Molecular Diagnostics

Immunosignaturing Platform Provides Pre-Symptom Diagnostics
Researchers have developed an immunosignature profiling technology aimed to provide people with a means of monitoring their health status and a means for early detection of disease by rapidly testing for many diseases at once from a single drop of blood. In addition, the versatile technology could be used to secure a nation’s blood supply or give early warning of a disease epidemic. More...21 Feb 2017
Urinary Biomarker Assay Detects Bladder Cancer
A new test for bladder cancer could enable general practitioners to test a urine sample and spare patients the discomfort of a cystoscopy in hospital which is the gold standard test for the detection of bladder cancer, but it is operator-dependent with a sensitivity of 90% to 97%. More...16 Feb 2017
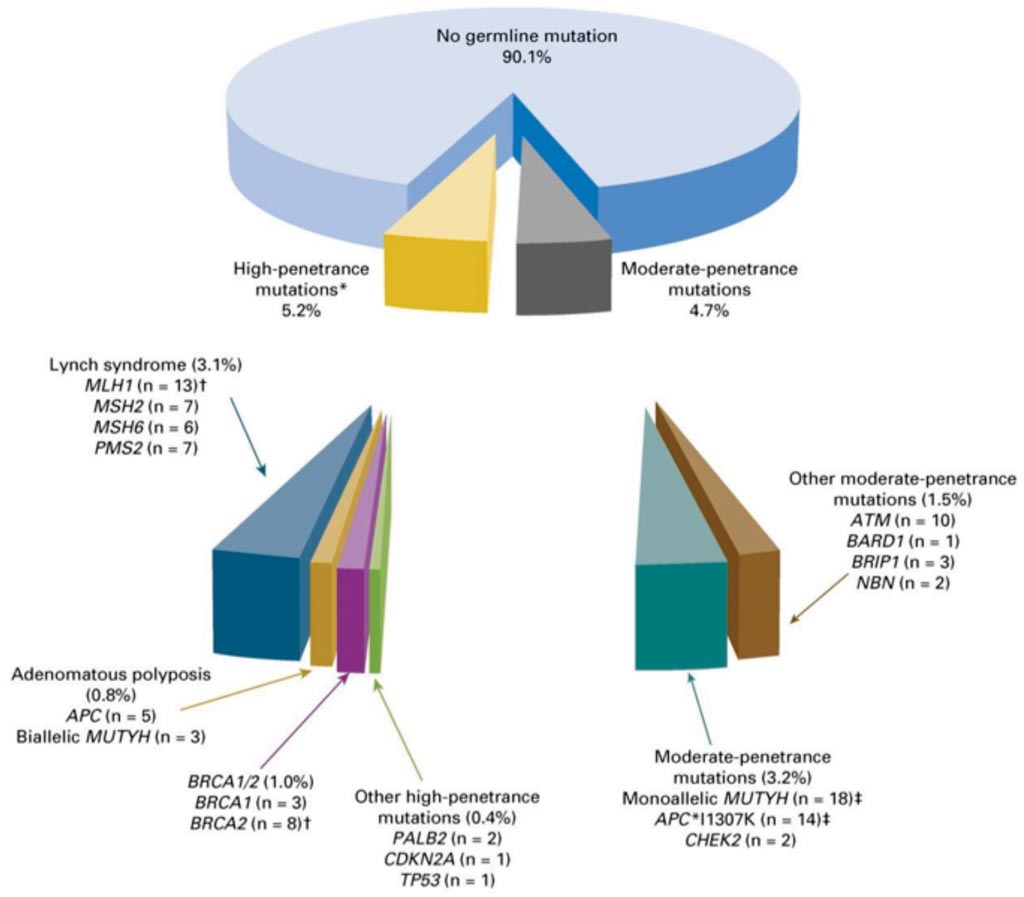
In Other News
Novel Risk Genes Identified for Bipolar Disorder
New Genetic Variants Discovered in Blood Group Systems
Genetic Study Identifies Developmental Disorders in Children
Blood Test Monitors Relapsed Serous Ovarian Cancer
Real-Time PCR Assay Developed for Detection of Candida
DNA Signature Linked to Prostate Cancer Severity
Precision Medicine Advances Pediatric Brain Tumor Diagnosis
Digital CTC Assay Improves Liver Cancer Diagnosis
Noninvasive Prenatal Testing of Single Gene Diseases Developed
Gene Panel Differentiates Survival Outcomes in Humans Infected with Ebola
LAMP-Kit Diagnoses Non-Falciparum Malaria
Liquid Biopsy Assists with Tumor Treatment Response Monitoring
Vaginal Microbes Denote Early Detection of Endometrial Cancer
Mutational Profile of Metastatic Breast Cancers Analyzed
Molecular Test Improves Diagnosis of Human Babesiosis
Biomarker Signatures Predict Aging Health Quality
Susceptibility Genes Distinct from Severity Genes in Crohn's Disease
Genetic Test Determines Patients Sensitivity to Cancer Drug
Genomic Sequencing Illuminates Recent Shigellosis Outbreaks
Genetic Cause Identified for Previously Unrecognized Developmental Disorder
Endometrial Cancer Mutations Detected in Uterine Lavage Fluid
DNA Levels in Blood Correlated with Ovarian Cancer Outcomes
Gene Activity Predicts Progression of Autoimmune Disease
Genetic Testing channel of LabMedica brings the latest in molecular genetics, cytogenetics, and epigenetics, and methods from PCR to FISH, and more.











