Genetic Locus Linked to Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy in Type II Diabetes
By LabMedica International staff writers
Posted on 24 Jun 2019
Results of a genome-wide association study (GWAS) have identified a genetic locus linked to the development of diabetic peripheral neuropathy (DPN) by individuals suffering from type II diabetes.Posted on 24 Jun 2019
DPN, which is a serious complication of diabetes, causes pain or numbness in the legs and an increased risk of foot ulcers. While genetic factors have been postulated to be involved in the etiology of DPN, their identity remains mostly unknown.
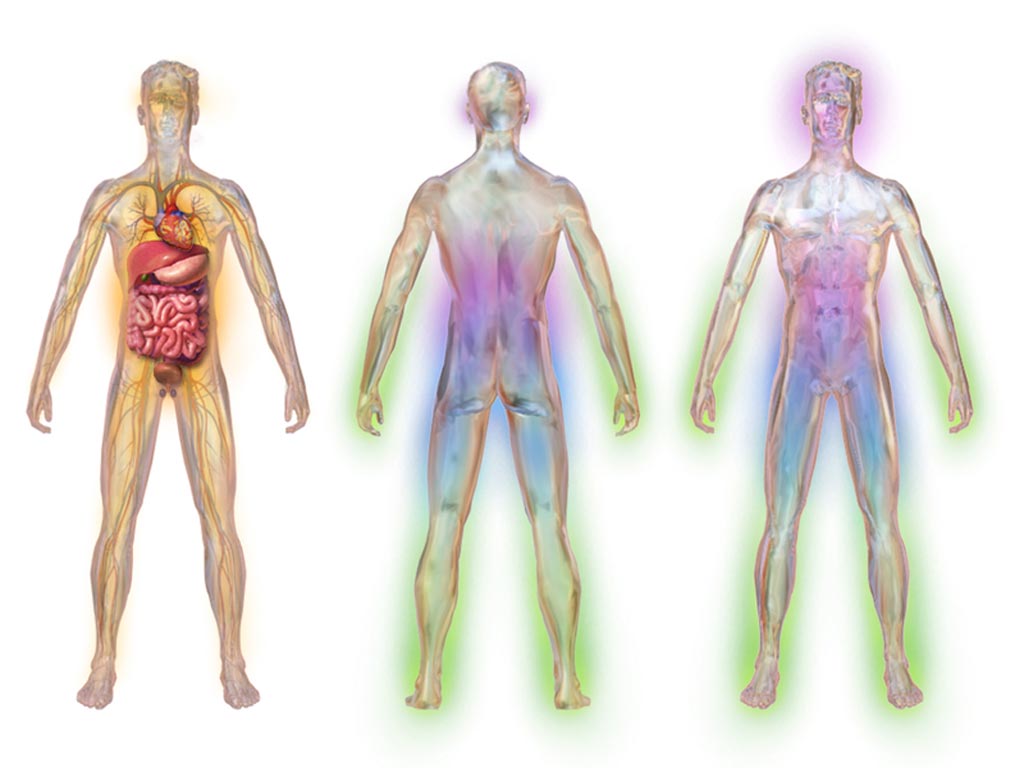
Image: An illustration depicting areas affected by diabetic peripheral neuropathy (DNP) (Photo courtesy of Wikimedia Commons).
To increase understanding of this genetic link, investigators at Harvard Medical School (Boston, MA, USA) conducted a systematic search for genetic variants influencing DPN risk using two well-characterized cohorts. Thus, a GWAS testing 6.8 million SNPs (single nucleotide polymorphisms) was carried out among participants of the ACCORD (Action to Control Cardiovascular Risk in Diabetes) clinical trial. Included were 4,384 cases with type II diabetes (TIID) and prevalent or incident DPN and 784 controls with TIID and no evidence of DPN at baseline or during follow-up. Replication of significant loci was sought among subjects with TIID (791 DPN-positive cases and 158 DPN-negative controls) from the BARI 2D (Bypass Angioplasty Revascularization Investigation 2 Diabetes) trial.
Results revealed a region on chromosome 2q24 showing a strong influence on the risk of developing DPN in type II diabetes. While the precise mechanisms remain to be elucidated, there were indications that genetic variants in this region may affect a sodium channel, which regulates the transmission of sensory signals in peripheral nerves.
"People carrying the less frequent variant at that location were protected from neuropathy and people carrying the more common variant at that same location were predisposed to this complication," said senior author Dr. Allesandro Doria, professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School. "We found that people with the protective allele have higher amounts of this sodium channel. This suggests that the sodium channel in the peripheral nerves might be used to protect people from neuropathy, by developing a drug that activates this channel."
Results of the DPN GWAS were published in the May 24, 2019, online edition of the journal Diabetes.
Related Links:
Harvard Medical School