Loss of MicroRNA Induces Pro-Metastatic Changes in Pancreatic Cancer Cells
By LabMedica International staff writers
Posted on 14 Jun 2016
Reduced activity of a specific microRNA (miRNA) is apparent in chronically inflamed pancreatic tissue and in early stages of pancreatic cancer (pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma or PDAC) even before tumor formation.Posted on 14 Jun 2016
PDAC is characterized by very early metastasis, which has led some researchers to postulate that metastasis-associated changes may occur prior to actual tumor formation. To confirm this hypothesis investigators at the German Cancer Research Center (Heidelberg, Germany) analyzed levels of miRNAs known to be linked to PDAC.
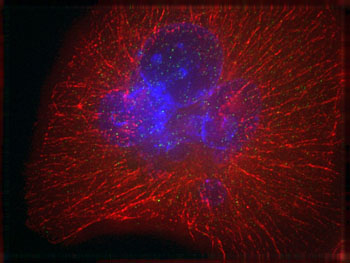
Image: A pancreatic cancer cell. The nucleus is stained blue, while the fibers of the cytoskeleton are labelled with a red fluorescent dye (Photo courtesy of Dr. Nathalie Giese, Chirurgische Universitätsklinik Heidelberg, Germany).
MicroRNAs are a class of about 20 nucleotides-long RNA fragments that block gene expression by attaching to molecules of messenger RNA in a fashion that prevents them from transmitting the protein synthesizing instructions they had received from the DNA. With their capacity to fine-tune protein expression via sequence-specific interactions, miRNAs help regulate cell maintenance and differentiation.
The investigators reported in the May 23, 2016, online edition of the journal Cancer Research that they had identified the microRNA miR-192 as an epigenetically regulated suppressor gene with predictive value in PDAC. Levels of miR-192 were downregulated by promoter methylation in both PDAC and chronic pancreatitis (CP), a risk factor that leads to a 15-fold increase in the likelihood of contracting pancreatic cancer.
Functional studies in vitro and in mouse models of PDAC showed that overexpression of miR-192 was sufficient to reduce cell proliferation and invasion. Mechanistic analyses correlated changes in miR-192 promoter methylation and expression with epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT).
Cell proliferation and invasion were linked to altered expression of the miR-192 target gene SERPINE1, which encodes the protein plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 (PAI-1), an established regulator of these properties in PDAC cells. These results suggested that miR-192 downregulation established an invasive capacity in these pancreatic cells even before they transformed into cancer cells.
"We think that the cells often already have metastatic capacity before even transforming into cancer cells," said senior author Dr. Jörg Hoheisel, head of the division of functional genome analysis at the German Cancer Research Center. "To check this hypothesis, we searched the tumor cells for molecular changes that are indicative of the tendency to spread early. Our interpretation of these results is that epigenetic changes that occur already in inflamed pancreatic tissue lead to reduced production of miR-192. This means that the cells acquire the capacity of invasion and metastasis, which initially has no consequences. The actual transformation into cancer cells is caused by other, unrelated factors and can occur later. The result is cancer cells that are capable, from the very start, to invade surrounding tissue and spread metastases."
Related Links:
German Cancer Research Center













