Unusual Blood Clots Characterized in Leprosy Patients
|
By LabMedica International staff writers Posted on 03 Apr 2018 |
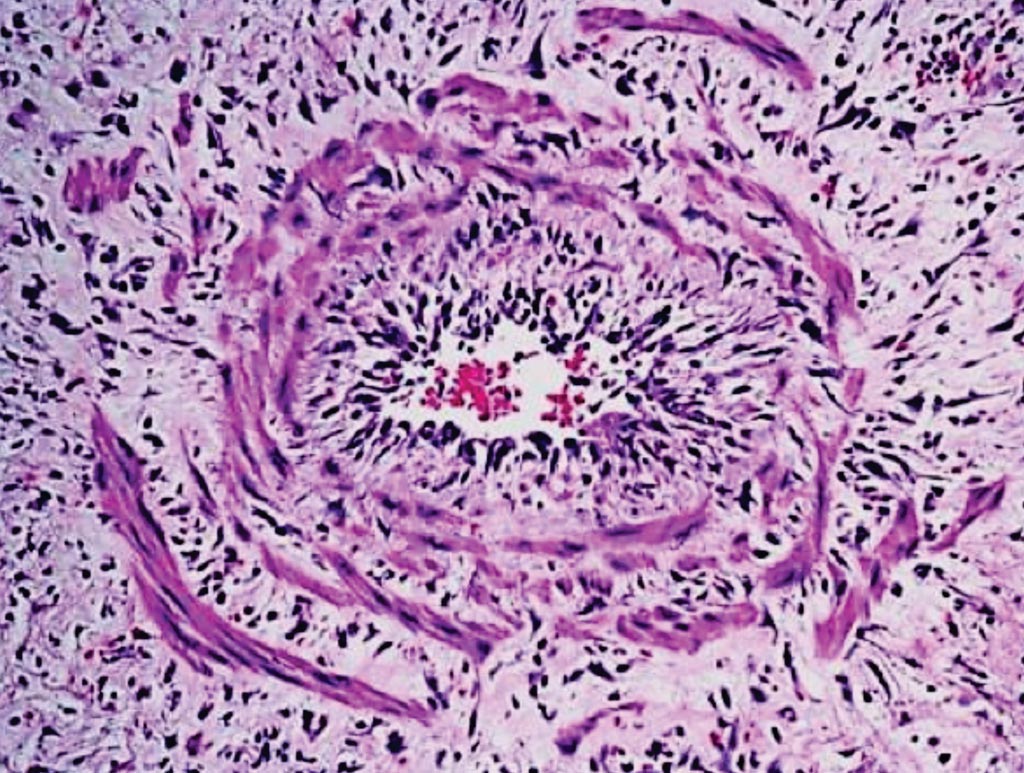
Image: A histopathology of a deep vein inflammatory infiltrate with wall dissociated by edema, observed in a skin lesion of a leprosy patient suffering an erythema nodosum leprosum episode (Photo courtesy of Oswaldo Cruz Institute).
Leprosy is a chronic infection by Mycobacterium leprae and causes body-wide symptoms, deformities, and disability. It remains a public health problem worldwide, despite the existence of antibiotic combinations that can cure it.
Hemostatic disorders are frequently associated with acute and chronic infections due to the fact that platelet functions, blood coagulation and fibrinolysis are intimately correlated with the immune system. For years, doctors have observed that some patients with leprosy develop unusual blood clots, which can lead to stroke or heart attack.
Scientists at the Oswaldo Cruz Institute (Rio de Janeiro, Brazil) analyzed two groups of patients: a prospective group, which plasma samples were collected before multidrug therapy against leprosy, composed of 11 non-reactional (multibacillary leprosy; MB-NR), being 10 lepromatous leprosy (LL) and one borderline lepromatous (BL). The erythema nodosum leprosum patients group (MB-ENL) included 13 LL and one BL individuals. These two groups include six females, 19 males with median age of 45.2 years, ranging from 23 to 80. The retrospective cohort was composed of 638 leprosy outpatients at an Outpatient Unit, from 2012 to 2014, where 35 patients presented the leprosum clot during serum harvesting.
The team performed SDS-PAGE and protein content was measured with the commercially available 2D Quant-Kit. Spots were taken from the gel, digested with trypsin and analyzed by spectrometry using the MALDI-TOF/TOF 5800. The mass spectrometry protein identifications were obtained with a 5800 Proteomics Analyzer.
The scientists applied the STA-R Evolution instrument to determine partial thromboplastin time (aPPT) and prothrombin time (PT) in all plasma samples. The levels of von Willebrand and soluble tissue factor, C4 complement, and anti-cardiolipin IgM antibody in the serum of leprosy patients were determined using the following commercial kits: Human von Willebrand Factor ELISA kit and Human Tissue Factor ELISA kit and C4 turbiquest, respectively.
The team found that patients both experiencing a reactional episode and those with non-reactional leprosy had factors in their blood, including plasmatic fibrinogen, anti-cardiolipin antibodies, von Willebrand factor, and soluble tissue factor, promoting blood coagulation. Formation of leprosum clots, they showed, was correlated with increased levels of soluble tissue factor and von Willebrand factor. Tests on leprosum clots revealed high contents of lipids and fibrinogen, and showed higher levels of two proteins, complement component 3 and 4 and inter-alpha- trypsin inhibitor family heavy chain-related protein (IHRP), compared to clots from patients without leprosy.
The authors propose that multibacillary patients with high levels of fibrinogen could be beneficiated from a prophylactic use of xanthine derivatives such as pentoxifylline, in order to prevent some of the acute clinical symptoms observed during severe cases of leprosy reactional episodes, such as cyanosis and tissue necrosis, probably related with superficial vein thrombosis. The study was published on March 22, 2018, in the journal PLOS Neglected Tropical Diseases.
Related Links:
Oswaldo Cruz Institute
Hemostatic disorders are frequently associated with acute and chronic infections due to the fact that platelet functions, blood coagulation and fibrinolysis are intimately correlated with the immune system. For years, doctors have observed that some patients with leprosy develop unusual blood clots, which can lead to stroke or heart attack.
Scientists at the Oswaldo Cruz Institute (Rio de Janeiro, Brazil) analyzed two groups of patients: a prospective group, which plasma samples were collected before multidrug therapy against leprosy, composed of 11 non-reactional (multibacillary leprosy; MB-NR), being 10 lepromatous leprosy (LL) and one borderline lepromatous (BL). The erythema nodosum leprosum patients group (MB-ENL) included 13 LL and one BL individuals. These two groups include six females, 19 males with median age of 45.2 years, ranging from 23 to 80. The retrospective cohort was composed of 638 leprosy outpatients at an Outpatient Unit, from 2012 to 2014, where 35 patients presented the leprosum clot during serum harvesting.
The team performed SDS-PAGE and protein content was measured with the commercially available 2D Quant-Kit. Spots were taken from the gel, digested with trypsin and analyzed by spectrometry using the MALDI-TOF/TOF 5800. The mass spectrometry protein identifications were obtained with a 5800 Proteomics Analyzer.
The scientists applied the STA-R Evolution instrument to determine partial thromboplastin time (aPPT) and prothrombin time (PT) in all plasma samples. The levels of von Willebrand and soluble tissue factor, C4 complement, and anti-cardiolipin IgM antibody in the serum of leprosy patients were determined using the following commercial kits: Human von Willebrand Factor ELISA kit and Human Tissue Factor ELISA kit and C4 turbiquest, respectively.
The team found that patients both experiencing a reactional episode and those with non-reactional leprosy had factors in their blood, including plasmatic fibrinogen, anti-cardiolipin antibodies, von Willebrand factor, and soluble tissue factor, promoting blood coagulation. Formation of leprosum clots, they showed, was correlated with increased levels of soluble tissue factor and von Willebrand factor. Tests on leprosum clots revealed high contents of lipids and fibrinogen, and showed higher levels of two proteins, complement component 3 and 4 and inter-alpha- trypsin inhibitor family heavy chain-related protein (IHRP), compared to clots from patients without leprosy.
The authors propose that multibacillary patients with high levels of fibrinogen could be beneficiated from a prophylactic use of xanthine derivatives such as pentoxifylline, in order to prevent some of the acute clinical symptoms observed during severe cases of leprosy reactional episodes, such as cyanosis and tissue necrosis, probably related with superficial vein thrombosis. The study was published on March 22, 2018, in the journal PLOS Neglected Tropical Diseases.
Related Links:
Oswaldo Cruz Institute
Latest Immunology News
- Cancer Mutation ‘Fingerprints’ to Improve Prediction of Immunotherapy Response
- Immune Signature Identified in Treatment-Resistant Myasthenia Gravis
- New Biomarker Predicts Chemotherapy Response in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
- Blood Test Identifies Lung Cancer Patients Who Can Benefit from Immunotherapy Drug
- Whole-Genome Sequencing Approach Identifies Cancer Patients Benefitting From PARP-Inhibitor Treatment
- Ultrasensitive Liquid Biopsy Demonstrates Efficacy in Predicting Immunotherapy Response
- Blood Test Could Identify Colon Cancer Patients to Benefit from NSAIDs
- Blood Test Could Detect Adverse Immunotherapy Effects
- Routine Blood Test Can Predict Who Benefits Most from CAR T-Cell Therapy
- New Test Distinguishes Vaccine-Induced False Positives from Active HIV Infection
- Gene Signature Test Predicts Response to Key Breast Cancer Treatment
- Chip Captures Cancer Cells from Blood to Help Select Right Breast Cancer Treatment
- Blood-Based Liquid Biopsy Model Analyzes Immunotherapy Effectiveness
- Signature Genes Predict T-Cell Expansion in Cancer Immunotherapy
- Molecular Microscope Diagnostic System Assesses Lung Transplant Rejection
- Blood Test Tracks Treatment Resistance in High-Grade Serous Ovarian Cancer
Channels
Clinical Chemistry
view channelNew Blood Test Index Offers Earlier Detection of Liver Scarring
Metabolic fatty liver disease is highly prevalent and often silent, yet it can progress to fibrosis, cirrhosis, and liver failure. Current first-line blood test scores frequently return indeterminate results,... Read more
Electronic Nose Smells Early Signs of Ovarian Cancer in Blood
Ovarian cancer is often diagnosed at a late stage because its symptoms are vague and resemble those of more common conditions. Unlike breast cancer, there is currently no reliable screening method, and... Read moreMolecular Diagnostics
view channel
Simple One-Hour Saliva Test Detects Common Cancers
Early detection is critical for improving cancer outcomes, yet many diagnostic tests rely on invasive procedures such as blood draws or biopsies. Researchers are exploring simpler approaches that could... Read more
Blood Test Could Help Guide Treatment Decisions in Germ Cell Tumors
Chemotherapy is often highly effective for germ cell tumors, but in a subset of patients, the disease does not respond well to standard treatment. For these individuals, doctors may consider high-dose... Read moreHematology
view channel
Rapid Cartridge-Based Test Aims to Expand Access to Hemoglobin Disorder Diagnosis
Sickle cell disease and beta thalassemia are hemoglobin disorders that often require referral to specialized laboratories for definitive diagnosis, delaying results for patients and clinicians.... Read more
New Guidelines Aim to Improve AL Amyloidosis Diagnosis
Light chain (AL) amyloidosis is a rare, life-threatening bone marrow disorder in which abnormal amyloid proteins accumulate in organs. Approximately 3,260 people in the United States are diagnosed... Read moreImmunology
view channel
Cancer Mutation ‘Fingerprints’ to Improve Prediction of Immunotherapy Response
Cancer cells accumulate thousands of genetic mutations, but not all mutations affect tumors in the same way. Some make cancer cells more visible to the immune system, while others allow tumors to evade... Read more
Immune Signature Identified in Treatment-Resistant Myasthenia Gravis
Myasthenia gravis is a rare autoimmune disorder in which immune attack at the neuromuscular junction causes fluctuating weakness that can impair vision, movement, speech, swallowing, and breathing.... Read more
New Biomarker Predicts Chemotherapy Response in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
Triple-negative breast cancer is an aggressive form of breast cancer in which patients often show widely varying responses to chemotherapy. Predicting who will benefit from treatment remains challenging,... Read moreBlood Test Identifies Lung Cancer Patients Who Can Benefit from Immunotherapy Drug
Small cell lung cancer (SCLC) is an aggressive disease with limited treatment options, and even newly approved immunotherapies do not benefit all patients. While immunotherapy can extend survival for some,... Read morePathology
view channel
Novel mcPCR Technology to Transform Testing of Clinical Samples
DNA methylation is an important biological marker used in the diagnosis and monitoring of many diseases, including cancer. These chemical modifications to DNA influence gene activity and can reveal early... Read more
Sex Differences in Alzheimer’s Biomarkers Linked to Faster Cognitive Decline
Sex differences in Alzheimer’s disease present ongoing diagnostic challenges, with women often experiencing a disproportionate disease burden even when preclinical amyloid-beta levels are similar to men.... Read moreTechnology
view channel
AI Model Outperforms Clinicians in Rare Disease Detection
Rare diseases affect an estimated 300 million people worldwide, yet diagnosis is often protracted and error-prone. Many conditions present with heterogeneous signs that overlap with common disorders, leading... Read more
AI-Driven Diagnostic Demonstrates High Accuracy in Detecting Periprosthetic Joint Infection
Periprosthetic joint infection (PJI) is a rare but serious complication affecting 1% to 2% of primary joint replacement surgeries. The condition occurs when bacteria or fungi infect tissues around an implanted... Read moreIndustry
view channel
Cepheid Joins CDC Initiative to Strengthen U.S. Pandemic Testing Preparednesss
Cepheid (Sunnyvale, CA, USA) has been selected by the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) as one of four national collaborators in a federal initiative to speed rapid diagnostic technologies... Read more
QuidelOrtho Collaborates with Lifotronic to Expand Global Immunoassay Portfolio
QuidelOrtho (San Diego, CA, USA) has entered a long-term strategic supply agreement with Lifotronic Technology (Shenzhen, China) to expand its global immunoassay portfolio and accelerate customer access... Read more








 (3) (1).png)











