Image Recognition Software Increases Accuracy of Malaria Diagnosis
|
By LabMedica International staff writers Posted on 31 Aug 2014 |
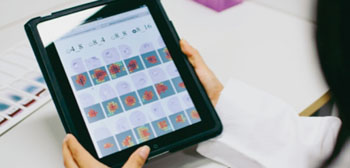
Image: The parasite detection method is based on computer vision algorithms similar to those used in facial recognition systems combined with visualization of only the diagnostically most relevant areas. Tablet computers can be utilized in viewing the images (Photo courtesy of the Institute for Molecular Medicine).
A facial recognition software program has been adapted to assist in the identification of the malaria parasite by microscopic examination of blood smears.
To develop a simpler, more effective visual method to diagnose malaria, a team of Scandinavian researchers coopted computer vision algorithms similar to those used in facial recognition systems. The program operates on a digitalized image of a thin layer of blood that had been smeared on a microscope slide. The algorithm analyzes more than 50,000 red blood cells per sample and ranks them according to likelihood of the cell being infected. The program then generates a panel of images of about a hundred cells most likely to contain the parasite. This panel is then evaluated by an experience microscopist who makes the final diagnosis.
To verify the technique Giemsa-stained thin blood films with Plasmodium falciparum ring-stage trophozoites (n = 27) and uninfected controls (n = 20) were digitally scanned with an oil immersion objective to capture approximately 50,000 erythrocytes per sample. Parasite candidate regions were identified based on color and object size, followed by extraction of image features (local binary patterns, local contrast, and Scale-invariant feature transform descriptors) used as input to a support vector machine classifier. The classifier was trained on digital slides from ten patients and validated on six samples.
From each digitized area of a blood smear, a panel with the 128 most probable parasite candidate regions was generated. Two expert microscopists were asked to visually inspect the panel on a tablet computer and to judge whether the patient was infected with P. falciparum. The method achieved a diagnostic sensitivity and specificity of 95% and 100% as well as 90% and 100% for the two readers respectively using the diagnostic tool. Parasitemia was separately calculated by an automated system and the correlation coefficient between manual and automated parasitemia counts was 0.97.
"We are not suggesting that the whole malaria diagnostic process could or should be automated. Rather, our aim is to develop methods that are significantly less labor intensive than the traditional ones and have a potential to considerably increase the throughput in malaria diagnostics," said senior author Dr. Johan Lundin, research director at the Institute for Molecular Medicine (Helsinki, Finland).
The study with complete description of the new diagnostic approach was published in the August 21, 2014, online edition of the journal PLOS One.
Related Links:
Institute for Molecular Medicine
To develop a simpler, more effective visual method to diagnose malaria, a team of Scandinavian researchers coopted computer vision algorithms similar to those used in facial recognition systems. The program operates on a digitalized image of a thin layer of blood that had been smeared on a microscope slide. The algorithm analyzes more than 50,000 red blood cells per sample and ranks them according to likelihood of the cell being infected. The program then generates a panel of images of about a hundred cells most likely to contain the parasite. This panel is then evaluated by an experience microscopist who makes the final diagnosis.
To verify the technique Giemsa-stained thin blood films with Plasmodium falciparum ring-stage trophozoites (n = 27) and uninfected controls (n = 20) were digitally scanned with an oil immersion objective to capture approximately 50,000 erythrocytes per sample. Parasite candidate regions were identified based on color and object size, followed by extraction of image features (local binary patterns, local contrast, and Scale-invariant feature transform descriptors) used as input to a support vector machine classifier. The classifier was trained on digital slides from ten patients and validated on six samples.
From each digitized area of a blood smear, a panel with the 128 most probable parasite candidate regions was generated. Two expert microscopists were asked to visually inspect the panel on a tablet computer and to judge whether the patient was infected with P. falciparum. The method achieved a diagnostic sensitivity and specificity of 95% and 100% as well as 90% and 100% for the two readers respectively using the diagnostic tool. Parasitemia was separately calculated by an automated system and the correlation coefficient between manual and automated parasitemia counts was 0.97.
"We are not suggesting that the whole malaria diagnostic process could or should be automated. Rather, our aim is to develop methods that are significantly less labor intensive than the traditional ones and have a potential to considerably increase the throughput in malaria diagnostics," said senior author Dr. Johan Lundin, research director at the Institute for Molecular Medicine (Helsinki, Finland).
The study with complete description of the new diagnostic approach was published in the August 21, 2014, online edition of the journal PLOS One.
Related Links:
Institute for Molecular Medicine
Latest Microbiology News
- Blood-Based Viral Signature Identified in Crohn’s Disease
- Hidden Gut Viruses Linked to Colorectal Cancer Risk
- Three-Test Panel Launched for Detection of Liver Fluke Infections
- Rapid Test Promises Faster Answers for Drug-Resistant Infections
- CRISPR-Based Technology Neutralizes Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria
- Comprehensive Review Identifies Gut Microbiome Signatures Associated With Alzheimer’s Disease
- AI-Powered Platform Enables Rapid Detection of Drug-Resistant C. Auris Pathogens
- New Test Measures How Effectively Antibiotics Kill Bacteria
- New Antimicrobial Stewardship Standards for TB Care to Optimize Diagnostics
- New UTI Diagnosis Method Delivers Antibiotic Resistance Results 24 Hours Earlier
- Breakthroughs in Microbial Analysis to Enhance Disease Prediction
- Blood-Based Diagnostic Method Could Identify Pediatric LRTIs
- Rapid Diagnostic Test Matches Gold Standard for Sepsis Detection
- Rapid POC Tuberculosis Test Provides Results Within 15 Minutes
- Rapid Assay Identifies Bloodstream Infection Pathogens Directly from Patient Samples
- Blood-Based Molecular Signatures to Enable Rapid EPTB Diagnosis
Channels
Clinical Chemistry
view channelNew Blood Test Index Offers Earlier Detection of Liver Scarring
Metabolic fatty liver disease is highly prevalent and often silent, yet it can progress to fibrosis, cirrhosis, and liver failure. Current first-line blood test scores frequently return indeterminate results,... Read more
Electronic Nose Smells Early Signs of Ovarian Cancer in Blood
Ovarian cancer is often diagnosed at a late stage because its symptoms are vague and resemble those of more common conditions. Unlike breast cancer, there is currently no reliable screening method, and... Read moreMolecular Diagnostics
view channel
Swab Test Helps Transplant Patients Receive Right Anti-Rejection Medication Dose
Tacrolimus is widely used to prevent organ rejection in transplant recipients, but achieving the correct dose early is critical. If levels are too low, the transplanted organ may be rejected; if too high,... Read more
Blood Test Predicts Which Bladder Cancer Patients May Safely Skip Surgery
Muscle-invasive bladder cancer (MIBC) often requires removal of the bladder, a procedure that significantly affects quality of life and carries a risk of complications. While newer treatments have improved... Read moreHematology
view channel
Rapid Cartridge-Based Test Aims to Expand Access to Hemoglobin Disorder Diagnosis
Sickle cell disease and beta thalassemia are hemoglobin disorders that often require referral to specialized laboratories for definitive diagnosis, delaying results for patients and clinicians.... Read more
New Guidelines Aim to Improve AL Amyloidosis Diagnosis
Light chain (AL) amyloidosis is a rare, life-threatening bone marrow disorder in which abnormal amyloid proteins accumulate in organs. Approximately 3,260 people in the United States are diagnosed... Read moreImmunology
view channel
New Biomarker Predicts Chemotherapy Response in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
Triple-negative breast cancer is an aggressive form of breast cancer in which patients often show widely varying responses to chemotherapy. Predicting who will benefit from treatment remains challenging,... Read moreBlood Test Identifies Lung Cancer Patients Who Can Benefit from Immunotherapy Drug
Small cell lung cancer (SCLC) is an aggressive disease with limited treatment options, and even newly approved immunotherapies do not benefit all patients. While immunotherapy can extend survival for some,... Read more
Whole-Genome Sequencing Approach Identifies Cancer Patients Benefitting From PARP-Inhibitor Treatment
Targeted cancer therapies such as PARP inhibitors can be highly effective, but only for patients whose tumors carry specific DNA repair defects. Identifying these patients accurately remains challenging,... Read more
Ultrasensitive Liquid Biopsy Demonstrates Efficacy in Predicting Immunotherapy Response
Immunotherapy has transformed cancer treatment, but only a small proportion of patients experience lasting benefit, with response rates often remaining between 10% and 20%. Clinicians currently lack reliable... Read morePathology
view channel
Molecular Imaging to Reduce Need for Melanoma Biopsies
Melanoma is the deadliest form of skin cancer and accounts for the vast majority of skin cancer-related deaths. Because early melanomas can closely resemble benign moles, clinicians often rely on visual... Read more
Urine Specimen Collection System Improves Diagnostic Accuracy and Efficiency
Urine testing is a critical, non-invasive diagnostic tool used to detect conditions such as pregnancy, urinary tract infections, metabolic disorders, cancer, and kidney disease. However, contaminated or... Read moreTechnology
view channel
AI-Driven Diagnostic Demonstrates High Accuracy in Detecting Periprosthetic Joint Infection
Periprosthetic joint infection (PJI) is a rare but serious complication affecting 1% to 2% of primary joint replacement surgeries. The condition occurs when bacteria or fungi infect tissues around an implanted... Read more
Blood Test “Clocks” Predict Start of Alzheimer’s Symptoms
More than 7 million Americans live with Alzheimer’s disease, and related health and long-term care costs are projected to reach nearly USD 400 billion in 2025. The disease has no cure, and symptoms often... Read moreIndustry
view channel
Cepheid Joins CDC Initiative to Strengthen U.S. Pandemic Testing Preparednesss
Cepheid (Sunnyvale, CA, USA) has been selected by the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) as one of four national collaborators in a federal initiative to speed rapid diagnostic technologies... Read more
QuidelOrtho Collaborates with Lifotronic to Expand Global Immunoassay Portfolio
QuidelOrtho (San Diego, CA, USA) has entered a long-term strategic supply agreement with Lifotronic Technology (Shenzhen, China) to expand its global immunoassay portfolio and accelerate customer access... Read more




















