Statins Slow Growth of Cancers with p53 Structural Mutations
By LabMedica International staff writers
Posted on 09 Feb 2017
Cancer researchers have demonstrated the ability of cancer-lowering statin drugs to slow the growth of certain types of cancers with p53 mutations.Posted on 09 Feb 2017
Most cancers fail to propagate unless the p53 gene is inactivated through mutation, or if the p53 protein becomes inactivated. Investigators at the University of Kansas Medical Center looked for chemical compounds that could inhibit the activity of structurally mutated p53 proteins that can accelerate cancer progression, while not harming proteins produced by healthy p53 genes.
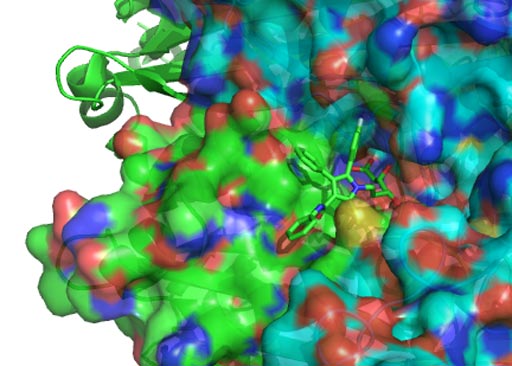
Image: Atorvastatin bound to HMG-CoA reductase (Photo courtesy of Wikimedia Commons).
Toward this end, the investigators screened nearly 9,000 compounds - including 2,400 that were [U.S.] Food and Drug Administration-approved drugs – to identify any that might degrade mutant p53.
The investigators reported in the November 2016 issue of Nature Cell Biology that statins, cholesterol-lowering drugs such as Lipitor (atorvastatin), Crestor (rosuvastatin) and Mevacor (lovastatin), were degradation inducers for conformational or misfolded p53 mutants with minimal effects on wild-type p53 (wtp53) and DNA contact mutants. The statins impacted only structurally mutated (misfolded) p53, as opposed to p53 mutated at the site of DNA binding.
Statins act by competitively inhibiting the enzyme HMG-CoA reductase, the first committed enzyme of the mevalonate pathway. Because statins are similar in structure to HMG-CoA on a molecular level, they fit into the enzyme's active site and compete with the native substrate (HMG-CoA). This competition reduces the rate by which HMG-CoA reductase is able to produce mevalonate, the next molecule in the cascade that eventually produces cholesterol. By inhibiting HMG-CoA reductase, statins block the pathway for synthesizing cholesterol in the liver.
In the current study, the investigators found that specific reduction of mevalonate-5-phosphate by statins induced CHIP (C terminus of HSC70-Interacting Protein) ubiquitin ligase-mediated nuclear export, ubiquitylation, and degradation of mutated p53 by impairing interaction of this protein with DNAJA1 (DNAJ heat shock protein family (Hsp40) member A1). DNAJA1 a member of the DNAJ family of proteins, which act as heat shock protein 70 co-chaperones. Heat shock proteins facilitate protein folding, trafficking, prevention of aggregation, and proteolytic degradation. Members of this family are characterized by a highly conserved N-terminal J domain, which mediates the interaction with heat shock protein 70 to recruit substrates and regulate ATP hydrolysis activity. Knockdown of DNAJA1 induced CHIP-mediated mutated p53 degradation, while its overexpression prevented statin-induced degradation of this protein.
In a study in which mice carrying human tumors expressing mutant p53, were treated with high doses of statins for 21 days, it was found that the tumors grew poorly in mice treated with statins compared to the controls, and that the statins worked only on structurally mutated p53, as opposed to p53 mutated at the site of DNA binding.
"We found that only the structural mutation is affected," said senior author Dr. Tomoo Iwakuma, associate professor of cancer biology at the University of Kansas Medical Center. "Which explains why clinical studies with statins were inconclusive. Mutant p53 makes human cancer cells more metastatic and resistant to chemotherapy. That is a primary reason to get rid of it -- to improve survival in cancer patients."













