New Test Predicts If Brain Tumor Is Likely to Grow Back
|
By LabMedica International staff writers Posted on 27 Nov 2023 |
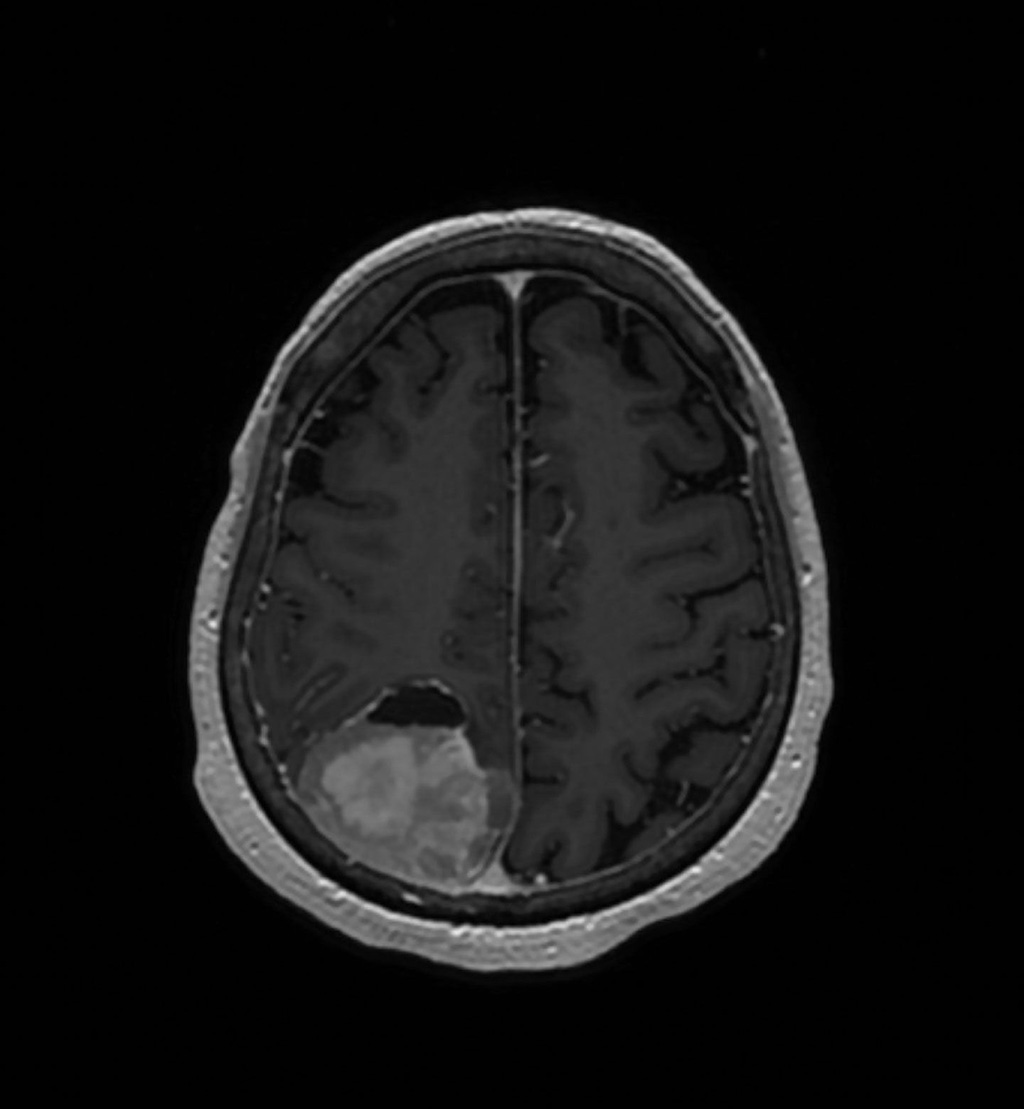
Meningioma, a brain tumor that originates in the membranes surrounding the brain, often goes unnoticed due to its slow growth. Patients typically become aware of their condition when neurological symptoms like numbness, vision impairment, or personality changes occur. Current treatment methods include surgery for tumor removal and radiation to prevent regrowth. The tumors are treated according to their categorization by the World Health Organization into different grades based on their severity. Typically, Grade 1 meningiomas don't receive radiation if they are fully removed surgically. However, about 20% of these cases see tumor recurrence. Patients with more aggressive Grade 2 and 3 tumors usually undergo radiation post-surgery, despite the potential for serious side effects like memory loss and cognitive decline. The need for radiation treatment, particularly for Grade 2 tumors, still remains questionable.
Now, a collaborative team from UC San Francisco (San Francisco, CA, USA) and Northwestern Medicine (Chicago, IL, USA), along with 10 other medical institutions, has discovered a highly effective method to guide treatment decisions for meningioma patients. This method involves analyzing gene expression patterns within the tumors. This new technique could change the treatment path for nearly one-third of meningioma patients. By examining tumor samples from 1,856 patients across the U.S., Europe, and Hong Kong, the researchers identified 34 genes whose expression patterns could predict tumor recurrence. Their findings suggest that only 20% of patients with low-grade tumors might need radiation, while 40% of those with higher-grade tumors might benefit from avoiding radiation. The next step for the research team involves validating this gene-expression testing approach in two upcoming clinical trials.
“There’s been a lot of controversy in the field in terms of who should receive radiotherapy and who shouldn’t,” said David Raleigh, MD, Ph.D., a radiation oncologist at the UCSF Brain Tumor Center. “Our biomarker takes the guessing game out of this and shows us which patients are likely to benefit from radiotherapy and which may get toxicity and possibly no benefit from radiation.”
“When to proceed with additional surgery, radiotherapy or simply to observe a small residual meningioma is not always clear,” added Stephen Magill, MD, PhD, assistant professor of neurological surgery at Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine. “This test adds information that can let us tailor our surgical and radiation approach to provide the best outcome for each patient and maximize both quality and quantity of life.”
Related Links:
UC San Francisco
Northwestern Medicine
Latest Molecular Diagnostics News
- Ultra-Sensitive DNA Test Identifies Relapse Risk in Aggressive Leukemia
- Blood Test Could Help Detect Gallbladder Cancer Earlier
- New Blood Test Score Detects Hidden Alcohol-Related Liver Disease
- New Blood Test Predicts Who Will Most Likely Live Longer
- Genetic Test Predicts Radiation Therapy Risk for Prostate Cancer Patients
- Genetic Test Aids Early Detection and Improved Treatment for Cancers
- New Genome Sequencing Technique Measures Epstein-Barr Virus in Blood
- Blood Test Boosts Early Detection of Brain Cancer
- Molecular Monitoring Approach Helps Bladder Cancer Patients Avoid Surgery
- Genetic Tests to Speed Diagnosis of Lymphatic Disorders
- Changes In Lymphatic Vessels Can Aid Early Identification of Aggressive Oral Cancer
- New Extraction Kit Enables Consistent, Scalable cfDNA Isolation from Multiple Biofluids
- New CSF Liquid Biopsy Assay Reveals Genomic Insights for CNS Tumors
- AI-Powered Liquid Biopsy Classifies Pediatric Brain Tumors with High Accuracy
- Group A Strep Molecular Test Delivers Definitive Results at POC in 15 Minutes
- Rapid Molecular Test Identifies Sepsis Patients Most Likely to Have Positive Blood Cultures
Channels
Clinical Chemistry
view channelNew Blood Test Index Offers Earlier Detection of Liver Scarring
Metabolic fatty liver disease is highly prevalent and often silent, yet it can progress to fibrosis, cirrhosis, and liver failure. Current first-line blood test scores frequently return indeterminate results,... Read more
Electronic Nose Smells Early Signs of Ovarian Cancer in Blood
Ovarian cancer is often diagnosed at a late stage because its symptoms are vague and resemble those of more common conditions. Unlike breast cancer, there is currently no reliable screening method, and... Read moreHematology
view channel
Rapid Cartridge-Based Test Aims to Expand Access to Hemoglobin Disorder Diagnosis
Sickle cell disease and beta thalassemia are hemoglobin disorders that often require referral to specialized laboratories for definitive diagnosis, delaying results for patients and clinicians.... Read more
New Guidelines Aim to Improve AL Amyloidosis Diagnosis
Light chain (AL) amyloidosis is a rare, life-threatening bone marrow disorder in which abnormal amyloid proteins accumulate in organs. Approximately 3,260 people in the United States are diagnosed... Read moreImmunology
view channel
New Biomarker Predicts Chemotherapy Response in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
Triple-negative breast cancer is an aggressive form of breast cancer in which patients often show widely varying responses to chemotherapy. Predicting who will benefit from treatment remains challenging,... Read moreBlood Test Identifies Lung Cancer Patients Who Can Benefit from Immunotherapy Drug
Small cell lung cancer (SCLC) is an aggressive disease with limited treatment options, and even newly approved immunotherapies do not benefit all patients. While immunotherapy can extend survival for some,... Read more
Whole-Genome Sequencing Approach Identifies Cancer Patients Benefitting From PARP-Inhibitor Treatment
Targeted cancer therapies such as PARP inhibitors can be highly effective, but only for patients whose tumors carry specific DNA repair defects. Identifying these patients accurately remains challenging,... Read more
Ultrasensitive Liquid Biopsy Demonstrates Efficacy in Predicting Immunotherapy Response
Immunotherapy has transformed cancer treatment, but only a small proportion of patients experience lasting benefit, with response rates often remaining between 10% and 20%. Clinicians currently lack reliable... Read moreMicrobiology
view channel
Hidden Gut Viruses Linked to Colorectal Cancer Risk
Colorectal cancer (CRC) remains a leading cause of cancer mortality in many Western countries, and existing risk-stratification approaches leave substantial room for improvement. Although age, diet, and... Read more
Three-Test Panel Launched for Detection of Liver Fluke Infections
Parasitic liver fluke infections remain endemic in parts of Asia, where transmission commonly occurs through consumption of raw freshwater fish or aquatic plants. Chronic infection is a well-established... Read morePathology
view channel
Molecular Imaging to Reduce Need for Melanoma Biopsies
Melanoma is the deadliest form of skin cancer and accounts for the vast majority of skin cancer-related deaths. Because early melanomas can closely resemble benign moles, clinicians often rely on visual... Read more
Urine Specimen Collection System Improves Diagnostic Accuracy and Efficiency
Urine testing is a critical, non-invasive diagnostic tool used to detect conditions such as pregnancy, urinary tract infections, metabolic disorders, cancer, and kidney disease. However, contaminated or... Read moreTechnology
view channel
Blood Test “Clocks” Predict Start of Alzheimer’s Symptoms
More than 7 million Americans live with Alzheimer’s disease, and related health and long-term care costs are projected to reach nearly USD 400 billion in 2025. The disease has no cure, and symptoms often... Read more
AI-Powered Biomarker Predicts Liver Cancer Risk
Liver cancer, or hepatocellular carcinoma, causes more than 800,000 deaths worldwide each year and often goes undetected until late stages. Even after treatment, recurrence rates reach 70% to 80%, contributing... Read more
Robotic Technology Unveiled for Automated Diagnostic Blood Draws
Routine diagnostic blood collection is a high‑volume task that can strain staffing and introduce human‑dependent variability, with downstream implications for sample quality and patient experience.... Read more
ADLM Launches First-of-Its-Kind Data Science Program for Laboratory Medicine Professionals
Clinical laboratories generate billions of test results each year, creating a treasure trove of data with the potential to support more personalized testing, improve operational efficiency, and enhance patient care.... Read moreIndustry
view channel
Cepheid Joins CDC Initiative to Strengthen U.S. Pandemic Testing Preparednesss
Cepheid (Sunnyvale, CA, USA) has been selected by the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) as one of four national collaborators in a federal initiative to speed rapid diagnostic technologies... Read more
QuidelOrtho Collaborates with Lifotronic to Expand Global Immunoassay Portfolio
QuidelOrtho (San Diego, CA, USA) has entered a long-term strategic supply agreement with Lifotronic Technology (Shenzhen, China) to expand its global immunoassay portfolio and accelerate customer access... Read more


















