Anti-Cancer Treatment Targets Activated Platelets in Tumor Microenvironment
By LabMedica International staff writers
Posted on 19 Feb 2019
A novel chemotherapeutic agent transport system is based on the binding of an antibody-drug conjugate specifically directed to a surface protein on activated platelets in the tumor microenvironment.Posted on 19 Feb 2019
Based on the premise that platelets in the blood are being increasingly recognized as mediators of tumor growth and metastasis, investigators at the Baker Heart and Diabetes Institute (Melbourne, Australia) hypothesized that activated platelets in the tumor microenvironment could provide a targeting epitope for tumor-directed chemotherapy.
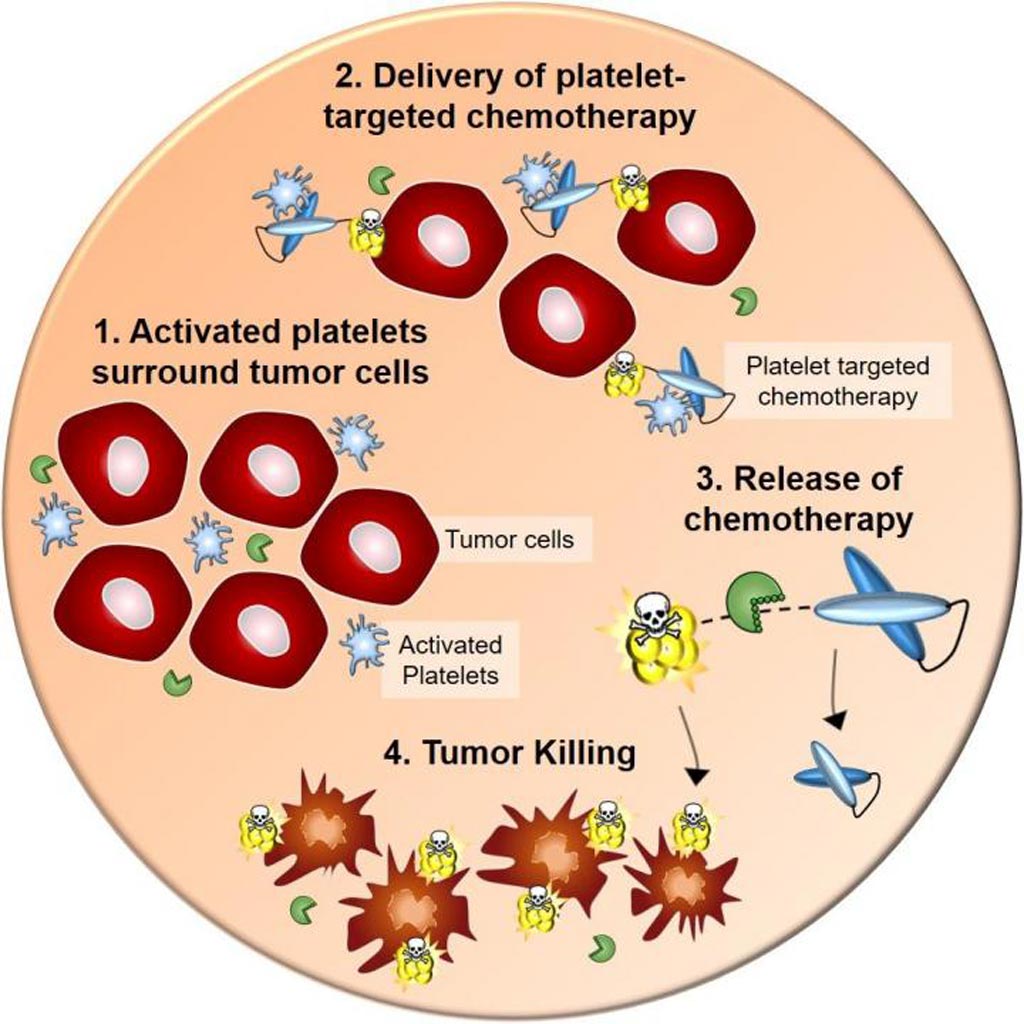
Image: The diagram illustrates the path of action of a new imaging and platelet targeting chemotherapy agent for the early detection and treatment of cancers (Photo courtesy of the Baker Heart and Diabetes Institute).
Toward this end, the investigators developed an antibody-drug conjugate (ADC), comprised of a single-chain antibody (scFv) against the platelet integrin GPIIb/IIIa (scFvGPIIb/IIIa) protein that was linked to the potent chemotherapeutic microtubule inhibitor, monomethyl auristatin E (MMAE). The targeting scFv selectively bound to an epitope that wass hidden on the low-affinity GPIIb/IIIa of circulating platelets but became exposed on the high affinity GPIIb/IIIa, which was expressed on activated platelets.
The scFv single-chain antibody was linked chemically to the highly potent microtubule inhibitor, monomethyl auristatin E. Monomethyl auristatin E (MMAE) is an antimitotic agent which inhibits cell division by blocking the polymerization of tubulin. Because of its toxicity, it cannot be used as a drug itself; instead, it is linked to an antibody, which directs it to the cancer cells. The chemical linker used to attach the scFv to the antibody (in this study valine-citrulline) is stable in extracellular fluid, but is cleaved by the enzyme cathepsin B once the conjugate has entered a tumor cell, thus activating the antimitotic mechanism.
To demonstrate the functionality of this novel anti-cancer ADC, with its unique activated platelet targeting, the investigators first confirmed the efficacy of scFvGPIIb/IIIa-MMAE for tumor killing in human cell lines of triple negative breast cancer, colorectal cancer, fibrosarcoma, and prostate cancer. Next, they used a triple negative breast cancer metastasis model for proof of concept in vivo studies.
Results published in the February 2019 issue of the journal Theranostics revealed that treatment of mice with scFvGPIIb/IIIa-MMAE resulted in significant regression of primary tumors and prevented metastasis without systemic side effects. Furthermore, the investigators showed that scFvGPIIb/IIIa-MMAE could be conjugated with the fluorescent dye Cyanine7 for in vivo imaging and potential diagnostic use.
"This activated platelet targeted chemotherapy approach also provides the means to deliver high concentrations of chemotherapy specifically to tumor cells whilst minimizing side effects and preventing tumor growth," said senior author Dr. Karlheinz Peter, deputy director, basic and translational science at the Baker Heart and Diabetes Institute. "This highly promising and unexpected discovery with immense importance for cancer diagnosis and therapy emerged from years of research on the function of platelets in heart disease. It is a good example of the importance of funding in basic research which often produces unexpected but highly relevant discoveries that ultimately will provide benefit for patients."
Related Links:
Baker Heart and Diabetes Institute