Prenatal Test Reduces Time of Detecting Chromosomal Abnormalities
|
By LabMedica International staff writers Posted on 24 Aug 2022 |
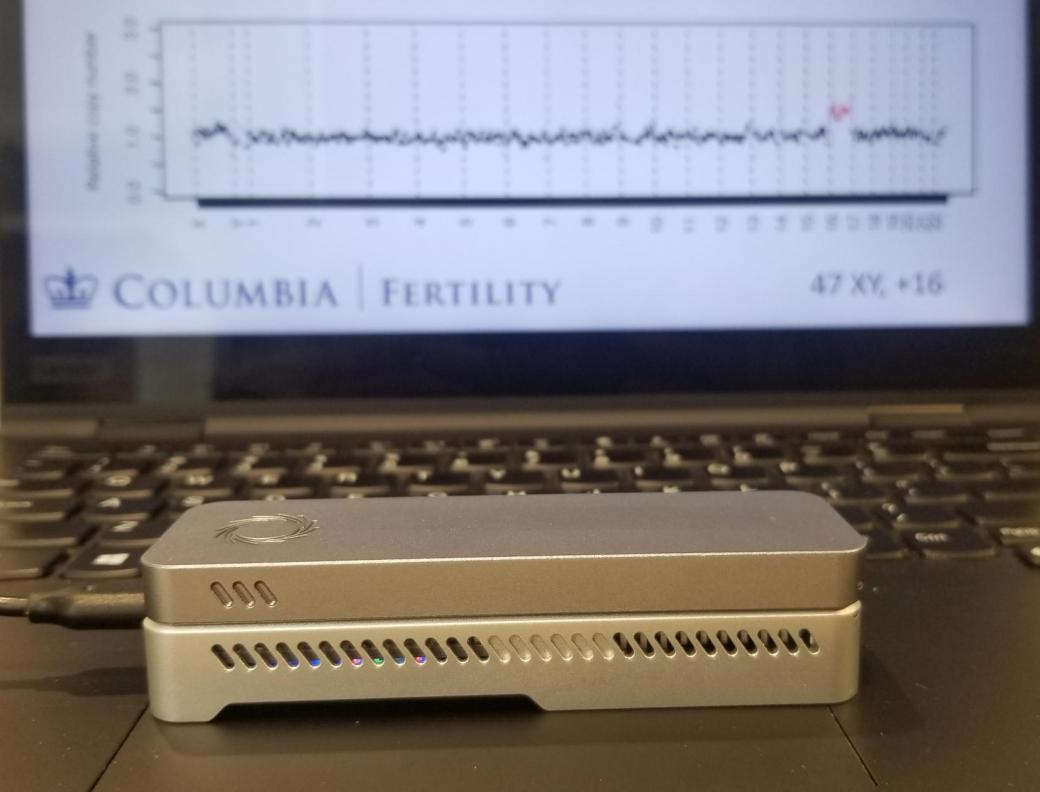
A newly developed prenatal test can determine if a fetus or embryo has the right number of chromosomes at a fraction of the time and cost of currently available clinical genetic tests.
Currently available prenatal genetic tests cost thousands of dollars and take days to weeks to deliver results, adding to the emotional and financial stress of fertility treatment and pregnancy and impacting treatment options.
Clinical Scientists from the Columbia University Irving Medical Center (New York, NY, USA) and their colleagues developed the new test, called STORK (Short-read Transpore Rapid Karyotyping), that can be used in the doctor's office at the point of care, delivers results in under two hours, and is about 10 times less expensive to process per sample than current tests. The nanopore-based sequencing technology was used to analyze tiny fragments of DNA 15,000 times faster than currently available chromosomal testing methods, significantly reducing the amount of time to get results. The test also uses much smaller equipment, about the size of a harmonica and weighing just 450 grams, making it accessible for use in physician offices.
The chromosomal abnormalities that this test can detect are, by far, the most common causes of miscarriage, structural anomalies, and developmental delays. Prenatal genetic testing is recommended for pregnant women who are age 35 or older, have a family history of genetic disorders, or have had one or more miscarriages. It is also used increasingly during in vitro fertilization (IVF) to test embryos prior to implantation to improve the chances of pregnancy and reduce the risk of miscarriage.
The team tested STORK in 218 blinded samples from miscarriages, pregnancies, via amniotic fluid or chorionic villi, and biopsies from embryos prior to implantation. Results were compared with those obtained using standard clinical testing. STORK results agreed with standard clinical testing in all of the pregnancy-related samples and in 98% of the embryos tested. For miscarriage samples, STORK was more accurate than standard testing and was determined to have correctly identified chromosome numbers in the 10 cases for which the two tests disagreed. An additional 60 pregnancy samples were tested with STORK at an independent certified laboratory, and those results were identical to results obtained with standard clinical testing.
Zev Williams, MD, PhD, Associate Professor of Women's Health and a senior author of the study, said, “The affordability of this test also means that individuals who have suffered a miscarriage do not have to wait until a second or third loss before insurance will cover expensive lab tests, leaving many women in the dark and often blaming themselves. Our study also shows that our rapid test was better than the gold standard for testing miscarriage samples, giving women who have suffered a pregnancy loss a sense of closure and the ability to take steps to prevent another loss.” The study was published on August 18, 2022 in the New England Journal of Medicine.
Latest Molecular Diagnostics News
- Simple One-Hour Saliva Test Detects Common Cancers
- Blood Test Could Help Guide Treatment Decisions in Germ Cell Tumors
- Blood Test Could Spot Common Post-Surgery Condition Early
- New Blood Test Can Help Predict Testicular Cancer Recurrence
- New Test Detects Alzheimer’s by Analyzing Altered Protein Shapes in Blood
- New Diagnostic Markers for Multiple Sclerosis Discovered in Cerebrospinal Fluid
- Cell-Free DNA Predicts Bloodstream Infections in Children with Leukemia
- Study Uses Blood Samples to Identify Diseases Years Before They Start
- MicroRNA-Based Method Predicts CKD and Cardiovascular Risk
- Swab Test Helps Transplant Patients Receive Right Anti-Rejection Medication Dose
- Blood Test Predicts Which Bladder Cancer Patients May Safely Skip Surgery
- Ultra-Sensitive DNA Test Identifies Relapse Risk in Aggressive Leukemia
- Blood Test Could Help Detect Gallbladder Cancer Earlier
- New Blood Test Score Detects Hidden Alcohol-Related Liver Disease
- New Blood Test Predicts Who Will Most Likely Live Longer
- Genetic Test Predicts Radiation Therapy Risk for Prostate Cancer Patients
Channels
Molecular Diagnostics
view channel
Simple One-Hour Saliva Test Detects Common Cancers
Early detection is critical for improving cancer outcomes, yet many diagnostic tests rely on invasive procedures such as blood draws or biopsies. Researchers are exploring simpler approaches that could... Read more
Blood Test Could Help Guide Treatment Decisions in Germ Cell Tumors
Chemotherapy is often highly effective for germ cell tumors, but in a subset of patients, the disease does not respond well to standard treatment. For these individuals, doctors may consider high-dose... Read moreHematology
view channel
Rapid Cartridge-Based Test Aims to Expand Access to Hemoglobin Disorder Diagnosis
Sickle cell disease and beta thalassemia are hemoglobin disorders that often require referral to specialized laboratories for definitive diagnosis, delaying results for patients and clinicians.... Read more
New Guidelines Aim to Improve AL Amyloidosis Diagnosis
Light chain (AL) amyloidosis is a rare, life-threatening bone marrow disorder in which abnormal amyloid proteins accumulate in organs. Approximately 3,260 people in the United States are diagnosed... Read moreImmunology
view channel
Cancer Mutation ‘Fingerprints’ to Improve Prediction of Immunotherapy Response
Cancer cells accumulate thousands of genetic mutations, but not all mutations affect tumors in the same way. Some make cancer cells more visible to the immune system, while others allow tumors to evade... Read more
Immune Signature Identified in Treatment-Resistant Myasthenia Gravis
Myasthenia gravis is a rare autoimmune disorder in which immune attack at the neuromuscular junction causes fluctuating weakness that can impair vision, movement, speech, swallowing, and breathing.... Read more
New Biomarker Predicts Chemotherapy Response in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
Triple-negative breast cancer is an aggressive form of breast cancer in which patients often show widely varying responses to chemotherapy. Predicting who will benefit from treatment remains challenging,... Read moreBlood Test Identifies Lung Cancer Patients Who Can Benefit from Immunotherapy Drug
Small cell lung cancer (SCLC) is an aggressive disease with limited treatment options, and even newly approved immunotherapies do not benefit all patients. While immunotherapy can extend survival for some,... Read moreMicrobiology
view channel
Rapid Sequencing Could Transform Tuberculosis Care
Tuberculosis remains the world’s leading cause of death from a single infectious agent, responsible for more than one million deaths each year. Diagnosing and monitoring the disease can be slow because... Read more
Blood-Based Viral Signature Identified in Crohn’s Disease
Crohn’s disease is a chronic inflammatory intestinal disorder affecting approximately 0.4% of the European population, with symptoms and progression that vary widely. Although viral components of the microbiome... Read morePathology
view channel
Novel mcPCR Technology to Transform Testing of Clinical Samples
DNA methylation is an important biological marker used in the diagnosis and monitoring of many diseases, including cancer. These chemical modifications to DNA influence gene activity and can reveal early... Read more
Sex Differences in Alzheimer’s Biomarkers Linked to Faster Cognitive Decline
Sex differences in Alzheimer’s disease present ongoing diagnostic challenges, with women often experiencing a disproportionate disease burden even when preclinical amyloid-beta levels are similar to men.... Read moreTechnology
view channel
AI Model Outperforms Clinicians in Rare Disease Detection
Rare diseases affect an estimated 300 million people worldwide, yet diagnosis is often protracted and error-prone. Many conditions present with heterogeneous signs that overlap with common disorders, leading... Read more
AI-Driven Diagnostic Demonstrates High Accuracy in Detecting Periprosthetic Joint Infection
Periprosthetic joint infection (PJI) is a rare but serious complication affecting 1% to 2% of primary joint replacement surgeries. The condition occurs when bacteria or fungi infect tissues around an implanted... Read moreIndustry
view channel
Cepheid Joins CDC Initiative to Strengthen U.S. Pandemic Testing Preparednesss
Cepheid (Sunnyvale, CA, USA) has been selected by the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) as one of four national collaborators in a federal initiative to speed rapid diagnostic technologies... Read more
QuidelOrtho Collaborates with Lifotronic to Expand Global Immunoassay Portfolio
QuidelOrtho (San Diego, CA, USA) has entered a long-term strategic supply agreement with Lifotronic Technology (Shenzhen, China) to expand its global immunoassay portfolio and accelerate customer access... Read more




















