Large GWAS Pinpoints Ovarian Cancer Risk Genes
By LabMedica International staff writers
Posted on 13 May 2019
Results of a large genome-wide association study identified 34 genes that are associated with an increased risk for developing the earliest stages of ovarian cancer.Posted on 13 May 2019
The current study, which was carried out by investigators at the University of California, Los Angeles (USA) and the Dana-Farber Cancer Institute (Boston, MA, USA), continued the assessment of large-scale genetic data that had been gathered over a period of more than 10 years by the Ovarian Cancer Association Consortium. Those investigators had found more than 30 regions in the genome associated with ovarian cancer after having compared the genetic profiles of about 25,000 women with ovarian cancer and 45,000 control subjects.
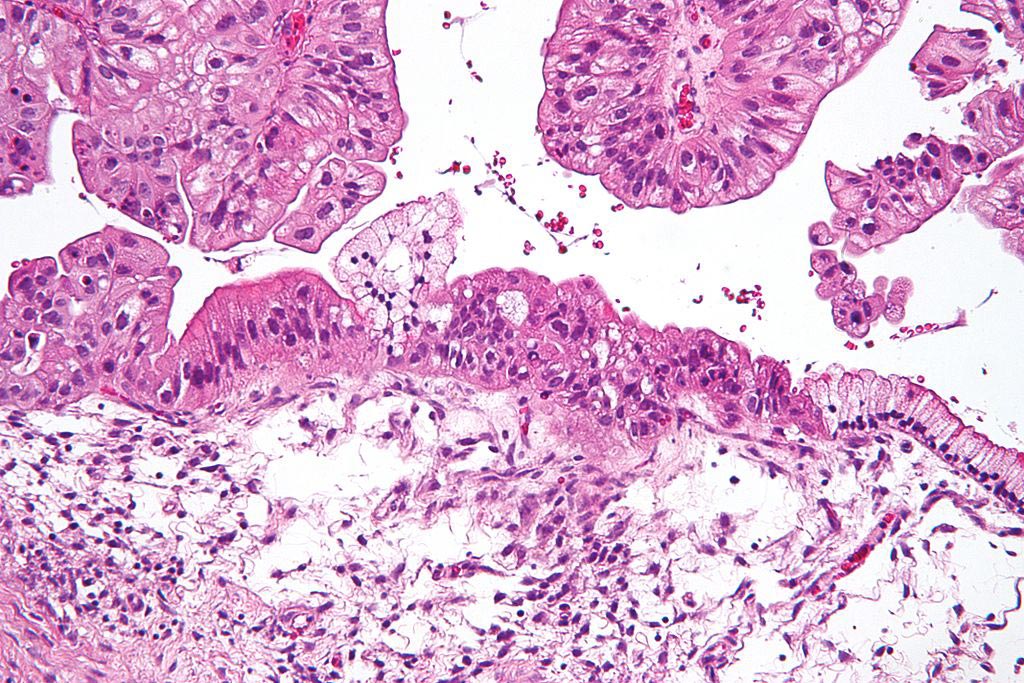
Image: A micrograph of a mucinous ovarian carcinoma (Photo courtesy of Wikimedia Commons).
Applying advanced analytical tools, the current team of investigators identified 34 genes that were associated with an increased risk for developing ovarian cancer. Furthermore, this study implicated at least one target gene for six out of 13 distinct genome-wide association study regions and pinpointed 23 new candidate susceptibility genes for high-grade serous ovarian cancer.
"If you detect ovarian cancer really early, then the survival rate is very high, nearly 90% percent," said contributing author Dr. Bogdan Pasaniuc, associate professor of pathology and laboratory medicine at the University of California, Los Angles. "But that does not happen often. Most cases are found at a later stage and survival drops dramatically. That is why we want to understand the genetics behind it - so we can do a better job at predicting who is at a higher risk of developing this cancer."
"Whenever you inherit a piece of DNA from your parents, you do not inherit just every base pair of the genome, you inherit big chunks," said Dr. Pasanuic. "That means that if you inherit a gene mutation in a given region, you inherit the entire region, which can carry 10 to 20 genes at a time. This makes it very hard to pinpoint specific genes from specific regions. With the identification of these genes, we now have a narrow list of genes that can help us better predict ovarian cancer risks in women who may have never known that they were at a higher risk for developing the disease. While we are not there yet, we are hoping this study will lead to better outcomes because we will be able to monitor women earlier, when the cancer is easier to treat."
The ovarian cancer study was published in the May 1, 2019, online edition of the journal Nature Genetics.
Related Links:
University of California, Los Angeles
Dana-Farber Cancer Institute









 Analyzer.jpg)