Fatal Fungal Infection Has Unique Growth Patterns
|
By LabMedica International staff writers Posted on 08 Sep 2016 |
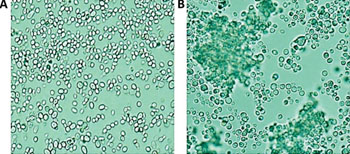
Image: A microscopic appearance of non-aggregate-forming isolates (A) and aggregate-forming isolates (B) of Candida auris in phosphate buffered saline suspensions (Photo courtesy of Public Health England).
The multidrug-resistant yeast Candida auris, which has caused fatal infections in some hospitalized patients, has at least two different growth patterns and some of its strains are as capable of causing disease as the most invasive type of yeast called Candida albicans.
Normally, a yeast copies itself and divides during growth, but the C. auris samples differ in their growth characteristics in the laboratory, with a proportion failing to separate after budding, resulting in the formation of large clumps of cells that could not be physically disrupted.
Mycology specialists at the Public Health England Mycology Reference Laboratory (Bristol, UK) characterized 12 C. auris isolates by ribosomal DNA (rDNA) gene sequencing targeting the 28S rRNA or by internal transcribed spacer 1 (ITS1) regions and matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization–time of flight (MALDI-TOF) analysis or by a combination of the two methods.
The scientists compared the pathogenicity, or disease-causing potential, of the C. auris samples taken from patients treated at six National Health Service hospitals in England with samples of other disease-causing Candida species. To do so, they injected young wax moth larvae (called Galleria mellonella, an insect model used to study human infection) with the assorted Candida samples to measure progression of disease. The investigators also found strain-specific differences in the behavior of C. auris, with the clumped strains being less capable of causing disease than the ones that did not clump. The strains that did not clump were as capable of causing disease as another type of Candida called C. albicans, which is currently believed to have the most disease-causing potential in the Candida family.
Elizabeth Johnson, PhD, director of the National Mycology Reference Laboratory and co-author of the study, said, “Despite receiving considerable attention since its first description, little is known concerning the disease-causing potential of this emerging fungal pathogen. We were surprised to find two very different growth forms of C. auris depending on the strain. We were also surprised by the virulence of this species because in most other types of Candida, the ability to cause disease relates to the organism's ability to form hyphae (fine, branching tube-like structures). C. auris is not able to form these hyphae in the laboratory or in the insect infection model, so we would have predicted reduced ability to cause disease.” The study was published on August 18, 2016, in the journal mSphere.
Related Links:
Public Health England Mycology Reference Laboratory
Normally, a yeast copies itself and divides during growth, but the C. auris samples differ in their growth characteristics in the laboratory, with a proportion failing to separate after budding, resulting in the formation of large clumps of cells that could not be physically disrupted.
Mycology specialists at the Public Health England Mycology Reference Laboratory (Bristol, UK) characterized 12 C. auris isolates by ribosomal DNA (rDNA) gene sequencing targeting the 28S rRNA or by internal transcribed spacer 1 (ITS1) regions and matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization–time of flight (MALDI-TOF) analysis or by a combination of the two methods.
The scientists compared the pathogenicity, or disease-causing potential, of the C. auris samples taken from patients treated at six National Health Service hospitals in England with samples of other disease-causing Candida species. To do so, they injected young wax moth larvae (called Galleria mellonella, an insect model used to study human infection) with the assorted Candida samples to measure progression of disease. The investigators also found strain-specific differences in the behavior of C. auris, with the clumped strains being less capable of causing disease than the ones that did not clump. The strains that did not clump were as capable of causing disease as another type of Candida called C. albicans, which is currently believed to have the most disease-causing potential in the Candida family.
Elizabeth Johnson, PhD, director of the National Mycology Reference Laboratory and co-author of the study, said, “Despite receiving considerable attention since its first description, little is known concerning the disease-causing potential of this emerging fungal pathogen. We were surprised to find two very different growth forms of C. auris depending on the strain. We were also surprised by the virulence of this species because in most other types of Candida, the ability to cause disease relates to the organism's ability to form hyphae (fine, branching tube-like structures). C. auris is not able to form these hyphae in the laboratory or in the insect infection model, so we would have predicted reduced ability to cause disease.” The study was published on August 18, 2016, in the journal mSphere.
Related Links:
Public Health England Mycology Reference Laboratory
Latest Microbiology News
- Hidden Gut Viruses Linked to Colorectal Cancer Risk
- Three-Test Panel Launched for Detection of Liver Fluke Infections
- Rapid Test Promises Faster Answers for Drug-Resistant Infections
- CRISPR-Based Technology Neutralizes Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria
- Comprehensive Review Identifies Gut Microbiome Signatures Associated With Alzheimer’s Disease
- AI-Powered Platform Enables Rapid Detection of Drug-Resistant C. Auris Pathogens
- New Test Measures How Effectively Antibiotics Kill Bacteria
- New Antimicrobial Stewardship Standards for TB Care to Optimize Diagnostics
- New UTI Diagnosis Method Delivers Antibiotic Resistance Results 24 Hours Earlier
- Breakthroughs in Microbial Analysis to Enhance Disease Prediction
- Blood-Based Diagnostic Method Could Identify Pediatric LRTIs
- Rapid Diagnostic Test Matches Gold Standard for Sepsis Detection
- Rapid POC Tuberculosis Test Provides Results Within 15 Minutes
- Rapid Assay Identifies Bloodstream Infection Pathogens Directly from Patient Samples
- Blood-Based Molecular Signatures to Enable Rapid EPTB Diagnosis
- 15-Minute Blood Test Diagnoses Life-Threatening Infections in Children
Channels
Clinical Chemistry
view channelNew Blood Test Index Offers Earlier Detection of Liver Scarring
Metabolic fatty liver disease is highly prevalent and often silent, yet it can progress to fibrosis, cirrhosis, and liver failure. Current first-line blood test scores frequently return indeterminate results,... Read more
Electronic Nose Smells Early Signs of Ovarian Cancer in Blood
Ovarian cancer is often diagnosed at a late stage because its symptoms are vague and resemble those of more common conditions. Unlike breast cancer, there is currently no reliable screening method, and... Read moreMolecular Diagnostics
view channel
Ultra-Sensitive DNA Test Identifies Relapse Risk in Aggressive Leukemia
Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is a rare but aggressive blood cancer in which relapse after allogeneic stem cell transplant remains a major clinical challenge, particularly for patients with NPM1-mutated disease.... Read more
Blood Test Could Help Detect Gallbladder Cancer Earlier
Gallbladder cancer is one of the deadliest gastrointestinal cancers because it is often diagnosed at an advanced stage when treatment options are limited. Early symptoms are minimal, and current screening... Read moreHematology
view channel
Rapid Cartridge-Based Test Aims to Expand Access to Hemoglobin Disorder Diagnosis
Sickle cell disease and beta thalassemia are hemoglobin disorders that often require referral to specialized laboratories for definitive diagnosis, delaying results for patients and clinicians.... Read more
New Guidelines Aim to Improve AL Amyloidosis Diagnosis
Light chain (AL) amyloidosis is a rare, life-threatening bone marrow disorder in which abnormal amyloid proteins accumulate in organs. Approximately 3,260 people in the United States are diagnosed... Read moreImmunology
view channel
New Biomarker Predicts Chemotherapy Response in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
Triple-negative breast cancer is an aggressive form of breast cancer in which patients often show widely varying responses to chemotherapy. Predicting who will benefit from treatment remains challenging,... Read moreBlood Test Identifies Lung Cancer Patients Who Can Benefit from Immunotherapy Drug
Small cell lung cancer (SCLC) is an aggressive disease with limited treatment options, and even newly approved immunotherapies do not benefit all patients. While immunotherapy can extend survival for some,... Read more
Whole-Genome Sequencing Approach Identifies Cancer Patients Benefitting From PARP-Inhibitor Treatment
Targeted cancer therapies such as PARP inhibitors can be highly effective, but only for patients whose tumors carry specific DNA repair defects. Identifying these patients accurately remains challenging,... Read more
Ultrasensitive Liquid Biopsy Demonstrates Efficacy in Predicting Immunotherapy Response
Immunotherapy has transformed cancer treatment, but only a small proportion of patients experience lasting benefit, with response rates often remaining between 10% and 20%. Clinicians currently lack reliable... Read morePathology
view channel
Molecular Imaging to Reduce Need for Melanoma Biopsies
Melanoma is the deadliest form of skin cancer and accounts for the vast majority of skin cancer-related deaths. Because early melanomas can closely resemble benign moles, clinicians often rely on visual... Read more
Urine Specimen Collection System Improves Diagnostic Accuracy and Efficiency
Urine testing is a critical, non-invasive diagnostic tool used to detect conditions such as pregnancy, urinary tract infections, metabolic disorders, cancer, and kidney disease. However, contaminated or... Read moreTechnology
view channel
Blood Test “Clocks” Predict Start of Alzheimer’s Symptoms
More than 7 million Americans live with Alzheimer’s disease, and related health and long-term care costs are projected to reach nearly USD 400 billion in 2025. The disease has no cure, and symptoms often... Read more
AI-Powered Biomarker Predicts Liver Cancer Risk
Liver cancer, or hepatocellular carcinoma, causes more than 800,000 deaths worldwide each year and often goes undetected until late stages. Even after treatment, recurrence rates reach 70% to 80%, contributing... Read more
Robotic Technology Unveiled for Automated Diagnostic Blood Draws
Routine diagnostic blood collection is a high‑volume task that can strain staffing and introduce human‑dependent variability, with downstream implications for sample quality and patient experience.... Read more
ADLM Launches First-of-Its-Kind Data Science Program for Laboratory Medicine Professionals
Clinical laboratories generate billions of test results each year, creating a treasure trove of data with the potential to support more personalized testing, improve operational efficiency, and enhance patient care.... Read moreIndustry
view channel
Cepheid Joins CDC Initiative to Strengthen U.S. Pandemic Testing Preparednesss
Cepheid (Sunnyvale, CA, USA) has been selected by the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) as one of four national collaborators in a federal initiative to speed rapid diagnostic technologies... Read more
QuidelOrtho Collaborates with Lifotronic to Expand Global Immunoassay Portfolio
QuidelOrtho (San Diego, CA, USA) has entered a long-term strategic supply agreement with Lifotronic Technology (Shenzhen, China) to expand its global immunoassay portfolio and accelerate customer access... Read more


















