Dysregulation of Retinoic Acid Signaling in Stem Cells Spurs Tumor Growth
By LabMedica International staff writers
Posted on 05 Nov 2018
A team of cancer researchers identified the retinoic acid molecular signaling pathway as being a factor that helps to prevent the development of colorectal cancer.Posted on 05 Nov 2018
Investigators at the Christiana Care Health System (Wilmington, DE, USA) were studying the factors controlling the differentiation of colon cancer stem cells (SCs) into undifferentiated tumor cells or, in some cases, into differentiated (non-cancerous) colon cells. Since tumor development is driven by stem cell overpopulation, and in light of earlier findings that the enzyme aldehyde dehydrogenase (ALDH) was both a marker for SCs in many tissues and a key enzyme in retinoid acid (RA) signaling, the investigators examined RA signaling in normal and malignant colonic SCs.
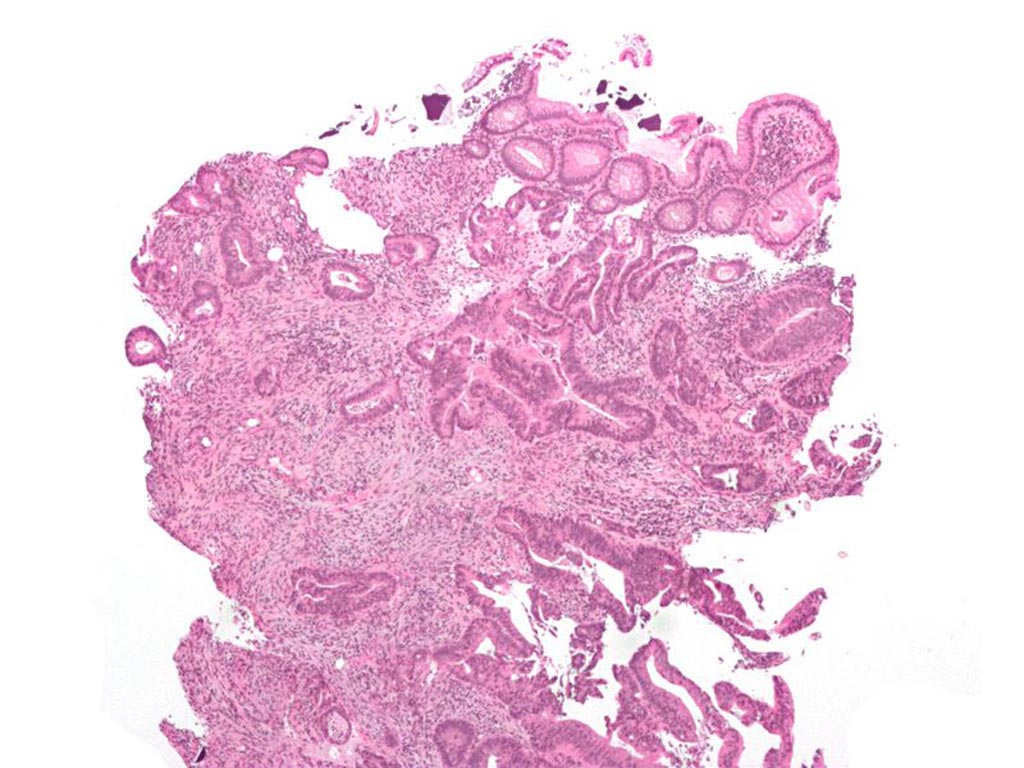
Image: Invasive adenocarcinoma (the most common type of colorectal cancer). The cancerous cells are seen in the center and at the bottom right of the image (blue). Near normal colon-lining cells are seen at the top right of the image (Photo courtesy of Wikimedia Commons).
The investigators analyzed normal and malignant colonic tissues and colorectal cancer (CRC) cell lines to see if retinoid receptors (RXR & RAR) were exclusively expressed in ALDH+ SCs, and if RA signaling changed during CRC development. Specifically, they determined whether RA signaling regulated cancer SC proliferation, differentiation, sphere formation, and population size.
Results published in the October 5, 2018, online edition of the journal Oncotarget revealed that RXR & RAR were expressed in ALDH+ colonic SCs, but not in normal cells. Western blotting/immunostaining of CRCs revealed that RA signaling components became overexpressed in parallel with ALDH overexpression, which coincided with the known overpopulation of ALDH+ SCs that occurs during, and drives, CRC development.
Treatment of SCs with all-trans retinoic acid (ATRA) was found to decrease proliferation, sphere formation, and ALDH+ SC population size and to induce differentiation. Thus, dysregulation of RA signaling in colonic SCs likely contributed to overpopulation of ALDH+ SCs and CRC growth.
“Our findings point to a number of possibilities for developing more effective stem cell targeting therapies for advanced colorectal cancer,” said senior author Dr. Bruce Boman, a senior research scientist at the Christiana Care Health System. “Our thinking has shifted to the insight that cancers originate in tissue stem cells through dysregulation or malfunction of the self-renewal process, and that cancer stem cells drive tumor growth. It follows that the optimal way to treat cancer (especially advanced cancer) is to eliminate cancer stem cells. We discovered that the retinoic acid or RA signaling pathway acts to induce differentiation of colon cancer stem cells and reduce cancer stem cell overpopulation, which puts the brakes on the primary mechanism that drives colon cancer development.”
Related Links:
Christiana Care Health System