Cardiomyopathy Linked to Faulty Regulation of Heart Protein Succinylation
By LabMedica International staff writers
Posted on 28 Apr 2016
The enzyme SIRT5, also known as sirtuin (silent mating type information regulation 2 homolog) 5, was found to play a critical role in maintaining healthy cardiac function by regulating the lysine succinylation modification of heart cell proteins.Posted on 28 Apr 2016
Lysine succinylation is a recently discovered protein posttranslational modification (PTM), and SIRT5 is an efficient desuccinylase enzyme. Although many mammalian proteins have been found to be regulated by lysine succinylation and SIRT5, the physiological significance of succinylation and SIRT5 remains unknown.
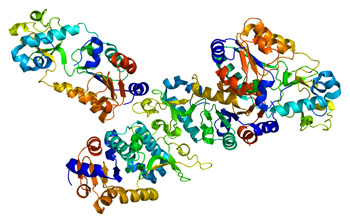
Image: A model of the structure of the SIRT5 protein (Photo courtesy of Wikimedia Commons).
To better understand the consequences of protein succinylation, investigators at Cornell University (Ithaca, NY, USA) and their colleagues at Ecole Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne (Switzerland) profiled acyl-CoA molecules in various mouse tissues. They discovered that different tissues had different acyl-CoA profiles and that succinyl-CoA was the most abundant acyl-CoA molecule in the heart. This observation prompted them to examine protein lysine succinylation in different mouse tissues in the presence and absence of SIRT5.
The investigators reported in the April 5, 2016, online edition of the journal Proceedings of the [U.S.] National Academy of Sciences that protein lysine succinylation predominantly accumulated in the heart in mice that had been genetically engineered to lack the gene for Sirt5. Using proteomic studies, they were able to identify many cardiac proteins regulated by SIRT5.
In particular, they found that ECHA (also known as HADHA or hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase/3-ketoacyl-CoA thiolase/enoyl-CoA hydratase (trifunctional protein), alpha subunit), a protein involved in fatty acid oxidation, was a major enzyme that was regulated by SIRT5 and affected heart function. Sirt5 knockout (KO) mice had lower ECHA activity, increased long-chain acyl-CoAs, and decreased ATP in the heart under fasting conditions. On the physiological level, it was found that Sirt5 KO mice developed hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, as evident from the increased heart weight relative to body weight in these animals.
"Our research suggests that perhaps one way to improve heart function is to find a way to improve SIRT5 activity," said senior author Dr. Hening Lin, professor of chemistry and chemical biology at Cornell University.
"The identification of this new role of SIRT5 in cardiomyopathy assigns an important role of this druggable enzyme in one of the major cardiac diseases," said contributing author Dr. Johan Auwerx, professor of energy metabolism at the Ecole Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne. "It can be expected that pharmacological interference with these pathways will lead to new therapies for cardiomyopathy that, as such, can extend healthy life span."
Related Links:
Cornell University
Ecole Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne