Transformative Fingertip Blood Collection Device Produces Lab-Quality Test Results
|
By LabMedica International staff writers Posted on 08 Dec 2023 |
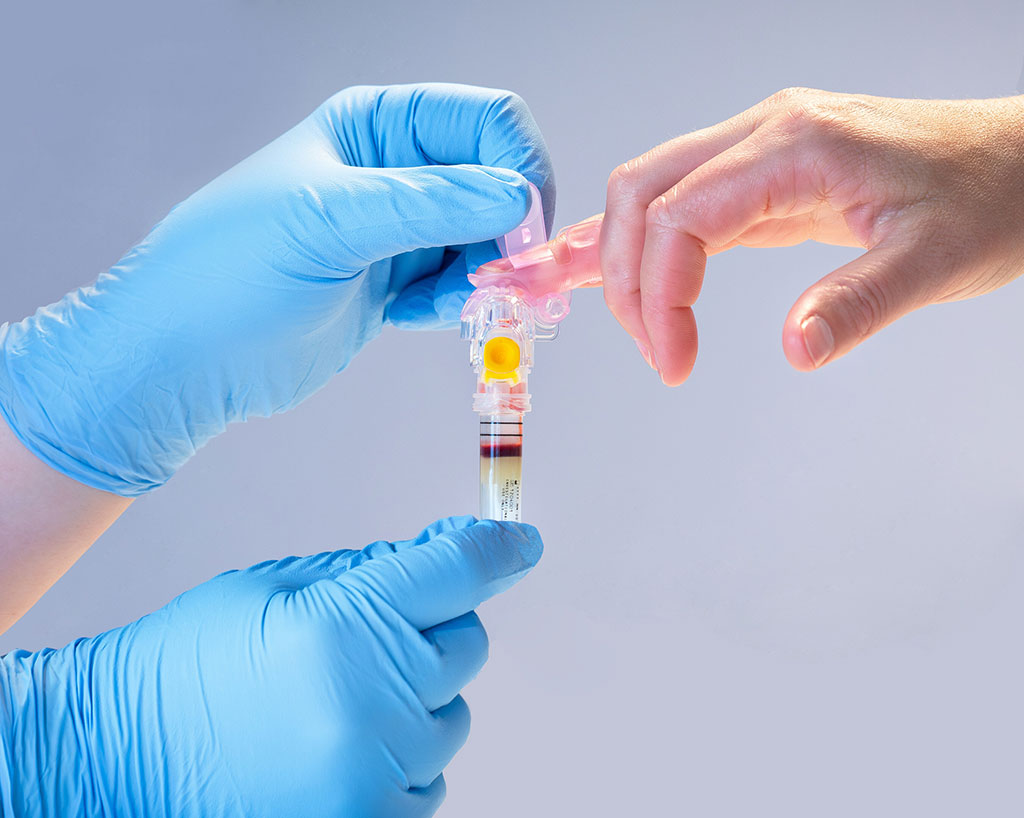
The traditional process of "blood work" for patients typically involves a visit to a laboratory service center where a professional, such as a nurse or phlebotomist, draws blood from the patient's vein. Now, a new blood collection device is set to revolutionize this standard procedure by allowing blood testing in more accessible and convenient locations, offering advantages for patients, healthcare providers, and collection sites.
Becton, Dickinson and Company’s (BD, Franklin Lakes, NJ, USA) BD MiniDraw Capillary Blood Collection System is an innovative device that collects blood samples through a fingerstick, yielding laboratory-quality results for several common blood tests. Unlike the conventional venous blood draw, this system is less invasive, utilizing capillary blood from the patient's finger, which can be done by a trained healthcare worker without the need for a vein puncture by a phlebotomist. The device’s design enables the acquisition of lab-quality results from a smaller blood volume than what is typically required for venous collections. Moreover, it offers more convenience to patients by allowing blood collection at new venues, such as retail pharmacies, potentially enhancing the overall patient experience and revolutionizing diagnostic testing.
The use of the BD MiniDraw Collection System benefits patients by enabling them to have blood drawn in familiar places they frequently visit, like retail pharmacies or grocery stores. These locations often have extended operating hours and may be more conveniently located near their homes or workplaces. For these alternative collection sites, such as retail settings, the system not only complements existing health and wellness programs, like vaccine administration but also has the potential to increase foot traffic. Healthcare providers can benefit too, as capillary blood collection could be offered right in a physician's office without needing specialized phlebotomy staff. This ease and reduced invasiveness of the process might lead to improved patient compliance with blood testing, which is crucial for regular health assessments and could aid in the early detection and better management of chronic diseases.
BD has received 510(k) clearance from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for the BD MiniDraw Collection System. This clearance covers low-volume blood collection for various tests, including lipid panels, select chemistry tests, and hemoglobin and hematocrit (H&H) testing, which are some of the most frequently requested laboratory tests. They are essential for diagnosing and monitoring various chronic conditions, from hypertension to high cholesterol. Looking ahead, BD aims to broaden the range of blood tests facilitated by the BD MiniDraw Collection System.
"Because the BD MiniDraw Collection System enables blood collection at non-traditional sites that may be more convenient—like your local pharmacy rather than a standalone lab—we can expand health equity and access, and make it easier for patients to get the blood tests they need both for preventative care and the management of chronic conditions," said Dave Hickey, executive vice president and president of Life Sciences for BD. "This innovation is our strategy and pipeline coming to life, and proof of our commitment to enabling diagnostics and care in alternate settings."
Related Links:
BD
Latest Pathology News
- Sex Differences in Alzheimer’s Biomarkers Linked to Faster Cognitive Decline
- World’s First Optical Microneedle Device to Enable Blood-Sampling-Free Clinical Testing
- Novel mcPCR Technology to Transform Testing of Clinical Samples
- Pathogen-Agnostic Testing Reveals Hidden Respiratory Threats in Negative Samples
- Molecular Imaging to Reduce Need for Melanoma Biopsies
- Urine Specimen Collection System Improves Diagnostic Accuracy and Efficiency
- AI-Powered 3D Scanning System Speeds Cancer Screening
- Single Sample Classifier Predicts Cancer-Associated Fibroblast Subtypes in Patient Samples
- New AI-Driven Platform Standardizes Tuberculosis Smear Microscopy Workflow
- AI Tool Uses Blood Biomarkers to Predict Transplant Complications Before Symptoms Appear
- High-Resolution Cancer Virus Imaging Uncovers Potential Therapeutic Targets
- Research Consortium Harnesses AI and Spatial Biology to Advance Cancer Discovery
- AI Tool Helps See How Cells Work Together Inside Diseased Tissue
- AI-Powered Microscope Diagnoses Malaria in Blood Smears Within Minutes
- Engineered Yeast Cells Enable Rapid Testing of Cancer Immunotherapy
- First-Of-Its-Kind Test Identifies Autism Risk at Birth
Channels
Clinical Chemistry
view channelNew Blood Test Index Offers Earlier Detection of Liver Scarring
Metabolic fatty liver disease is highly prevalent and often silent, yet it can progress to fibrosis, cirrhosis, and liver failure. Current first-line blood test scores frequently return indeterminate results,... Read more
Electronic Nose Smells Early Signs of Ovarian Cancer in Blood
Ovarian cancer is often diagnosed at a late stage because its symptoms are vague and resemble those of more common conditions. Unlike breast cancer, there is currently no reliable screening method, and... Read moreMolecular Diagnostics
view channel
Simple One-Hour Saliva Test Detects Common Cancers
Early detection is critical for improving cancer outcomes, yet many diagnostic tests rely on invasive procedures such as blood draws or biopsies. Researchers are exploring simpler approaches that could... Read more
Blood Test Could Help Guide Treatment Decisions in Germ Cell Tumors
Chemotherapy is often highly effective for germ cell tumors, but in a subset of patients, the disease does not respond well to standard treatment. For these individuals, doctors may consider high-dose... Read moreHematology
view channel
Rapid Cartridge-Based Test Aims to Expand Access to Hemoglobin Disorder Diagnosis
Sickle cell disease and beta thalassemia are hemoglobin disorders that often require referral to specialized laboratories for definitive diagnosis, delaying results for patients and clinicians.... Read more
New Guidelines Aim to Improve AL Amyloidosis Diagnosis
Light chain (AL) amyloidosis is a rare, life-threatening bone marrow disorder in which abnormal amyloid proteins accumulate in organs. Approximately 3,260 people in the United States are diagnosed... Read moreImmunology
view channel
Cancer Mutation ‘Fingerprints’ to Improve Prediction of Immunotherapy Response
Cancer cells accumulate thousands of genetic mutations, but not all mutations affect tumors in the same way. Some make cancer cells more visible to the immune system, while others allow tumors to evade... Read more
Immune Signature Identified in Treatment-Resistant Myasthenia Gravis
Myasthenia gravis is a rare autoimmune disorder in which immune attack at the neuromuscular junction causes fluctuating weakness that can impair vision, movement, speech, swallowing, and breathing.... Read more
New Biomarker Predicts Chemotherapy Response in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
Triple-negative breast cancer is an aggressive form of breast cancer in which patients often show widely varying responses to chemotherapy. Predicting who will benefit from treatment remains challenging,... Read moreBlood Test Identifies Lung Cancer Patients Who Can Benefit from Immunotherapy Drug
Small cell lung cancer (SCLC) is an aggressive disease with limited treatment options, and even newly approved immunotherapies do not benefit all patients. While immunotherapy can extend survival for some,... Read moreMicrobiology
view channel
Rapid Sequencing Could Transform Tuberculosis Care
Tuberculosis remains the world’s leading cause of death from a single infectious agent, responsible for more than one million deaths each year. Diagnosing and monitoring the disease can be slow because... Read more
Blood-Based Viral Signature Identified in Crohn’s Disease
Crohn’s disease is a chronic inflammatory intestinal disorder affecting approximately 0.4% of the European population, with symptoms and progression that vary widely. Although viral components of the microbiome... Read moreTechnology
view channel
AI Model Outperforms Clinicians in Rare Disease Detection
Rare diseases affect an estimated 300 million people worldwide, yet diagnosis is often protracted and error-prone. Many conditions present with heterogeneous signs that overlap with common disorders, leading... Read more
AI-Driven Diagnostic Demonstrates High Accuracy in Detecting Periprosthetic Joint Infection
Periprosthetic joint infection (PJI) is a rare but serious complication affecting 1% to 2% of primary joint replacement surgeries. The condition occurs when bacteria or fungi infect tissues around an implanted... Read moreIndustry
view channel
Cepheid Joins CDC Initiative to Strengthen U.S. Pandemic Testing Preparednesss
Cepheid (Sunnyvale, CA, USA) has been selected by the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) as one of four national collaborators in a federal initiative to speed rapid diagnostic technologies... Read more
QuidelOrtho Collaborates with Lifotronic to Expand Global Immunoassay Portfolio
QuidelOrtho (San Diego, CA, USA) has entered a long-term strategic supply agreement with Lifotronic Technology (Shenzhen, China) to expand its global immunoassay portfolio and accelerate customer access... Read more




















