Rapid Automated Immunoassay for HTLV I/II Antibodies Now Available
|
By LabMedica International staff writers Posted on 05 Aug 2015 |

Image: The Elecsys benchtop analyzer was designed for small to medium workloads (Photo courtesy of Roche).
An automated immunoassay for the detection of antibodies against human T-lymphotropic virus I or II (HTLV-I/II) in donated blood and routine diagnostic samples and is now available for use by blood centers and clinical laboratories.
The Roche (Basel, Switzerland) HTLV-I/II immunoassay was designed for use on the Elecsys benchtop analyzer. This IVD instrument is powered by enhanced chemiluminescence (ECL) technology, which provides precise and reliable patient results that contribute to better patient care.
The Elecys instrument uses two electrochemically active substances, a ruthenium complex and tripropylamine (TPA). These reagents are involved in the reaction that leads to the emission of light. Ruthenium and TPA are non-isotopic and highly stable at base state. Only when voltage is applied and the labeled compound is repeatedly excited do the reactants begin emitting photons. To start the reaction, voltage is applied between the working and counter electrode, and an electrical field is created, ensuring a precisely controlled and timed reaction.
The operation is performed on a solution containing sample and reagents that are aspirated into the measuring cell. A magnetic field is applied, and the paramagnetic beads (coated with antigen/antibody complexes bound by streptavidin-biotin) are bound to the surface of the measuring cell. ProCell solution is introduced in order to separate the bound immunoassay complexes from the free remaining particles and to provide TPA, which is essential for the ECL-reaction. The test procedure requires about 18 minutes to run a single test.
“Globally there are around 20 million people infected with HTLV-I/II, many of whom are unknown carriers. If the virus is undetected in donors, the risk of spreading the infection increases,” said Roland Diggelmann, COO of the Roche Diagnostics Division. “Roche is uniquely positioned to help blood centers improve their testing efficiency, based on our broad assay portfolio and integrated molecular and serology laboratory solutions.”
Related Links:
Roche
The Roche (Basel, Switzerland) HTLV-I/II immunoassay was designed for use on the Elecsys benchtop analyzer. This IVD instrument is powered by enhanced chemiluminescence (ECL) technology, which provides precise and reliable patient results that contribute to better patient care.
The Elecys instrument uses two electrochemically active substances, a ruthenium complex and tripropylamine (TPA). These reagents are involved in the reaction that leads to the emission of light. Ruthenium and TPA are non-isotopic and highly stable at base state. Only when voltage is applied and the labeled compound is repeatedly excited do the reactants begin emitting photons. To start the reaction, voltage is applied between the working and counter electrode, and an electrical field is created, ensuring a precisely controlled and timed reaction.
The operation is performed on a solution containing sample and reagents that are aspirated into the measuring cell. A magnetic field is applied, and the paramagnetic beads (coated with antigen/antibody complexes bound by streptavidin-biotin) are bound to the surface of the measuring cell. ProCell solution is introduced in order to separate the bound immunoassay complexes from the free remaining particles and to provide TPA, which is essential for the ECL-reaction. The test procedure requires about 18 minutes to run a single test.
“Globally there are around 20 million people infected with HTLV-I/II, many of whom are unknown carriers. If the virus is undetected in donors, the risk of spreading the infection increases,” said Roland Diggelmann, COO of the Roche Diagnostics Division. “Roche is uniquely positioned to help blood centers improve their testing efficiency, based on our broad assay portfolio and integrated molecular and serology laboratory solutions.”
Related Links:
Roche
Latest Hematology News
- Rapid Cartridge-Based Test Aims to Expand Access to Hemoglobin Disorder Diagnosis
- New Guidelines Aim to Improve AL Amyloidosis Diagnosis
- Automated Hemostasis System Helps Labs of All Sizes Optimize Workflow
- Fast and Easy Test Could Revolutionize Blood Transfusions
- High-Sensitivity Blood Test Improves Assessment of Clotting Risk in Heart Disease Patients
- AI Algorithm Effectively Distinguishes Alpha Thalassemia Subtypes
- MRD Tests Could Predict Survival in Leukemia Patients
- Platelet Activity Blood Test in Middle Age Could Identify Early Alzheimer’s Risk
- Microvesicles Measurement Could Detect Vascular Injury in Sickle Cell Disease Patients
- ADLM’s New Coagulation Testing Guidance to Improve Care for Patients on Blood Thinners
- Viscoelastic Testing Could Improve Treatment of Maternal Hemorrhage
- Pioneering Model Measures Radiation Exposure in Blood for Precise Cancer Treatments
- Platelets Could Improve Early and Minimally Invasive Detection of Cancer
- Portable and Disposable Device Obtains Platelet-Rich Plasma Without Complex Equipment
- Disposable Cartridge-Based Test Delivers Rapid and Accurate CBC Results
- First Point-of-Care Heparin Monitoring Test Provides Results in Under 15 Minutes

Channels
Clinical Chemistry
view channel
Electronic Nose Smells Early Signs of Ovarian Cancer in Blood
Ovarian cancer is often diagnosed at a late stage because its symptoms are vague and resemble those of more common conditions. Unlike breast cancer, there is currently no reliable screening method, and... Read more
Simple Blood Test Offers New Path to Alzheimer’s Assessment in Primary Care
Timely evaluation of cognitive symptoms in primary care is often limited by restricted access to specialized diagnostics and invasive confirmatory procedures. Clinicians need accessible tools to determine... Read moreMolecular Diagnostics
view channel
New Blood Test Predicts Who Will Most Likely Live Longer
As people age, it becomes increasingly difficult to determine who is likely to maintain stable health and who may face serious decline. Traditional indicators such as age, cholesterol, and physical activity... Read more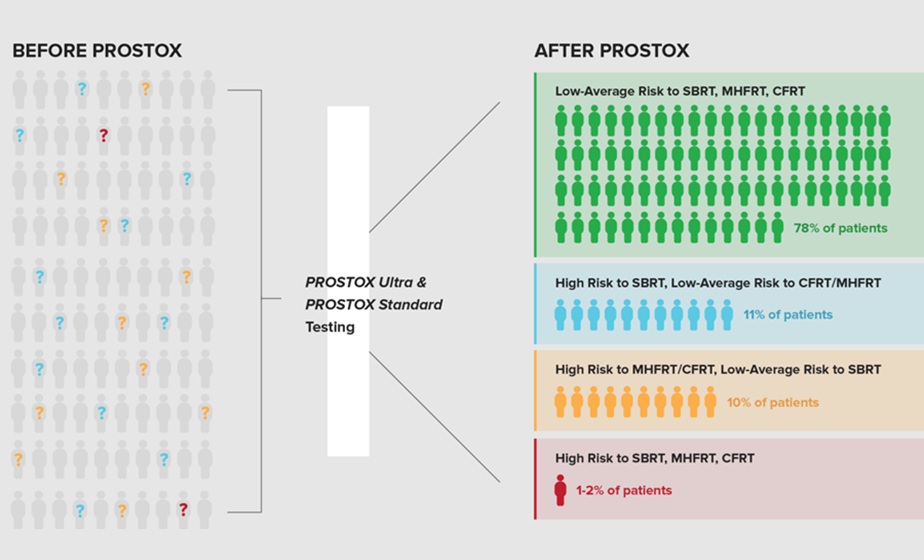
Genetic Test Predicts Radiation Therapy Risk for Prostate Cancer Patients
External beam radiation therapy is widely used to treat localized prostate cancer, which has a five-year survival rate exceeding 99%. However, more than 20% of patients develop persistent urinary side... Read moreHematology
view channel
Rapid Cartridge-Based Test Aims to Expand Access to Hemoglobin Disorder Diagnosis
Sickle cell disease and beta thalassemia are hemoglobin disorders that often require referral to specialized laboratories for definitive diagnosis, delaying results for patients and clinicians.... Read more
New Guidelines Aim to Improve AL Amyloidosis Diagnosis
Light chain (AL) amyloidosis is a rare, life-threatening bone marrow disorder in which abnormal amyloid proteins accumulate in organs. Approximately 3,260 people in the United States are diagnosed... Read moreImmunology
view channel
New Biomarker Predicts Chemotherapy Response in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
Triple-negative breast cancer is an aggressive form of breast cancer in which patients often show widely varying responses to chemotherapy. Predicting who will benefit from treatment remains challenging,... Read moreBlood Test Identifies Lung Cancer Patients Who Can Benefit from Immunotherapy Drug
Small cell lung cancer (SCLC) is an aggressive disease with limited treatment options, and even newly approved immunotherapies do not benefit all patients. While immunotherapy can extend survival for some,... Read more
Whole-Genome Sequencing Approach Identifies Cancer Patients Benefitting From PARP-Inhibitor Treatment
Targeted cancer therapies such as PARP inhibitors can be highly effective, but only for patients whose tumors carry specific DNA repair defects. Identifying these patients accurately remains challenging,... Read more
Ultrasensitive Liquid Biopsy Demonstrates Efficacy in Predicting Immunotherapy Response
Immunotherapy has transformed cancer treatment, but only a small proportion of patients experience lasting benefit, with response rates often remaining between 10% and 20%. Clinicians currently lack reliable... Read moreMicrobiology
view channel
Three-Test Panel Launched for Detection of Liver Fluke Infections
Parasitic liver fluke infections remain endemic in parts of Asia, where transmission commonly occurs through consumption of raw freshwater fish or aquatic plants. Chronic infection is a well-established... Read more
Rapid Test Promises Faster Answers for Drug-Resistant Infections
Drug-resistant pathogens continue to pose a growing threat in healthcare facilities, where delayed detection can impede outbreak control and increase mortality. Candida auris is notoriously difficult to... Read more
CRISPR-Based Technology Neutralizes Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria
Antibiotic resistance has accelerated into a global health crisis, with projections estimating more than 10 million deaths per year by 2050 as drug-resistant “superbugs” continue to spread.... Read more
Comprehensive Review Identifies Gut Microbiome Signatures Associated With Alzheimer’s Disease
Alzheimer’s disease affects approximately 6.7 million people in the United States and nearly 50 million worldwide, yet early cognitive decline remains difficult to characterize. Increasing evidence suggests... Read morePathology
view channel
Urine Specimen Collection System Improves Diagnostic Accuracy and Efficiency
Urine testing is a critical, non-invasive diagnostic tool used to detect conditions such as pregnancy, urinary tract infections, metabolic disorders, cancer, and kidney disease. However, contaminated or... Read more
AI-Powered 3D Scanning System Speeds Cancer Screening
Cytology remains a cornerstone of cancer detection, requiring specialists to examine bodily fluids and cells under a microscope. This labor-intensive process involves inspecting up to one million cells... Read moreIndustry
view channel
QuidelOrtho Collaborates with Lifotronic to Expand Global Immunoassay Portfolio
QuidelOrtho (San Diego, CA, USA) has entered a long-term strategic supply agreement with Lifotronic Technology (Shenzhen, China) to expand its global immunoassay portfolio and accelerate customer access... Read more