High-Tech Microscope Constructed for Low Cost
|
By LabMedica International staff writers Posted on 08 Dec 2014 |
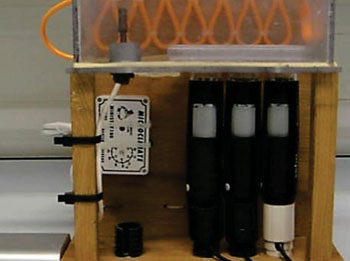
Image: The low cost microscope system constructed to perform multiple simultaneous time-lapse studies on various cell types (Photo courtesy of Adam Lynch).
The direct visualization of cells for the purpose of studying their motility has typically required expensive microscopy equipment; however, recent advances in digital sensors mean that it is now possible to image cells for a fraction of the price of a standard microscope.
The development and performance of an expandable cell motility system has been described that employs inexpensive, commercially available digital Universal Serial Bus (USB) microscopes to image various cell types using time-lapse and perform tracking assays.
Scientists at Brunel University (Uxbridge, UK) constructed the apparatus from cheaply bought materials. Various lighting sources were tested, and ultimately a light-emitting diode (LED) strip desk lamp was selected. An incubation chamber was developed to fit over the top of the stage and the chamber was made from transparent acrylic to allow visualization inside.
The three microscopes used were identical models (VMS-004D, Veho; Southampton, UK) in order to prevent any discrepancies. These microscopes use a complementary metal–oxide–semiconductor (CMOS) image sensor with 1.3 mega-pixel resolution. Magnification has two set levels, from approximately ×20 minimum to around ×400 maximum, achieved using a focusing wheel. To enhance stability, magnification and to allow for observation of live samples in liquid (cells) the microscopes were inverted.
The imaging capability of the system was compared to a conventional inverted microscope fitted with a 1.3 megapixel camera. The highest magnification on the conventional microscope was greater than the constructed system, but the maximum pixel resolution of images was the same. Spatial resolution on the conventional microscope was higher and intra-cellular detail could be seen at the highest magnification that could not be distinguished in the innovative system when images were enlarged to match the size.
The authors concluded that the novel cell tracking system had the ability to perform multiple simultaneous time-lapse studies on various cell types. Due to its low-cost, portability and commercially available components they believe that this system has the potential to enable time-lapse studies by non-specialist departments, and may be a practical solution for scientists with limited financial resources. The study was published on August 14, 2014, in the journal Public Library of Science ONE.
Related Links:
Brunel University
Veho
The development and performance of an expandable cell motility system has been described that employs inexpensive, commercially available digital Universal Serial Bus (USB) microscopes to image various cell types using time-lapse and perform tracking assays.
Scientists at Brunel University (Uxbridge, UK) constructed the apparatus from cheaply bought materials. Various lighting sources were tested, and ultimately a light-emitting diode (LED) strip desk lamp was selected. An incubation chamber was developed to fit over the top of the stage and the chamber was made from transparent acrylic to allow visualization inside.
The three microscopes used were identical models (VMS-004D, Veho; Southampton, UK) in order to prevent any discrepancies. These microscopes use a complementary metal–oxide–semiconductor (CMOS) image sensor with 1.3 mega-pixel resolution. Magnification has two set levels, from approximately ×20 minimum to around ×400 maximum, achieved using a focusing wheel. To enhance stability, magnification and to allow for observation of live samples in liquid (cells) the microscopes were inverted.
The imaging capability of the system was compared to a conventional inverted microscope fitted with a 1.3 megapixel camera. The highest magnification on the conventional microscope was greater than the constructed system, but the maximum pixel resolution of images was the same. Spatial resolution on the conventional microscope was higher and intra-cellular detail could be seen at the highest magnification that could not be distinguished in the innovative system when images were enlarged to match the size.
The authors concluded that the novel cell tracking system had the ability to perform multiple simultaneous time-lapse studies on various cell types. Due to its low-cost, portability and commercially available components they believe that this system has the potential to enable time-lapse studies by non-specialist departments, and may be a practical solution for scientists with limited financial resources. The study was published on August 14, 2014, in the journal Public Library of Science ONE.
Related Links:
Brunel University
Veho
Latest Technology News
- Blood Test “Clocks” Predict Start of Alzheimer’s Symptoms
- AI-Powered Biomarker Predicts Liver Cancer Risk
- Robotic Technology Unveiled for Automated Diagnostic Blood Draws
- ADLM Launches First-of-Its-Kind Data Science Program for Laboratory Medicine Professionals
- Aptamer Biosensor Technology to Transform Virus Detection
- AI Models Could Predict Pre-Eclampsia and Anemia Earlier Using Routine Blood Tests
- AI-Generated Sensors Open New Paths for Early Cancer Detection
- Pioneering Blood Test Detects Lung Cancer Using Infrared Imaging
- AI Predicts Colorectal Cancer Survival Using Clinical and Molecular Features
Channels
Clinical Chemistry
view channel
Simple Blood Test Offers New Path to Alzheimer’s Assessment in Primary Care
Timely evaluation of cognitive symptoms in primary care is often limited by restricted access to specialized diagnostics and invasive confirmatory procedures. Clinicians need accessible tools to determine... Read more
Existing Hospital Analyzers Can Identify Fake Liquid Medical Products
Counterfeit and substandard medicines remain a serious global health threat, with World Health Organization estimates suggesting that 10.5% of medicines in low- and middle-income countries are either fake... Read moreMolecular Diagnostics
view channel
New Genome Sequencing Technique Measures Epstein-Barr Virus in Blood
The Epstein–Barr virus (EBV) infects up to 95% of adults worldwide and remains in the body for life. While usually kept under control, the virus is linked to cancers such as Hodgkin’s lymphoma and autoimmune... Read more
Blood Test Boosts Early Detection of Brain Cancer
Brain and central nervous system (CNS) tumors are often diagnosed at an advanced stage, when treatment options are limited, and survival rates remain low. Around 300,000 new cases are diagnosed each year... Read moreHematology
view channel
Rapid Cartridge-Based Test Aims to Expand Access to Hemoglobin Disorder Diagnosis
Sickle cell disease and beta thalassemia are hemoglobin disorders that often require referral to specialized laboratories for definitive diagnosis, delaying results for patients and clinicians.... Read more
New Guidelines Aim to Improve AL Amyloidosis Diagnosis
Light chain (AL) amyloidosis is a rare, life-threatening bone marrow disorder in which abnormal amyloid proteins accumulate in organs. Approximately 3,260 people in the United States are diagnosed... Read moreImmunology
view channel
New Biomarker Predicts Chemotherapy Response in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
Triple-negative breast cancer is an aggressive form of breast cancer in which patients often show widely varying responses to chemotherapy. Predicting who will benefit from treatment remains challenging,... Read moreBlood Test Identifies Lung Cancer Patients Who Can Benefit from Immunotherapy Drug
Small cell lung cancer (SCLC) is an aggressive disease with limited treatment options, and even newly approved immunotherapies do not benefit all patients. While immunotherapy can extend survival for some,... Read more
Whole-Genome Sequencing Approach Identifies Cancer Patients Benefitting From PARP-Inhibitor Treatment
Targeted cancer therapies such as PARP inhibitors can be highly effective, but only for patients whose tumors carry specific DNA repair defects. Identifying these patients accurately remains challenging,... Read more
Ultrasensitive Liquid Biopsy Demonstrates Efficacy in Predicting Immunotherapy Response
Immunotherapy has transformed cancer treatment, but only a small proportion of patients experience lasting benefit, with response rates often remaining between 10% and 20%. Clinicians currently lack reliable... Read moreMicrobiology
view channel
Three-Test Panel Launched for Detection of Liver Fluke Infections
Parasitic liver fluke infections remain endemic in parts of Asia, where transmission commonly occurs through consumption of raw freshwater fish or aquatic plants. Chronic infection is a well-established... Read more
Rapid Test Promises Faster Answers for Drug-Resistant Infections
Drug-resistant pathogens continue to pose a growing threat in healthcare facilities, where delayed detection can impede outbreak control and increase mortality. Candida auris is notoriously difficult to... Read more
CRISPR-Based Technology Neutralizes Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria
Antibiotic resistance has accelerated into a global health crisis, with projections estimating more than 10 million deaths per year by 2050 as drug-resistant “superbugs” continue to spread.... Read more
Comprehensive Review Identifies Gut Microbiome Signatures Associated With Alzheimer’s Disease
Alzheimer’s disease affects approximately 6.7 million people in the United States and nearly 50 million worldwide, yet early cognitive decline remains difficult to characterize. Increasing evidence suggests... Read morePathology
view channel
Single Sample Classifier Predicts Cancer-Associated Fibroblast Subtypes in Patient Samples
Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) remains one of the deadliest cancers, in part because of its dense tumor microenvironment that influences how tumors grow and respond to treatment.... Read more
New AI-Driven Platform Standardizes Tuberculosis Smear Microscopy Workflow
Sputum smear microscopy remains central to tuberculosis treatment monitoring and follow-up, particularly in high‑burden settings where serial testing is routine. Yet consistent, repeatable bacillary assessment... Read more
AI Tool Uses Blood Biomarkers to Predict Transplant Complications Before Symptoms Appear
Stem cell and bone marrow transplants can be lifesaving, but serious complications may arise months after patients leave the hospital. One of the most dangerous is chronic graft-versus-host disease, in... Read moreIndustry
view channel
QuidelOrtho Collaborates with Lifotronic to Expand Global Immunoassay Portfolio
QuidelOrtho (San Diego, CA, USA) has entered a long-term strategic supply agreement with Lifotronic Technology (Shenzhen, China) to expand its global immunoassay portfolio and accelerate customer access... Read more