Novel Fluidic Nanodevices Created by Liquid 3D Printing
By LabMedica International staff writers
Posted on 08 May 2019
Researchers have used a novel three-dimensional (3D) printing technique to create an all-liquid fluidic device that is capable performing a wide range of applications - from making battery materials to screening drug candidates.Posted on 08 May 2019
Systems comprised of immiscible liquids held in non-equilibrium shapes by the interfacial assembly and jamming of nanoparticle-polymer surfactants have significant potential to advance catalysis, chemical separations, energy storage, and conversion. However, directing spatial functionality within them and coupling processes in both phases has remained a challenge.
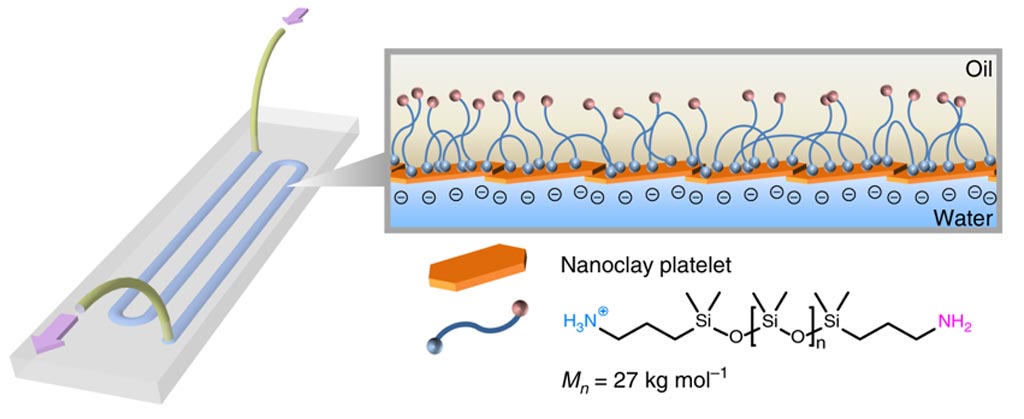
Image: The assembly of a three-dimensional printable fluidic device: When two liquids - one containing nanoscale clay particles and the other containing polymer particles - are printed onto the substrate, they come together at the interface of the two liquids and within milliseconds form a very thin channel or tube about one millimeter in diameter (Photo courtesy of the Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory).
Investigators at Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (CA, USA) exploited nanoclay-polymer surfactant assemblies at an oil-water interface to produce a semi-permeable membrane between the liquids. Flow channels were fabricated using micropatterned two-dimensional (2D) substrates and liquid-in-liquid three-dimensional printing. The anionic walls of the device were functionalized with cationic small molecules, enzymes, and colloidal nanocrystal catalysts. Three-dimensional printing was used to build bridges between channels, connecting them so that a chemical flowing through them encountered catalysts in a specific order, setting off a cascade of chemical reactions to make specific chemical compounds.
The investigators reported in the March 6, 2019, online edition of the journal Nature Communications that multi-step chemical transformations could be conducted within the channels under flow, as could selective mass transport across the liquid-liquid interface for in-line separations. Ultimately, these all-liquid systems were automated using pumps, detectors, and control systems, revealing a latent ability for chemical logic and learning.
"What we demonstrated is remarkable. Our three-dimensional printed device can be programmed to carry out multistep, complex chemical reactions on demand," said senior author Dr. Brett Helms, staff scientist at Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory. "What is even more amazing is that this versatile platform can be reconfigured to efficiently and precisely combine molecules to form very specific products, such as organic battery materials. The form and functions of these devices are only limited by the imagination of the researcher. Autonomous synthesis is an emerging area of interest in the chemistry and materials communities, and our technique for three-dimensional printing devices for all-liquid flow chemistry could help to play an important role in establishing the field."
Related Links:
Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory