Genetic Link Found Between Immune System and Lymphoma
|
By LabMedica International staff writers Posted on 12 Dec 2017 |
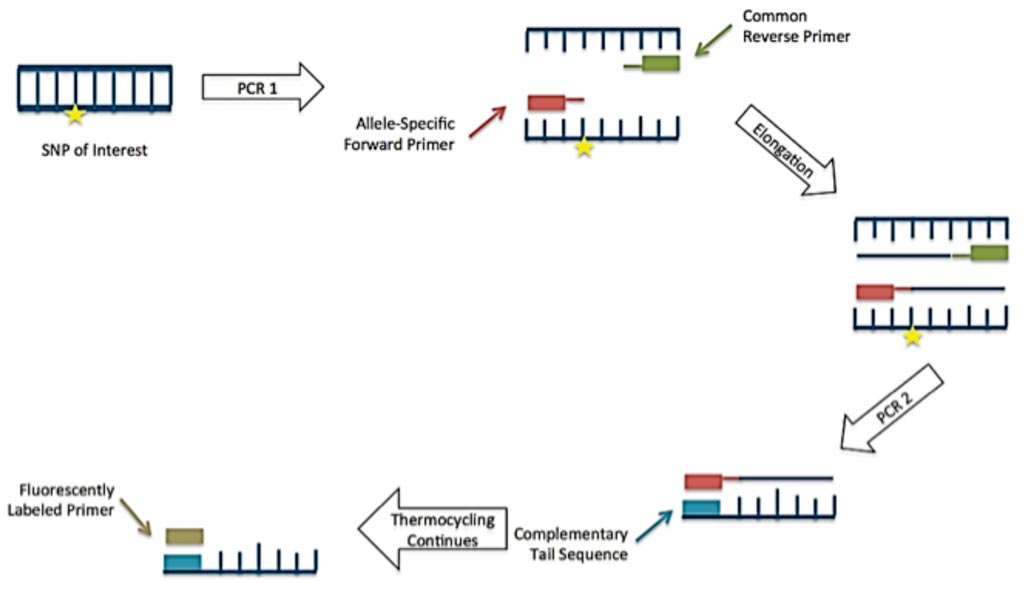
Image: A diagram of the Kompetitive Allele Specific Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR KASP) method (Photo courtesy of J.P. Livingstone).
Classical Hodgkin lymphoma (cHL) is a lymphoid malignancy of germinal center (GC) B-cell origin, which is characterized by Hodgkin and Reed–Sternberg (HRS) cells with a dominant background population of reactive inflammatory cells.
People who inherit genetic changes that alter the function of their immune system are at increased risk of developing Hodgkin lymphoma. Of the four major subtypes of cHL, nodular sclerosis Hodgkin lymphoma (NSHL) and mixed cellularity Hodgkin lymphoma (MCHL) account for 65% and 20% of cHL, respectively.
A large group of scientists collaborating with The Institute of Cancer Research (London, UK) analyzed genetic data from 5,314 cases of Hodgkin lymphoma and 16,749 controls, from four different European studies. They analyzed constitutional DNA from 1,717 cases, which were genotyped using the Illumina Oncoarray (Illumina Inc, San Diego, CA, USA). The fidelity of genome-wide association study (GWAS) imputation was assessed by the concordance between imputed and directly genotyped single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNP) in a subset of samples. Replication genotyping of UK samples was performed using Polymerase Chain Reaction Kompetitive Allele Specific (PCR KASP) chemistry.
The investigators identified six new single-letter changes in DNA that were linked to the development of Hodgkin lymphoma and five of these affect the way a type of white blood cell, called B cells, develop. The study also showed clear differences in genetic risk between two different subtypes of Hodgkin Lymphoma and NSHL and MCHL. For example, a single-letter change located in DNA near the gene LIM Domain Containing Preferred Translocation Partner In Lipoma (LPP) increased the risk of NSHL by 37%, but had little effect on the risk of developing MCHL.
Richard S. Houlston, FMedSci, FRS, a Professor of Molecular and Population Genetics and senior author of the study, said, “Hodgkin lymphoma is a cancer of immune cells called B cells, and our study links the risk of the disease to changes in the genes that control how B cells develop. Interestingly, we found that some of the genetic changes we have linked to Hodgkin lymphoma have previously been associated with the risk of autoimmune diseases such as multiple sclerosis and rheumatoid arthritis. The new information could point towards new ways of diagnosing, treating, or even helping to prevent Hodgkin lymphoma.” The study was published on December 1, 2017, in the journal Nature Communications.
Related Links:
The Institute of Cancer Research
Illumina Oncoarray
People who inherit genetic changes that alter the function of their immune system are at increased risk of developing Hodgkin lymphoma. Of the four major subtypes of cHL, nodular sclerosis Hodgkin lymphoma (NSHL) and mixed cellularity Hodgkin lymphoma (MCHL) account for 65% and 20% of cHL, respectively.
A large group of scientists collaborating with The Institute of Cancer Research (London, UK) analyzed genetic data from 5,314 cases of Hodgkin lymphoma and 16,749 controls, from four different European studies. They analyzed constitutional DNA from 1,717 cases, which were genotyped using the Illumina Oncoarray (Illumina Inc, San Diego, CA, USA). The fidelity of genome-wide association study (GWAS) imputation was assessed by the concordance between imputed and directly genotyped single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNP) in a subset of samples. Replication genotyping of UK samples was performed using Polymerase Chain Reaction Kompetitive Allele Specific (PCR KASP) chemistry.
The investigators identified six new single-letter changes in DNA that were linked to the development of Hodgkin lymphoma and five of these affect the way a type of white blood cell, called B cells, develop. The study also showed clear differences in genetic risk between two different subtypes of Hodgkin Lymphoma and NSHL and MCHL. For example, a single-letter change located in DNA near the gene LIM Domain Containing Preferred Translocation Partner In Lipoma (LPP) increased the risk of NSHL by 37%, but had little effect on the risk of developing MCHL.
Richard S. Houlston, FMedSci, FRS, a Professor of Molecular and Population Genetics and senior author of the study, said, “Hodgkin lymphoma is a cancer of immune cells called B cells, and our study links the risk of the disease to changes in the genes that control how B cells develop. Interestingly, we found that some of the genetic changes we have linked to Hodgkin lymphoma have previously been associated with the risk of autoimmune diseases such as multiple sclerosis and rheumatoid arthritis. The new information could point towards new ways of diagnosing, treating, or even helping to prevent Hodgkin lymphoma.” The study was published on December 1, 2017, in the journal Nature Communications.
Related Links:
The Institute of Cancer Research
Illumina Oncoarray
Latest Hematology News
- First Point-of-Care Heparin Monitoring Test Provides Results in Under 15 Minutes

- New Scoring System Predicts Risk of Developing Cancer from Common Blood Disorder
- Non-Invasive Prenatal Test for Fetal RhD Status Demonstrates 100% Accuracy
- WBC Count Could Predict Severity of COVID-19 Symptoms
- New Platelet Counting Technology to Help Labs Prevent Diagnosis Errors
- Streamlined Approach to Testing for Heparin-Induced Thrombocytopenia Improves Diagnostic Accuracy
- POC Hemostasis System Could Help Prevent Maternal Deaths
- New Test Assesses Oxygen Delivering Ability of Red Blood Cells by Measuring Their Shape
- Personalized CBC Testing Could Help Diagnose Early-Stage Diseases in Healthy Individuals
- Non-Invasive Test Solution Determines Fetal RhD Status from Maternal Plasma
- First-Of-Its-Kind Smartphone Technology Noninvasively Measures Blood Hemoglobin Levels at POC

- Next Gen CBC and Sepsis Diagnostic System Targets Faster, Earlier, Easier Results
- Newly Discovered Blood Group System to Help Identify and Treat Rare Patients
- Blood Platelet Score Detects Previously Unmeasured Risk of Heart Attack and Stroke
- Automated Benchtop System to Bring Blood Testing To Anyone, Anywhere
- New Hematology Analyzers Deliver Combined ESR and CBC/DIFF Results in 60 Seconds
Channels
Clinical Chemistry
view channel
AI-Powered Blood Test Accurately Detects Ovarian Cancer
Ovarian cancer ranks as the fifth leading cause of cancer-related deaths in women, largely due to late-stage diagnoses. Although over 90% of women exhibit symptoms in Stage I, only 20% are diagnosed in... Read more
Automated Decentralized cfDNA NGS Assay Identifies Alterations in Advanced Solid Tumors
Current circulating cell-free DNA (cfDNA) assays are typically centralized, requiring specialized handling and transportation of samples. Introducing a flexible, decentralized sequencing system at the... Read more
Mass Spectrometry Detects Bacteria Without Time-Consuming Isolation and Multiplication
Speed and accuracy are essential when diagnosing diseases. Traditionally, diagnosing bacterial infections involves the labor-intensive process of isolating pathogens and cultivating bacterial cultures,... Read more
First Comprehensive Syphilis Test to Definitively Diagnose Active Infection In 10 Minutes
In the United States, syphilis cases have surged by nearly 80% from 2018 to 2023, with 209,253 cases recorded in the most recent year of data. Syphilis, which can be transmitted sexually or from mother... Read moreHematology
view channel
First Point-of-Care Heparin Monitoring Test Provides Results in Under 15 Minutes
Heparin dosing requires careful management to avoid both bleeding and clotting complications. In high-risk situations like extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO), mortality rates can reach about 50%,... Read more
New Scoring System Predicts Risk of Developing Cancer from Common Blood Disorder
Clonal cytopenia of undetermined significance (CCUS) is a blood disorder commonly found in older adults, characterized by mutations in blood cells and a low blood count, but without any obvious cause or... Read moreImmunology
view channel
Stem Cell Test Predicts Treatment Outcome for Patients with Platinum-Resistant Ovarian Cancer
Epithelial ovarian cancer frequently responds to chemotherapy initially, but eventually, the tumor develops resistance to the therapy, leading to regrowth. This resistance is partially due to the activation... Read more
Machine Learning-Enabled Blood Test Predicts Immunotherapy Response in Lymphoma Patients
Chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy has emerged as one of the most promising recent developments in the treatment of blood cancers. However, over half of non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL) patients... Read moreMicrobiology
view channel
New Blood Test Detects Up to Five Infectious Diseases at POC
Researchers have developed a prototype flow-through assay capable of detecting up to five different infections, with results that can be quickly analyzed and transmitted via a specialized smartphone app.... Read more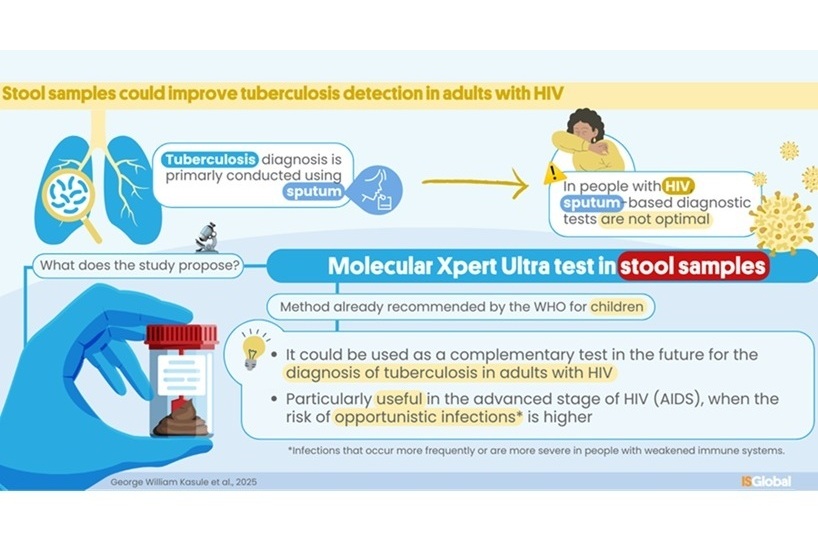
Molecular Stool Test Shows Potential for Diagnosing TB in Adults with HIV
Tuberculosis (TB), caused by the bacterium Mycobacterium tuberculosis, led to 1.25 million deaths in 2023, with 13% of those occurring in people living with HIV. The current primary diagnostic method for... Read morePathology
view channel
Groundbreaking Chest Pain Triage Algorithm to Transform Cardiac Care
Cardiovascular disease is responsible for a third of all deaths worldwide, and chest pain is the second most common reason for emergency department (ED) visits. With EDs often being some of the busiest... Read more
AI-Based Liquid Biopsy Approach to Revolutionize Brain Cancer Detection
Detecting brain cancers remains extremely challenging, with many patients only receiving a diagnosis at later stages after symptoms like headaches, seizures, or cognitive issues appear. Late-stage diagnoses... Read moreTechnology
view channel
Advanced Predictive Algorithms Identify Patients Having Undiagnosed Cancer
Two newly developed advanced predictive algorithms leverage a person’s health conditions and basic blood test results to accurately predict the likelihood of having an undiagnosed cancer, including ch... Read more
Light Signature Algorithm to Enable Faster and More Precise Medical Diagnoses
Every material or molecule interacts with light in a unique way, creating a distinct pattern, much like a fingerprint. Optical spectroscopy, which involves shining a laser on a material and observing how... Read more
Disposable Microchip Technology Could Selectively Detect HIV in Whole Blood Samples
As of the end of 2023, approximately 40 million people globally were living with HIV, and around 630,000 individuals died from AIDS-related illnesses that same year. Despite a substantial decline in deaths... Read more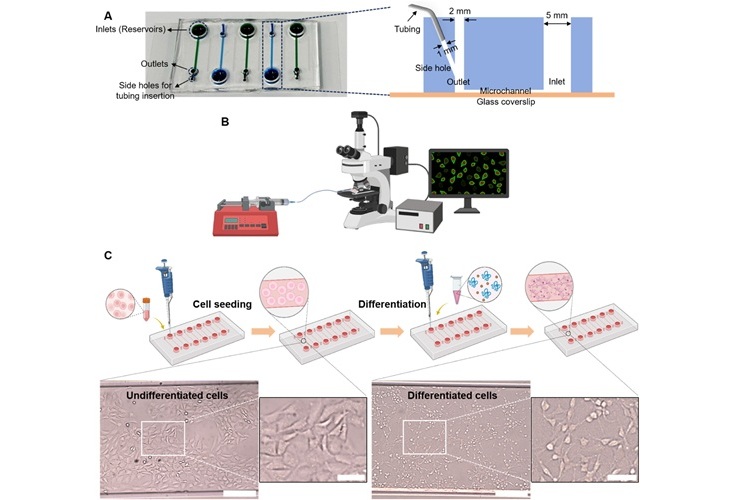
Pain-On-A-Chip Microfluidic Device Determines Types of Chronic Pain from Blood Samples
Chronic pain is a widespread condition that remains difficult to manage, and existing clinical methods for its treatment rely largely on self-reporting, which can be subjective and especially problematic... Read moreIndustry
view channel
Qiagen Acquires NGS Analysis Software Company Genoox
QIAGEN (Venlo, the Netherlands) has signed a definitive agreement to acquire Genoox (Tel Aviv, Israel), a provider of artificial intelligence (AI)-powered software that enables clinical labs to scale and... Read more
Cepheid and Oxford Nanopore Technologies Partner on Advancing Automated Sequencing-Based Solutions
Cepheid (Sunnyvale, CA, USA), a leading molecular diagnostics company, and Oxford Nanopore Technologies (Oxford, UK), the company behind a new generation of sequencing-based molecular analysis technologies,... Read more
Grifols and Tecan’s IBL Collaborate on Advanced Biomarker Panels
Grifols (Barcelona, Spain), one of the world’s leading producers of plasma-derived medicines and innovative diagnostic solutions, is expanding its offer in clinical diagnostics through a strategic partnership... Read more