rapid identification of the pathogens with their characteristic features, which is valuable for first screening analysis. The device has been easily adapted for fluorescence measurements, paving the way for the development of microfluidics-based immunochemical assays, illustrating a high potential of the device for numerous applications in spectroscopy-based point-of-care diagnostics.
Ulrich-Christian Schröder, a doctoral student and lead author of the study said, “Our device works by loading a few microliters of a patient's urine sample into a tiny chip, which is then rotated with a high angular velocity so that any bacteria is guided by centrifugal force through microfluidic channels to a small chamber where 'V-cup capture units' collect it for optical investigation. We were able to identify Escherichia coli and Enterococcus faecalis within 70 minutes, directly from patients' urine samples.” The study was published on August 11, 2015, in the journal Biomicrofluidics.
Related Links:
Jena University Hospital
WITec
Latest Microbiology News
- Hidden Gut Viruses Linked to Colorectal Cancer Risk
- Three-Test Panel Launched for Detection of Liver Fluke Infections
- Rapid Test Promises Faster Answers for Drug-Resistant Infections
- CRISPR-Based Technology Neutralizes Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria
- Comprehensive Review Identifies Gut Microbiome Signatures Associated With Alzheimer’s Disease
- AI-Powered Platform Enables Rapid Detection of Drug-Resistant C. Auris Pathogens
- New Test Measures How Effectively Antibiotics Kill Bacteria
- New Antimicrobial Stewardship Standards for TB Care to Optimize Diagnostics
- New UTI Diagnosis Method Delivers Antibiotic Resistance Results 24 Hours Earlier
- Breakthroughs in Microbial Analysis to Enhance Disease Prediction
- Blood-Based Diagnostic Method Could Identify Pediatric LRTIs
- Rapid Diagnostic Test Matches Gold Standard for Sepsis Detection
- Rapid POC Tuberculosis Test Provides Results Within 15 Minutes
- Rapid Assay Identifies Bloodstream Infection Pathogens Directly from Patient Samples
- Blood-Based Molecular Signatures to Enable Rapid EPTB Diagnosis
- 15-Minute Blood Test Diagnoses Life-Threatening Infections in Children
Channels
Clinical Chemistry
view channelNew Blood Test Index Offers Earlier Detection of Liver Scarring
Metabolic fatty liver disease is highly prevalent and often silent, yet it can progress to fibrosis, cirrhosis, and liver failure. Current first-line blood test scores frequently return indeterminate results,... Read more
Electronic Nose Smells Early Signs of Ovarian Cancer in Blood
Ovarian cancer is often diagnosed at a late stage because its symptoms are vague and resemble those of more common conditions. Unlike breast cancer, there is currently no reliable screening method, and... Read moreMolecular Diagnostics
view channel
Ultra-Sensitive DNA Test Identifies Relapse Risk in Aggressive Leukemia
Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is a rare but aggressive blood cancer in which relapse after allogeneic stem cell transplant remains a major clinical challenge, particularly for patients with NPM1-mutated disease.... Read more
Blood Test Could Help Detect Gallbladder Cancer Earlier
Gallbladder cancer is one of the deadliest gastrointestinal cancers because it is often diagnosed at an advanced stage when treatment options are limited. Early symptoms are minimal, and current screening... Read moreHematology
view channel
Rapid Cartridge-Based Test Aims to Expand Access to Hemoglobin Disorder Diagnosis
Sickle cell disease and beta thalassemia are hemoglobin disorders that often require referral to specialized laboratories for definitive diagnosis, delaying results for patients and clinicians.... Read more
New Guidelines Aim to Improve AL Amyloidosis Diagnosis
Light chain (AL) amyloidosis is a rare, life-threatening bone marrow disorder in which abnormal amyloid proteins accumulate in organs. Approximately 3,260 people in the United States are diagnosed... Read moreImmunology
view channel
New Biomarker Predicts Chemotherapy Response in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
Triple-negative breast cancer is an aggressive form of breast cancer in which patients often show widely varying responses to chemotherapy. Predicting who will benefit from treatment remains challenging,... Read moreBlood Test Identifies Lung Cancer Patients Who Can Benefit from Immunotherapy Drug
Small cell lung cancer (SCLC) is an aggressive disease with limited treatment options, and even newly approved immunotherapies do not benefit all patients. While immunotherapy can extend survival for some,... Read more
Whole-Genome Sequencing Approach Identifies Cancer Patients Benefitting From PARP-Inhibitor Treatment
Targeted cancer therapies such as PARP inhibitors can be highly effective, but only for patients whose tumors carry specific DNA repair defects. Identifying these patients accurately remains challenging,... Read more
Ultrasensitive Liquid Biopsy Demonstrates Efficacy in Predicting Immunotherapy Response
Immunotherapy has transformed cancer treatment, but only a small proportion of patients experience lasting benefit, with response rates often remaining between 10% and 20%. Clinicians currently lack reliable... Read moreMicrobiology
view channel
Hidden Gut Viruses Linked to Colorectal Cancer Risk
Colorectal cancer (CRC) remains a leading cause of cancer mortality in many Western countries, and existing risk-stratification approaches leave substantial room for improvement. Although age, diet, and... Read more
Three-Test Panel Launched for Detection of Liver Fluke Infections
Parasitic liver fluke infections remain endemic in parts of Asia, where transmission commonly occurs through consumption of raw freshwater fish or aquatic plants. Chronic infection is a well-established... Read morePathology
view channel
Molecular Imaging to Reduce Need for Melanoma Biopsies
Melanoma is the deadliest form of skin cancer and accounts for the vast majority of skin cancer-related deaths. Because early melanomas can closely resemble benign moles, clinicians often rely on visual... Read more
Urine Specimen Collection System Improves Diagnostic Accuracy and Efficiency
Urine testing is a critical, non-invasive diagnostic tool used to detect conditions such as pregnancy, urinary tract infections, metabolic disorders, cancer, and kidney disease. However, contaminated or... Read moreIndustry
view channel
Cepheid Joins CDC Initiative to Strengthen U.S. Pandemic Testing Preparednesss
Cepheid (Sunnyvale, CA, USA) has been selected by the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) as one of four national collaborators in a federal initiative to speed rapid diagnostic technologies... Read more
QuidelOrtho Collaborates with Lifotronic to Expand Global Immunoassay Portfolio
QuidelOrtho (San Diego, CA, USA) has entered a long-term strategic supply agreement with Lifotronic Technology (Shenzhen, China) to expand its global immunoassay portfolio and accelerate customer access... Read more




















