Chip-Based Blood Test Accurately Diagnoses Heart Attack in Minutes
|
By LabMedica International staff writers Posted on 17 Oct 2024 |

Heart attacks demand immediate medical attention to improve patient outcomes; however, while early diagnosis is crucial, it can be quite challenging—and nearly impossible outside of a clinical environment. Diagnosing heart attacks remains one of the most difficult tasks due to the wide variability of symptoms and subtle biological signals that can be easily overlooked in the early stages of an attack when medical intervention can be most beneficial. Individuals suspected of experiencing a heart attack typically undergo a series of tests to confirm the diagnosis, usually beginning with electrocardiograms that measure the heart's electrical activity—a procedure that takes about five minutes—and blood tests to identify the indicators of a heart attack, where lab results can take at least an hour and often require repetition. A new blood test has now been developed that can diagnose a heart attack in minutes rather than hours, and it has the potential to serve as a tool for first responders and individuals at home.
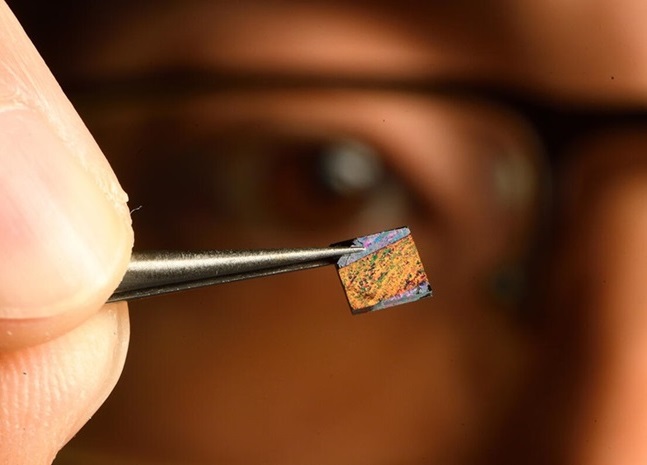
Researchers at Johns Hopkins University (Baltimore, MD, USA) have published their proof-of-concept work in Advanced Science, which can be modified to detect infectious diseases and cancer biomarkers. The focus of the research has been on developing diagnostic tools through biophotonics, utilizing laser light to identify biomarkers—bodily responses to various conditions, including diseases. In this instance, they applied the technology to detect the earliest signs in the blood that indicate a heart attack. The stand-alone blood test created by the team yields results in just five to seven minutes. They claim it is also more accurate and cost-effective than current methods.
Although initially designed for rapid diagnostic use in a clinical setting, the test could be adapted into a hand-held device for use by first responders in the field or even for personal use at home. Central to the invention is a small chip featuring a groundbreaking nanostructured surface for blood testing. The chip's "metasurface" amplifies electric and magnetic signals during Raman spectroscopy analysis, enabling heart attack biomarkers to be detected in seconds, even at ultra-low concentrations. This tool is sensitive enough to identify heart attack biomarkers that might not be detected by existing tests or might only be recognized later in the course of an attack. While primarily intended for diagnosing heart attacks, the researchers believe the tool could also be modified to detect cancer and infectious diseases. The team plans to refine the blood test further and undertake larger clinical trials in the future.
"We're talking about speed, we're talking about accuracy, and we're talking of the ability to perform measurements outside of a hospital," said Ishan Barman, Professor, Department of Mechanical Engineering. "In the future, we hope this could be made into a hand-held instrument like a Star Trek tricorder, where you have a drop of blood and then, voilà, in a few seconds you have detection."
Latest Technology News
- Blood Test “Clocks” Predict Start of Alzheimer’s Symptoms
- AI-Powered Biomarker Predicts Liver Cancer Risk
- Robotic Technology Unveiled for Automated Diagnostic Blood Draws
- ADLM Launches First-of-Its-Kind Data Science Program for Laboratory Medicine Professionals
- Aptamer Biosensor Technology to Transform Virus Detection
- AI Models Could Predict Pre-Eclampsia and Anemia Earlier Using Routine Blood Tests
- AI-Generated Sensors Open New Paths for Early Cancer Detection
- Pioneering Blood Test Detects Lung Cancer Using Infrared Imaging
Channels
Clinical Chemistry
view channel
Electronic Nose Smells Early Signs of Ovarian Cancer in Blood
Ovarian cancer is often diagnosed at a late stage because its symptoms are vague and resemble those of more common conditions. Unlike breast cancer, there is currently no reliable screening method, and... Read more
Simple Blood Test Offers New Path to Alzheimer’s Assessment in Primary Care
Timely evaluation of cognitive symptoms in primary care is often limited by restricted access to specialized diagnostics and invasive confirmatory procedures. Clinicians need accessible tools to determine... Read moreMolecular Diagnostics
view channel
New Blood Test Score Detects Hidden Alcohol-Related Liver Disease
Fatty liver disease affects nearly one in three adults worldwide and can be driven by metabolic conditions such as obesity and diabetes or by excessive alcohol use. In routine care, it is often difficult... Read more
New Blood Test Predicts Who Will Most Likely Live Longer
As people age, it becomes increasingly difficult to determine who is likely to maintain stable health and who may face serious decline. Traditional indicators such as age, cholesterol, and physical activity... Read moreHematology
view channel
Rapid Cartridge-Based Test Aims to Expand Access to Hemoglobin Disorder Diagnosis
Sickle cell disease and beta thalassemia are hemoglobin disorders that often require referral to specialized laboratories for definitive diagnosis, delaying results for patients and clinicians.... Read more
New Guidelines Aim to Improve AL Amyloidosis Diagnosis
Light chain (AL) amyloidosis is a rare, life-threatening bone marrow disorder in which abnormal amyloid proteins accumulate in organs. Approximately 3,260 people in the United States are diagnosed... Read moreImmunology
view channel
New Biomarker Predicts Chemotherapy Response in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
Triple-negative breast cancer is an aggressive form of breast cancer in which patients often show widely varying responses to chemotherapy. Predicting who will benefit from treatment remains challenging,... Read moreBlood Test Identifies Lung Cancer Patients Who Can Benefit from Immunotherapy Drug
Small cell lung cancer (SCLC) is an aggressive disease with limited treatment options, and even newly approved immunotherapies do not benefit all patients. While immunotherapy can extend survival for some,... Read more
Whole-Genome Sequencing Approach Identifies Cancer Patients Benefitting From PARP-Inhibitor Treatment
Targeted cancer therapies such as PARP inhibitors can be highly effective, but only for patients whose tumors carry specific DNA repair defects. Identifying these patients accurately remains challenging,... Read more
Ultrasensitive Liquid Biopsy Demonstrates Efficacy in Predicting Immunotherapy Response
Immunotherapy has transformed cancer treatment, but only a small proportion of patients experience lasting benefit, with response rates often remaining between 10% and 20%. Clinicians currently lack reliable... Read moreMicrobiology
view channel
Hidden Gut Viruses Linked to Colorectal Cancer Risk
Colorectal cancer (CRC) remains a leading cause of cancer mortality in many Western countries, and existing risk-stratification approaches leave substantial room for improvement. Although age, diet, and... Read more
Three-Test Panel Launched for Detection of Liver Fluke Infections
Parasitic liver fluke infections remain endemic in parts of Asia, where transmission commonly occurs through consumption of raw freshwater fish or aquatic plants. Chronic infection is a well-established... Read morePathology
view channel
Urine Specimen Collection System Improves Diagnostic Accuracy and Efficiency
Urine testing is a critical, non-invasive diagnostic tool used to detect conditions such as pregnancy, urinary tract infections, metabolic disorders, cancer, and kidney disease. However, contaminated or... Read more
AI-Powered 3D Scanning System Speeds Cancer Screening
Cytology remains a cornerstone of cancer detection, requiring specialists to examine bodily fluids and cells under a microscope. This labor-intensive process involves inspecting up to one million cells... Read moreIndustry
view channel
Cepheid Joins CDC Initiative to Strengthen U.S. Pandemic Testing Preparednesss
Cepheid (Sunnyvale, CA, USA) has been selected by the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) as one of four national collaborators in a federal initiative to speed rapid diagnostic technologies... Read more
QuidelOrtho Collaborates with Lifotronic to Expand Global Immunoassay Portfolio
QuidelOrtho (San Diego, CA, USA) has entered a long-term strategic supply agreement with Lifotronic Technology (Shenzhen, China) to expand its global immunoassay portfolio and accelerate customer access... Read more