Microfluidic Devices Created from Ordinary, Inexpensive Components
|
By LabMedica International staff writers Posted on 16 Feb 2012 |
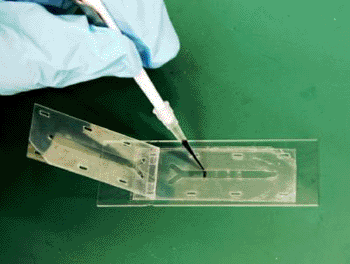
Image: NIST scientists combined a glass slide, plastic sheets, and double-sided tape to create an inexpensive and simple-to-build microfluidic device for exposing an array of cells to different concentrations of a chemical (Photo courtesy of Cooksey/NIST).
A glass slide, plastic sheets, and double-sided tape were combined to create a diffusion-based gradient generator, a tool that rapidly assesses how changing concentrations of specific chemicals affect living cells.
Exposing an array of cultured cells to a chemical gradient provides a solution where the chemical concentration changes gradually and predictably across the array. Such gradients are a rapid, high-throughput way to evaluate the effect on cell growth or toxicity.
Created by National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST; Gaithersburg, MD, USA) engineer Javier Atencia the gradient generator is built in layers, with each section precisely positioned with an alignment tab. The base is a glass slide, upon which is attached a strip of double-sided tape cut to have a row of four micrometer-sized channels. On top of this is placed a polystyrene strip cut to have two lines each of four tiny circular "wells" where each pair lines up with the ends of the channel below it. The next layer is another strip of double-sided tape, this time with a Y-shaped canal cut into it to serve as the flow path for the chemical gradient. Finally, a Mylar strip cut to have an identical Y-canal serves as the cover.
The hinged cover allows access to the wells for adding test cells. Once done, the cover is lowered and affixed, sealing the gradient generator. Fluid flow in and out of the system is accomplished using magnetic connectors. Under constant pressure, the flow assures a steady-state stream through the device and creates a diffusion gradient in each buried channel. Cells in the channels are simultaneously exposed to a range of chemical concentrations from high to low.
Conventional microfluidic systems usually mix fluids by pumping them in a circular motion or by twisting and folding them together. The new NIST system's gradient is created by diffusion––the gentle movement of matter from one point to another by random molecular motion. This greatly reduces the risk of cells being swept away or damaged by shearing forces in the test fluid.
The device was tested by loading it with cells genetically engineered to produce large amounts of green fluorescent protein (GFP) and then introduced cycloheximide (CHX), a chemical that shuts down ribosomes, the cell's protein factories. Cells exposed to the toxin quickly stop synthesizing GFP, decreasing fluorescence by an amount directly related to the concentration of CHX.
This is what the scientists observed in the gradient generator assays. The cells were exposed three times to CHX, and each time, the level of GFP fluorescence increased as the concentration of CHX in the gradient decreased, and vice versa.
The new device was described in the 2012 edition of the journal Lab-on-a-Chip.
Related Links:
National Institute of Standards and Technology
Exposing an array of cultured cells to a chemical gradient provides a solution where the chemical concentration changes gradually and predictably across the array. Such gradients are a rapid, high-throughput way to evaluate the effect on cell growth or toxicity.
Created by National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST; Gaithersburg, MD, USA) engineer Javier Atencia the gradient generator is built in layers, with each section precisely positioned with an alignment tab. The base is a glass slide, upon which is attached a strip of double-sided tape cut to have a row of four micrometer-sized channels. On top of this is placed a polystyrene strip cut to have two lines each of four tiny circular "wells" where each pair lines up with the ends of the channel below it. The next layer is another strip of double-sided tape, this time with a Y-shaped canal cut into it to serve as the flow path for the chemical gradient. Finally, a Mylar strip cut to have an identical Y-canal serves as the cover.
The hinged cover allows access to the wells for adding test cells. Once done, the cover is lowered and affixed, sealing the gradient generator. Fluid flow in and out of the system is accomplished using magnetic connectors. Under constant pressure, the flow assures a steady-state stream through the device and creates a diffusion gradient in each buried channel. Cells in the channels are simultaneously exposed to a range of chemical concentrations from high to low.
Conventional microfluidic systems usually mix fluids by pumping them in a circular motion or by twisting and folding them together. The new NIST system's gradient is created by diffusion––the gentle movement of matter from one point to another by random molecular motion. This greatly reduces the risk of cells being swept away or damaged by shearing forces in the test fluid.
The device was tested by loading it with cells genetically engineered to produce large amounts of green fluorescent protein (GFP) and then introduced cycloheximide (CHX), a chemical that shuts down ribosomes, the cell's protein factories. Cells exposed to the toxin quickly stop synthesizing GFP, decreasing fluorescence by an amount directly related to the concentration of CHX.
This is what the scientists observed in the gradient generator assays. The cells were exposed three times to CHX, and each time, the level of GFP fluorescence increased as the concentration of CHX in the gradient decreased, and vice versa.
The new device was described in the 2012 edition of the journal Lab-on-a-Chip.
Related Links:
National Institute of Standards and Technology
Latest Technology News
- AI Model Outperforms Clinicians in Rare Disease Detection
- AI-Driven Diagnostic Demonstrates High Accuracy in Detecting Periprosthetic Joint Infection
- Blood Test “Clocks” Predict Start of Alzheimer’s Symptoms
- AI-Powered Biomarker Predicts Liver Cancer Risk
- Robotic Technology Unveiled for Automated Diagnostic Blood Draws
- ADLM Launches First-of-Its-Kind Data Science Program for Laboratory Medicine Professionals
- Aptamer Biosensor Technology to Transform Virus Detection
- AI Models Could Predict Pre-Eclampsia and Anemia Earlier Using Routine Blood Tests
- AI-Generated Sensors Open New Paths for Early Cancer Detection
Channels
Clinical Chemistry
view channelNew Blood Test Index Offers Earlier Detection of Liver Scarring
Metabolic fatty liver disease is highly prevalent and often silent, yet it can progress to fibrosis, cirrhosis, and liver failure. Current first-line blood test scores frequently return indeterminate results,... Read more
Electronic Nose Smells Early Signs of Ovarian Cancer in Blood
Ovarian cancer is often diagnosed at a late stage because its symptoms are vague and resemble those of more common conditions. Unlike breast cancer, there is currently no reliable screening method, and... Read moreMolecular Diagnostics
view channel
Simple One-Hour Saliva Test Detects Common Cancers
Early detection is critical for improving cancer outcomes, yet many diagnostic tests rely on invasive procedures such as blood draws or biopsies. Researchers are exploring simpler approaches that could... Read more
Blood Test Could Help Guide Treatment Decisions in Germ Cell Tumors
Chemotherapy is often highly effective for germ cell tumors, but in a subset of patients, the disease does not respond well to standard treatment. For these individuals, doctors may consider high-dose... Read moreHematology
view channel
Rapid Cartridge-Based Test Aims to Expand Access to Hemoglobin Disorder Diagnosis
Sickle cell disease and beta thalassemia are hemoglobin disorders that often require referral to specialized laboratories for definitive diagnosis, delaying results for patients and clinicians.... Read more
New Guidelines Aim to Improve AL Amyloidosis Diagnosis
Light chain (AL) amyloidosis is a rare, life-threatening bone marrow disorder in which abnormal amyloid proteins accumulate in organs. Approximately 3,260 people in the United States are diagnosed... Read moreImmunology
view channel
Cancer Mutation ‘Fingerprints’ to Improve Prediction of Immunotherapy Response
Cancer cells accumulate thousands of genetic mutations, but not all mutations affect tumors in the same way. Some make cancer cells more visible to the immune system, while others allow tumors to evade... Read more
Immune Signature Identified in Treatment-Resistant Myasthenia Gravis
Myasthenia gravis is a rare autoimmune disorder in which immune attack at the neuromuscular junction causes fluctuating weakness that can impair vision, movement, speech, swallowing, and breathing.... Read more
New Biomarker Predicts Chemotherapy Response in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
Triple-negative breast cancer is an aggressive form of breast cancer in which patients often show widely varying responses to chemotherapy. Predicting who will benefit from treatment remains challenging,... Read moreBlood Test Identifies Lung Cancer Patients Who Can Benefit from Immunotherapy Drug
Small cell lung cancer (SCLC) is an aggressive disease with limited treatment options, and even newly approved immunotherapies do not benefit all patients. While immunotherapy can extend survival for some,... Read moreMicrobiology
view channel
Rapid Sequencing Could Transform Tuberculosis Care
Tuberculosis remains the world’s leading cause of death from a single infectious agent, responsible for more than one million deaths each year. Diagnosing and monitoring the disease can be slow because... Read more
Blood-Based Viral Signature Identified in Crohn’s Disease
Crohn’s disease is a chronic inflammatory intestinal disorder affecting approximately 0.4% of the European population, with symptoms and progression that vary widely. Although viral components of the microbiome... Read morePathology
view channel
Sex Differences in Alzheimer’s Biomarkers Linked to Faster Cognitive Decline
Sex differences in Alzheimer’s disease present ongoing diagnostic challenges, with women often experiencing a disproportionate disease burden even when preclinical amyloid-beta levels are similar to men.... Read more
World’s First Optical Microneedle Device to Enable Blood-Sampling-Free Clinical Testing
Blood sampling is one of the most common clinical procedures, but it can be difficult or uncomfortable for many patients, especially older adults or individuals with certain medical conditions.... Read moreIndustry
view channel
Cepheid Joins CDC Initiative to Strengthen U.S. Pandemic Testing Preparednesss
Cepheid (Sunnyvale, CA, USA) has been selected by the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) as one of four national collaborators in a federal initiative to speed rapid diagnostic technologies... Read more
QuidelOrtho Collaborates with Lifotronic to Expand Global Immunoassay Portfolio
QuidelOrtho (San Diego, CA, USA) has entered a long-term strategic supply agreement with Lifotronic Technology (Shenzhen, China) to expand its global immunoassay portfolio and accelerate customer access... Read more




















