Novel Test May Enable Quick Reliable Detection of Sepsis
|
By LabMedica International staff writers Posted on 20 Jun 2016 |
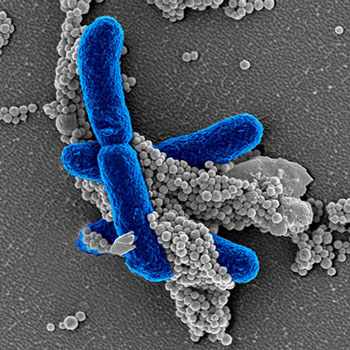
Image: In the new pathogen-detection technology, engineered FcMBL proteins coupled to magnetic beads (grey) specifically bind to carbohydrate molecules on the surface of pathogens, like infectious E. coli (blue) in this electron micrograph, or on fragments of dead pathogens circulating in the bloodstream. After isolation in a magnetic field, the total pathogenic material is quantified with a second FcMBL protein linked to a color-producing enzyme (Photo courtesy of Wyss Institute at Harvard University).
Researchers have developed a rapid specific diagnostic assay that could help physicians decide within an hour whether a patient has a systemic infection. Its potential to detect pathogen materials was demonstrated in animal studies and a prospective human clinical study, whose results also suggested that it could also serve as a companion diagnostic to monitor antibiotic and dialysis-like sepsis therapies.
The current standard-of-care for detecting blood-borne infections is blood culture, but this takes days, only identifies pathogens in less than 30% of patients with fulminant infections, and is not able to detect toxic fragments of dead pathogens that also drive the exaggerated inflammatory reactions leading to sepsis. Biomarkers that report elevated inflammation are used to monitor treatment of patients with sepsis, but they fail to distinguish inflammation triggered by infectious pathogens from that induced by non-infectious causes (e.g. burns, traumas, surgeries).
The assay was developed and tested by a research team from Wyss Institute for Biologically Inspired Engineering at Harvard University (Boston, MA, USA) led by Donald Ingber, MD, PhD, Wyss Institute’s founding director, and professor at Harvard Medical School and Boston Children’s Hospital: "Our pathogen detection technology solves both dilemmas: it quickly reports whether infectious pathogens are present in the body, even at early stages of infection before sepsis develops; And it can more specifically identify patients who have excessive inflammation due to systemic infection, rather than other causes," said Prof. Ingber, "This assay could become a real game changer in this clinical area, and it also should lead to more judicious use of antibiotics."
"In a cohort of emergency room patients with suspected sepsis, we saw that the assay picked up infection within an hour in 85% of patients who exhibited clinical symptoms of sepsis, and equally importantly it did not falsely predict infection in healthy subjects or patients with inflammation triggered by other causes, such as trauma. On the other hand, blood cultures that we performed in parallel using the same samples only detected pathogens in 18% of the cases," said Nathan Shapiro, MD, PhD, director, Translational Research, Center for Vascular Biology Research at BIDMC, who worked with the team.
The assay technology is based on magnetic beads to FcMBL, a genetically engineered pathogen-binding protein previously developed by Prof. Ingber and Michael Super, a Wyss senior staff scientist who co-leads the pathogen-detection effort. By recognizing surface carbohydrate molecules, FcMBL binds to pathogens and pathogen-released fragments – pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs). The team previously established FcMBL as a key component of an advanced dialysis-like, pathogen-extracting therapeutic device, and of a method for fast retrieval of infectious pathogens from complex clinical samples to enable identification and antibody susceptibilities.
"In our latest work, we show that the FcMBL-based pathogen-detecting assay is considerably faster and more accurate than any other available assay for systemic infection. We are currently working to ready it for high-throughput use in clinical and point-of-care situations," said co-lead-author Mark Cartwright, PhD, staff scientist at Wyss.
As a prerequisite to their clinical study, the team had successfully tested the assay in rat and pig models infected with pathogenic E. coli. "The animal models clearly told us that the assay can sensitively trace spikes of PAMPs released during antibiotic therapy, or residual infectious PAMP materials, even when no living bacteria circulate anymore in blood but they remain hidden inside internal organs. Thus, this assay could be an excellent tool for monitoring ongoing infection and responses to antibiotics and dialysis-like therapies for severe infections and sepsis," said Mike Super, PhD.
The findings suggest that this technology, with its rapid handling time, high sensitivity and broad specificity, could provide a real advance for diagnosing infections in clinical microbiology laboratories and point-of-care settings.
The study, by Cartwright M et al, was published online June 12, 2016, in the journal eBioMedicine.
Related Links:
Wyss Institute
The current standard-of-care for detecting blood-borne infections is blood culture, but this takes days, only identifies pathogens in less than 30% of patients with fulminant infections, and is not able to detect toxic fragments of dead pathogens that also drive the exaggerated inflammatory reactions leading to sepsis. Biomarkers that report elevated inflammation are used to monitor treatment of patients with sepsis, but they fail to distinguish inflammation triggered by infectious pathogens from that induced by non-infectious causes (e.g. burns, traumas, surgeries).
The assay was developed and tested by a research team from Wyss Institute for Biologically Inspired Engineering at Harvard University (Boston, MA, USA) led by Donald Ingber, MD, PhD, Wyss Institute’s founding director, and professor at Harvard Medical School and Boston Children’s Hospital: "Our pathogen detection technology solves both dilemmas: it quickly reports whether infectious pathogens are present in the body, even at early stages of infection before sepsis develops; And it can more specifically identify patients who have excessive inflammation due to systemic infection, rather than other causes," said Prof. Ingber, "This assay could become a real game changer in this clinical area, and it also should lead to more judicious use of antibiotics."
"In a cohort of emergency room patients with suspected sepsis, we saw that the assay picked up infection within an hour in 85% of patients who exhibited clinical symptoms of sepsis, and equally importantly it did not falsely predict infection in healthy subjects or patients with inflammation triggered by other causes, such as trauma. On the other hand, blood cultures that we performed in parallel using the same samples only detected pathogens in 18% of the cases," said Nathan Shapiro, MD, PhD, director, Translational Research, Center for Vascular Biology Research at BIDMC, who worked with the team.
The assay technology is based on magnetic beads to FcMBL, a genetically engineered pathogen-binding protein previously developed by Prof. Ingber and Michael Super, a Wyss senior staff scientist who co-leads the pathogen-detection effort. By recognizing surface carbohydrate molecules, FcMBL binds to pathogens and pathogen-released fragments – pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs). The team previously established FcMBL as a key component of an advanced dialysis-like, pathogen-extracting therapeutic device, and of a method for fast retrieval of infectious pathogens from complex clinical samples to enable identification and antibody susceptibilities.
"In our latest work, we show that the FcMBL-based pathogen-detecting assay is considerably faster and more accurate than any other available assay for systemic infection. We are currently working to ready it for high-throughput use in clinical and point-of-care situations," said co-lead-author Mark Cartwright, PhD, staff scientist at Wyss.
As a prerequisite to their clinical study, the team had successfully tested the assay in rat and pig models infected with pathogenic E. coli. "The animal models clearly told us that the assay can sensitively trace spikes of PAMPs released during antibiotic therapy, or residual infectious PAMP materials, even when no living bacteria circulate anymore in blood but they remain hidden inside internal organs. Thus, this assay could be an excellent tool for monitoring ongoing infection and responses to antibiotics and dialysis-like therapies for severe infections and sepsis," said Mike Super, PhD.
The findings suggest that this technology, with its rapid handling time, high sensitivity and broad specificity, could provide a real advance for diagnosing infections in clinical microbiology laboratories and point-of-care settings.
The study, by Cartwright M et al, was published online June 12, 2016, in the journal eBioMedicine.
Related Links:
Wyss Institute
Latest Microbiology News
- Hidden Gut Viruses Linked to Colorectal Cancer Risk
- Three-Test Panel Launched for Detection of Liver Fluke Infections
- Rapid Test Promises Faster Answers for Drug-Resistant Infections
- CRISPR-Based Technology Neutralizes Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria
- Comprehensive Review Identifies Gut Microbiome Signatures Associated With Alzheimer’s Disease
- AI-Powered Platform Enables Rapid Detection of Drug-Resistant C. Auris Pathogens
- New Test Measures How Effectively Antibiotics Kill Bacteria
- New Antimicrobial Stewardship Standards for TB Care to Optimize Diagnostics
- New UTI Diagnosis Method Delivers Antibiotic Resistance Results 24 Hours Earlier
- Breakthroughs in Microbial Analysis to Enhance Disease Prediction
- Blood-Based Diagnostic Method Could Identify Pediatric LRTIs
- Rapid Diagnostic Test Matches Gold Standard for Sepsis Detection
- Rapid POC Tuberculosis Test Provides Results Within 15 Minutes
- Rapid Assay Identifies Bloodstream Infection Pathogens Directly from Patient Samples
- Blood-Based Molecular Signatures to Enable Rapid EPTB Diagnosis
- 15-Minute Blood Test Diagnoses Life-Threatening Infections in Children
Channels
Clinical Chemistry
view channelNew Blood Test Index Offers Earlier Detection of Liver Scarring
Metabolic fatty liver disease is highly prevalent and often silent, yet it can progress to fibrosis, cirrhosis, and liver failure. Current first-line blood test scores frequently return indeterminate results,... Read more
Electronic Nose Smells Early Signs of Ovarian Cancer in Blood
Ovarian cancer is often diagnosed at a late stage because its symptoms are vague and resemble those of more common conditions. Unlike breast cancer, there is currently no reliable screening method, and... Read moreMolecular Diagnostics
view channel
Ultra-Sensitive DNA Test Identifies Relapse Risk in Aggressive Leukemia
Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is a rare but aggressive blood cancer in which relapse after allogeneic stem cell transplant remains a major clinical challenge, particularly for patients with NPM1-mutated disease.... Read more
Blood Test Could Help Detect Gallbladder Cancer Earlier
Gallbladder cancer is one of the deadliest gastrointestinal cancers because it is often diagnosed at an advanced stage when treatment options are limited. Early symptoms are minimal, and current screening... Read moreHematology
view channel
Rapid Cartridge-Based Test Aims to Expand Access to Hemoglobin Disorder Diagnosis
Sickle cell disease and beta thalassemia are hemoglobin disorders that often require referral to specialized laboratories for definitive diagnosis, delaying results for patients and clinicians.... Read more
New Guidelines Aim to Improve AL Amyloidosis Diagnosis
Light chain (AL) amyloidosis is a rare, life-threatening bone marrow disorder in which abnormal amyloid proteins accumulate in organs. Approximately 3,260 people in the United States are diagnosed... Read moreImmunology
view channel
New Biomarker Predicts Chemotherapy Response in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
Triple-negative breast cancer is an aggressive form of breast cancer in which patients often show widely varying responses to chemotherapy. Predicting who will benefit from treatment remains challenging,... Read moreBlood Test Identifies Lung Cancer Patients Who Can Benefit from Immunotherapy Drug
Small cell lung cancer (SCLC) is an aggressive disease with limited treatment options, and even newly approved immunotherapies do not benefit all patients. While immunotherapy can extend survival for some,... Read more
Whole-Genome Sequencing Approach Identifies Cancer Patients Benefitting From PARP-Inhibitor Treatment
Targeted cancer therapies such as PARP inhibitors can be highly effective, but only for patients whose tumors carry specific DNA repair defects. Identifying these patients accurately remains challenging,... Read more
Ultrasensitive Liquid Biopsy Demonstrates Efficacy in Predicting Immunotherapy Response
Immunotherapy has transformed cancer treatment, but only a small proportion of patients experience lasting benefit, with response rates often remaining between 10% and 20%. Clinicians currently lack reliable... Read morePathology
view channel
Molecular Imaging to Reduce Need for Melanoma Biopsies
Melanoma is the deadliest form of skin cancer and accounts for the vast majority of skin cancer-related deaths. Because early melanomas can closely resemble benign moles, clinicians often rely on visual... Read more
Urine Specimen Collection System Improves Diagnostic Accuracy and Efficiency
Urine testing is a critical, non-invasive diagnostic tool used to detect conditions such as pregnancy, urinary tract infections, metabolic disorders, cancer, and kidney disease. However, contaminated or... Read moreTechnology
view channel
Blood Test “Clocks” Predict Start of Alzheimer’s Symptoms
More than 7 million Americans live with Alzheimer’s disease, and related health and long-term care costs are projected to reach nearly USD 400 billion in 2025. The disease has no cure, and symptoms often... Read more
AI-Powered Biomarker Predicts Liver Cancer Risk
Liver cancer, or hepatocellular carcinoma, causes more than 800,000 deaths worldwide each year and often goes undetected until late stages. Even after treatment, recurrence rates reach 70% to 80%, contributing... Read more
Robotic Technology Unveiled for Automated Diagnostic Blood Draws
Routine diagnostic blood collection is a high‑volume task that can strain staffing and introduce human‑dependent variability, with downstream implications for sample quality and patient experience.... Read more
ADLM Launches First-of-Its-Kind Data Science Program for Laboratory Medicine Professionals
Clinical laboratories generate billions of test results each year, creating a treasure trove of data with the potential to support more personalized testing, improve operational efficiency, and enhance patient care.... Read moreIndustry
view channel
Cepheid Joins CDC Initiative to Strengthen U.S. Pandemic Testing Preparednesss
Cepheid (Sunnyvale, CA, USA) has been selected by the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) as one of four national collaborators in a federal initiative to speed rapid diagnostic technologies... Read more
QuidelOrtho Collaborates with Lifotronic to Expand Global Immunoassay Portfolio
QuidelOrtho (San Diego, CA, USA) has entered a long-term strategic supply agreement with Lifotronic Technology (Shenzhen, China) to expand its global immunoassay portfolio and accelerate customer access... Read more


















