Panel of MicroRNAs Differentiates Uncomplicated and Severe Malaria in Children
|
By LabMedica International staff writers Posted on 25 Jan 2021 |
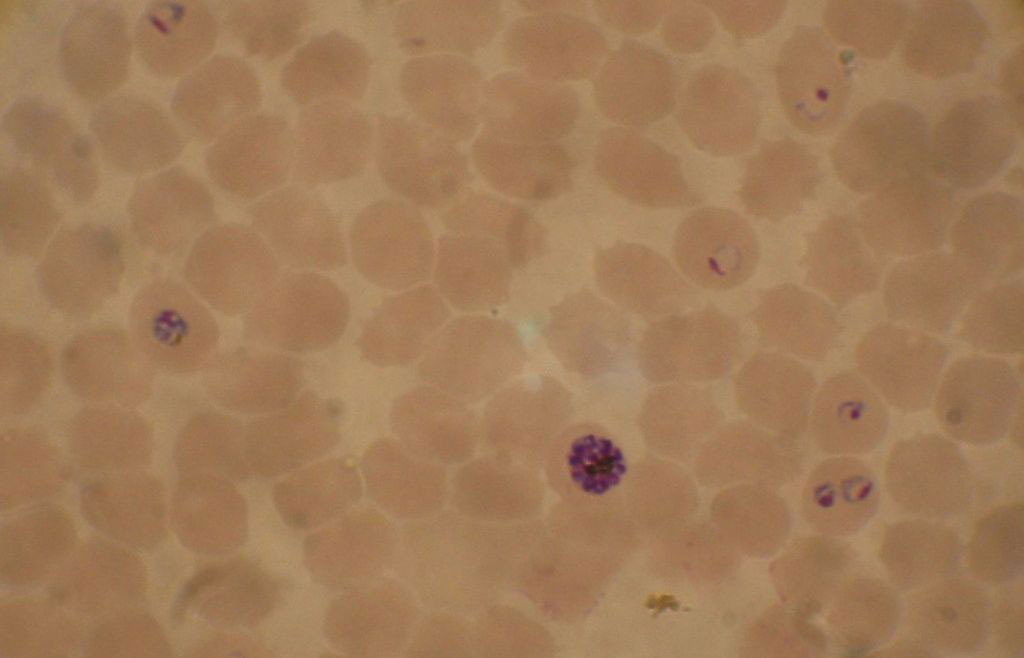
Image: Blood smear from a P. falciparum culture: several red blood cells have ring stages inside them while close to the center is a schizont and on the left a trophozoite (Photo courtesy of Wikimedia Commons)
MicroRNAs (miRNAs), which are rapidly released from damaged tissues into the host fluids, constitute a promising biomarker for the prognosis of severe malaria.
MiRNAs comprise a class of about 20 nucleotides-long RNA fragments that block gene expression by attaching to molecules of messenger RNA in a fashion that prevents them from transmitting the protein synthesizing instructions they had received from the DNA. With their capacity to fine-tune protein expression via sequence-specific interactions, miRNAs help regulate cell maintenance and differentiation. In addition to miRNAs playing an essential role in tumor development, dysregulation of certain miRNAs has been associated with many different diseases, such as dementia and cardiovascular conditions.
Investigators at the Barcelona Institute for Global Health (Spain) postulated that miRNA levels in plasma would be expressed differentially among children with severe and uncomplicated malaria due to parasite sequestration in vital organs of severely ill children. A characteristic of severe malaria is the sequestration of Plasmodium falciparum infected red blood cells in vital organs such as the lungs, kidneys, or brain. Resulting organ damage triggers the release of miRNAs into body fluids, including the blood.
To prove their hypothesis, the investigators used advanced sequencing techniques to identify miRNAs released by human brain endothelial cells growing in culture when the cultures were exposed to red blood cells infected by P. falciparum. They then applied next-generation sequencing to evaluate the differential expression of these miRNAs in severe malaria (SM) and in uncomplicated malaria (UM) in children living in Mozambique.
Results revealed that six miRNAs were associated with in vitro P. falciparum cytoadhesion, severity in children, and P. falciparum biomass. The six miRNAs were found to be elevated in children with severe malaria. One of the miRNAs was positively related to the amount of a parasite-derived protein HRP2 (histidine rich protein 2). Previous studies had found that the concentration of HRP2 could be used to quantify growth of the parasite in vitro and to define severe malaria in patients.
"We hypothesized that miRNA levels in plasma would be differently expressed in children with severe and uncomplicated malaria, due to parasite sequestration in vital organs," said senior author Dr. Alfredo Mayor, an associate research professor at the Barcelona Institute for Global Health."Our results indicate that the different pathological events in severe and uncomplicated malaria lead to differential expression of miRNAs in plasma. These miRNAs could be used as prognostic biomarkers of disease, but we need larger studies to validate this."
The malaria microRNA study was published in the February 2021 online edition of the journal Emerging Infectious Diseases.
Related Links:
Barcelona Institute for Global Health
MiRNAs comprise a class of about 20 nucleotides-long RNA fragments that block gene expression by attaching to molecules of messenger RNA in a fashion that prevents them from transmitting the protein synthesizing instructions they had received from the DNA. With their capacity to fine-tune protein expression via sequence-specific interactions, miRNAs help regulate cell maintenance and differentiation. In addition to miRNAs playing an essential role in tumor development, dysregulation of certain miRNAs has been associated with many different diseases, such as dementia and cardiovascular conditions.
Investigators at the Barcelona Institute for Global Health (Spain) postulated that miRNA levels in plasma would be expressed differentially among children with severe and uncomplicated malaria due to parasite sequestration in vital organs of severely ill children. A characteristic of severe malaria is the sequestration of Plasmodium falciparum infected red blood cells in vital organs such as the lungs, kidneys, or brain. Resulting organ damage triggers the release of miRNAs into body fluids, including the blood.
To prove their hypothesis, the investigators used advanced sequencing techniques to identify miRNAs released by human brain endothelial cells growing in culture when the cultures were exposed to red blood cells infected by P. falciparum. They then applied next-generation sequencing to evaluate the differential expression of these miRNAs in severe malaria (SM) and in uncomplicated malaria (UM) in children living in Mozambique.
Results revealed that six miRNAs were associated with in vitro P. falciparum cytoadhesion, severity in children, and P. falciparum biomass. The six miRNAs were found to be elevated in children with severe malaria. One of the miRNAs was positively related to the amount of a parasite-derived protein HRP2 (histidine rich protein 2). Previous studies had found that the concentration of HRP2 could be used to quantify growth of the parasite in vitro and to define severe malaria in patients.
"We hypothesized that miRNA levels in plasma would be differently expressed in children with severe and uncomplicated malaria, due to parasite sequestration in vital organs," said senior author Dr. Alfredo Mayor, an associate research professor at the Barcelona Institute for Global Health."Our results indicate that the different pathological events in severe and uncomplicated malaria lead to differential expression of miRNAs in plasma. These miRNAs could be used as prognostic biomarkers of disease, but we need larger studies to validate this."
The malaria microRNA study was published in the February 2021 online edition of the journal Emerging Infectious Diseases.
Related Links:
Barcelona Institute for Global Health
Latest Microbiology News
- Blood-Based Viral Signature Identified in Crohn’s Disease
- Hidden Gut Viruses Linked to Colorectal Cancer Risk
- Three-Test Panel Launched for Detection of Liver Fluke Infections
- Rapid Test Promises Faster Answers for Drug-Resistant Infections
- CRISPR-Based Technology Neutralizes Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria
- Comprehensive Review Identifies Gut Microbiome Signatures Associated With Alzheimer’s Disease
- AI-Powered Platform Enables Rapid Detection of Drug-Resistant C. Auris Pathogens
- New Test Measures How Effectively Antibiotics Kill Bacteria
- New Antimicrobial Stewardship Standards for TB Care to Optimize Diagnostics
- New UTI Diagnosis Method Delivers Antibiotic Resistance Results 24 Hours Earlier
- Breakthroughs in Microbial Analysis to Enhance Disease Prediction
- Blood-Based Diagnostic Method Could Identify Pediatric LRTIs
- Rapid Diagnostic Test Matches Gold Standard for Sepsis Detection
- Rapid POC Tuberculosis Test Provides Results Within 15 Minutes
- Rapid Assay Identifies Bloodstream Infection Pathogens Directly from Patient Samples
- Blood-Based Molecular Signatures to Enable Rapid EPTB Diagnosis
Channels
Clinical Chemistry
view channelNew Blood Test Index Offers Earlier Detection of Liver Scarring
Metabolic fatty liver disease is highly prevalent and often silent, yet it can progress to fibrosis, cirrhosis, and liver failure. Current first-line blood test scores frequently return indeterminate results,... Read more
Electronic Nose Smells Early Signs of Ovarian Cancer in Blood
Ovarian cancer is often diagnosed at a late stage because its symptoms are vague and resemble those of more common conditions. Unlike breast cancer, there is currently no reliable screening method, and... Read moreHematology
view channel
Rapid Cartridge-Based Test Aims to Expand Access to Hemoglobin Disorder Diagnosis
Sickle cell disease and beta thalassemia are hemoglobin disorders that often require referral to specialized laboratories for definitive diagnosis, delaying results for patients and clinicians.... Read more
New Guidelines Aim to Improve AL Amyloidosis Diagnosis
Light chain (AL) amyloidosis is a rare, life-threatening bone marrow disorder in which abnormal amyloid proteins accumulate in organs. Approximately 3,260 people in the United States are diagnosed... Read moreImmunology
view channel
Immune Signature Identified in Treatment-Resistant Myasthenia Gravis
Myasthenia gravis is a rare autoimmune disorder in which immune attack at the neuromuscular junction causes fluctuating weakness that can impair vision, movement, speech, swallowing, and breathing.... Read more
New Biomarker Predicts Chemotherapy Response in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
Triple-negative breast cancer is an aggressive form of breast cancer in which patients often show widely varying responses to chemotherapy. Predicting who will benefit from treatment remains challenging,... Read moreBlood Test Identifies Lung Cancer Patients Who Can Benefit from Immunotherapy Drug
Small cell lung cancer (SCLC) is an aggressive disease with limited treatment options, and even newly approved immunotherapies do not benefit all patients. While immunotherapy can extend survival for some,... Read more
Whole-Genome Sequencing Approach Identifies Cancer Patients Benefitting From PARP-Inhibitor Treatment
Targeted cancer therapies such as PARP inhibitors can be highly effective, but only for patients whose tumors carry specific DNA repair defects. Identifying these patients accurately remains challenging,... Read moreMicrobiology
view channel
Blood-Based Viral Signature Identified in Crohn’s Disease
Crohn’s disease is a chronic inflammatory intestinal disorder affecting approximately 0.4% of the European population, with symptoms and progression that vary widely. Although viral components of the microbiome... Read more
Hidden Gut Viruses Linked to Colorectal Cancer Risk
Colorectal cancer (CRC) remains a leading cause of cancer mortality in many Western countries, and existing risk-stratification approaches leave substantial room for improvement. Although age, diet, and... Read morePathology
view channel
Molecular Imaging to Reduce Need for Melanoma Biopsies
Melanoma is the deadliest form of skin cancer and accounts for the vast majority of skin cancer-related deaths. Because early melanomas can closely resemble benign moles, clinicians often rely on visual... Read more
Urine Specimen Collection System Improves Diagnostic Accuracy and Efficiency
Urine testing is a critical, non-invasive diagnostic tool used to detect conditions such as pregnancy, urinary tract infections, metabolic disorders, cancer, and kidney disease. However, contaminated or... Read moreTechnology
view channel
AI-Driven Diagnostic Demonstrates High Accuracy in Detecting Periprosthetic Joint Infection
Periprosthetic joint infection (PJI) is a rare but serious complication affecting 1% to 2% of primary joint replacement surgeries. The condition occurs when bacteria or fungi infect tissues around an implanted... Read more
Blood Test “Clocks” Predict Start of Alzheimer’s Symptoms
More than 7 million Americans live with Alzheimer’s disease, and related health and long-term care costs are projected to reach nearly USD 400 billion in 2025. The disease has no cure, and symptoms often... Read moreIndustry
view channel
Cepheid Joins CDC Initiative to Strengthen U.S. Pandemic Testing Preparednesss
Cepheid (Sunnyvale, CA, USA) has been selected by the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) as one of four national collaborators in a federal initiative to speed rapid diagnostic technologies... Read more
QuidelOrtho Collaborates with Lifotronic to Expand Global Immunoassay Portfolio
QuidelOrtho (San Diego, CA, USA) has entered a long-term strategic supply agreement with Lifotronic Technology (Shenzhen, China) to expand its global immunoassay portfolio and accelerate customer access... Read more




















