LAMP Assay Developed to Diagnose High HBV DNA Levels
|
By LabMedica International staff writers Posted on 05 May 2021 |

Image: The AMPLIX real-time polymerase chain reaction system (Photo courtesy of Biosynex)
Worldwide, 257 million people are chronically infected with hepatitis B virus (HBV) and 887,000 annually die from cirrhosis or liver cancer. Since more than 95% of HBV-infected people live in low-income and middle-income countries (LMICs) and only 12-25% of infected people are eligible for anti-HBV therapy.
Loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) assay is a nucleic acid test (NAT) using DNA polymerase with high auto-cycling strand displacement activity and six specially designed primers. LAMP has the following characteristics allowing its use as a rapid, reliable and inexpensive point-of-care test in LMICs with a high amplification efficiency enabling rapid detection of nucleic acids.
A large team of medical scientists associated with the Pasteur Institute (Paris, France) designed Pan-genotypic primer sets on conserved HBV gene regions. Accuracy of LAMP to identify highly viremic patients was evaluated in 400 and 550 HBV-infected people in France and Senegal, respectively. Analytical validation was performed using real-time turbidimetric LAMP (Loopamp LA-500, Eiken Chemical, Japan). Viral loads were quantified using an AMPLIX real-time PCR (Biosynex, Illkirch-Graffenstaden France).
The team reported that their primers successfully detected eight major HBV genotypes/sub-genotypes (A1/2/3/B/C/D/E/F) with a detection limit ranging between 40-400 IU/mL. In France, the area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUROC), sensitivity and specificity of bead-based extraction and real-time turbidimetric LAMP were 0.95, 91.1% and 86.0%, respectively, to diagnose HBV DNA ≥20,000 IU/mL; and 0.98, 98.0% and 94.6% for ≥200,000 IU/mL. The performance did not vary by viral genotypes. In Senegal, using a field-adapted method, reagent-free boil-and-spin extraction and inexpensive end-point fluorescence detection, the AUROC, sensitivity and specificity were 0.95, 98.7% and 91.5%, respectively, to diagnose HBV DNA ≥200,000 IU/mL. The assay was not adapted to discriminate low-level viremia.
The authors concluded that they had developed a simple, rapid (60 minutes), and inexpensive (USD 8/assay) alternative to PCR to diagnose high viremia ≥200,000 IU/mL. HBV-LAMP may contribute to eliminating HBV mother-to-child transmission by identifying high-risk pregnant women eligible for antiviral prophylaxis in resource-limited countries. The study was published on April 7, 2021 in the journal Clinical Microbiology and Infection.
Related Links:
Pasteur Institute
Eiken Chemical
Biosynex
Loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) assay is a nucleic acid test (NAT) using DNA polymerase with high auto-cycling strand displacement activity and six specially designed primers. LAMP has the following characteristics allowing its use as a rapid, reliable and inexpensive point-of-care test in LMICs with a high amplification efficiency enabling rapid detection of nucleic acids.
A large team of medical scientists associated with the Pasteur Institute (Paris, France) designed Pan-genotypic primer sets on conserved HBV gene regions. Accuracy of LAMP to identify highly viremic patients was evaluated in 400 and 550 HBV-infected people in France and Senegal, respectively. Analytical validation was performed using real-time turbidimetric LAMP (Loopamp LA-500, Eiken Chemical, Japan). Viral loads were quantified using an AMPLIX real-time PCR (Biosynex, Illkirch-Graffenstaden France).
The team reported that their primers successfully detected eight major HBV genotypes/sub-genotypes (A1/2/3/B/C/D/E/F) with a detection limit ranging between 40-400 IU/mL. In France, the area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUROC), sensitivity and specificity of bead-based extraction and real-time turbidimetric LAMP were 0.95, 91.1% and 86.0%, respectively, to diagnose HBV DNA ≥20,000 IU/mL; and 0.98, 98.0% and 94.6% for ≥200,000 IU/mL. The performance did not vary by viral genotypes. In Senegal, using a field-adapted method, reagent-free boil-and-spin extraction and inexpensive end-point fluorescence detection, the AUROC, sensitivity and specificity were 0.95, 98.7% and 91.5%, respectively, to diagnose HBV DNA ≥200,000 IU/mL. The assay was not adapted to discriminate low-level viremia.
The authors concluded that they had developed a simple, rapid (60 minutes), and inexpensive (USD 8/assay) alternative to PCR to diagnose high viremia ≥200,000 IU/mL. HBV-LAMP may contribute to eliminating HBV mother-to-child transmission by identifying high-risk pregnant women eligible for antiviral prophylaxis in resource-limited countries. The study was published on April 7, 2021 in the journal Clinical Microbiology and Infection.
Related Links:
Pasteur Institute
Eiken Chemical
Biosynex
Latest Molecular Diagnostics News
- Study Uses Blood Samples to Identify Diseases Years Before They Start
- MicroRNA-Based Method Predicts CKD and Cardiovascular Risk
- Swab Test Helps Transplant Patients Receive Right Anti-Rejection Medication Dose
- Blood Test Predicts Which Bladder Cancer Patients May Safely Skip Surgery
- Ultra-Sensitive DNA Test Identifies Relapse Risk in Aggressive Leukemia
- Blood Test Could Help Detect Gallbladder Cancer Earlier
- New Blood Test Score Detects Hidden Alcohol-Related Liver Disease
- New Blood Test Predicts Who Will Most Likely Live Longer
- Genetic Test Predicts Radiation Therapy Risk for Prostate Cancer Patients
- Genetic Test Aids Early Detection and Improved Treatment for Cancers
- New Genome Sequencing Technique Measures Epstein-Barr Virus in Blood
- Blood Test Boosts Early Detection of Brain Cancer
- Molecular Monitoring Approach Helps Bladder Cancer Patients Avoid Surgery
- Genetic Tests to Speed Diagnosis of Lymphatic Disorders
- Changes In Lymphatic Vessels Can Aid Early Identification of Aggressive Oral Cancer
- New Extraction Kit Enables Consistent, Scalable cfDNA Isolation from Multiple Biofluids
Channels
Clinical Chemistry
view channelNew Blood Test Index Offers Earlier Detection of Liver Scarring
Metabolic fatty liver disease is highly prevalent and often silent, yet it can progress to fibrosis, cirrhosis, and liver failure. Current first-line blood test scores frequently return indeterminate results,... Read more
Electronic Nose Smells Early Signs of Ovarian Cancer in Blood
Ovarian cancer is often diagnosed at a late stage because its symptoms are vague and resemble those of more common conditions. Unlike breast cancer, there is currently no reliable screening method, and... Read moreMolecular Diagnostics
view channel
Study Uses Blood Samples to Identify Diseases Years Before They Start
Chronic diseases such as lupus, rheumatoid arthritis, Crohn’s disease, colon cancer, and heart failure often develop silently for years before symptoms appear. By the time they are diagnosed, significant... Read more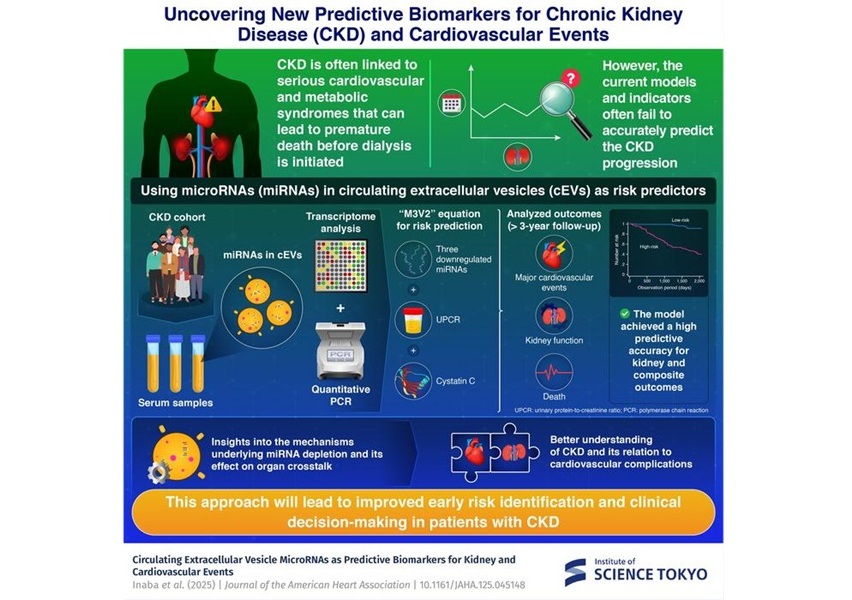
MicroRNA-Based Method Predicts CKD and Cardiovascular Risk
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) affects more than 850 million people worldwide and is a rapidly growing public health threat. Although it progressively damages kidney function, many patients die prematurely... Read moreHematology
view channel
Rapid Cartridge-Based Test Aims to Expand Access to Hemoglobin Disorder Diagnosis
Sickle cell disease and beta thalassemia are hemoglobin disorders that often require referral to specialized laboratories for definitive diagnosis, delaying results for patients and clinicians.... Read more
New Guidelines Aim to Improve AL Amyloidosis Diagnosis
Light chain (AL) amyloidosis is a rare, life-threatening bone marrow disorder in which abnormal amyloid proteins accumulate in organs. Approximately 3,260 people in the United States are diagnosed... Read moreImmunology
view channel
Immune Signature Identified in Treatment-Resistant Myasthenia Gravis
Myasthenia gravis is a rare autoimmune disorder in which immune attack at the neuromuscular junction causes fluctuating weakness that can impair vision, movement, speech, swallowing, and breathing.... Read more
New Biomarker Predicts Chemotherapy Response in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
Triple-negative breast cancer is an aggressive form of breast cancer in which patients often show widely varying responses to chemotherapy. Predicting who will benefit from treatment remains challenging,... Read moreBlood Test Identifies Lung Cancer Patients Who Can Benefit from Immunotherapy Drug
Small cell lung cancer (SCLC) is an aggressive disease with limited treatment options, and even newly approved immunotherapies do not benefit all patients. While immunotherapy can extend survival for some,... Read more
Whole-Genome Sequencing Approach Identifies Cancer Patients Benefitting From PARP-Inhibitor Treatment
Targeted cancer therapies such as PARP inhibitors can be highly effective, but only for patients whose tumors carry specific DNA repair defects. Identifying these patients accurately remains challenging,... Read morePathology
view channel
Molecular Imaging to Reduce Need for Melanoma Biopsies
Melanoma is the deadliest form of skin cancer and accounts for the vast majority of skin cancer-related deaths. Because early melanomas can closely resemble benign moles, clinicians often rely on visual... Read more
Urine Specimen Collection System Improves Diagnostic Accuracy and Efficiency
Urine testing is a critical, non-invasive diagnostic tool used to detect conditions such as pregnancy, urinary tract infections, metabolic disorders, cancer, and kidney disease. However, contaminated or... Read moreTechnology
view channel
AI-Driven Diagnostic Demonstrates High Accuracy in Detecting Periprosthetic Joint Infection
Periprosthetic joint infection (PJI) is a rare but serious complication affecting 1% to 2% of primary joint replacement surgeries. The condition occurs when bacteria or fungi infect tissues around an implanted... Read more
Blood Test “Clocks” Predict Start of Alzheimer’s Symptoms
More than 7 million Americans live with Alzheimer’s disease, and related health and long-term care costs are projected to reach nearly USD 400 billion in 2025. The disease has no cure, and symptoms often... Read moreIndustry
view channel
Cepheid Joins CDC Initiative to Strengthen U.S. Pandemic Testing Preparednesss
Cepheid (Sunnyvale, CA, USA) has been selected by the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) as one of four national collaborators in a federal initiative to speed rapid diagnostic technologies... Read more
QuidelOrtho Collaborates with Lifotronic to Expand Global Immunoassay Portfolio
QuidelOrtho (San Diego, CA, USA) has entered a long-term strategic supply agreement with Lifotronic Technology (Shenzhen, China) to expand its global immunoassay portfolio and accelerate customer access... Read more




















