Development of Rett Syndrome Linked to Membrane Transport Protein Deficiency
By LabMedica International staff writers
Posted on 13 Jan 2016
Neurological disease researchers have found a potential therapeutic approach for the treatment of Rett syndrome that is based on modulation of the calcium transporter protein KCC2.Posted on 13 Jan 2016
KCC2 (potassium-calcium cotransporter 2) is a neuron-specific chloride potassium symporter (membrane transport protein) responsible for establishing the chloride ion gradient in neurons through the maintenance of low intracellular chloride concentrations. It is a critical mediator of synaptic inhibition, cellular protection against excitotoxicity, and may also act as a modulator of neuroplasticity. Animals with reduced expression of this transporter exhibit severe motor deficits, epileptiform activity, and spasticity. KCC2 knockout animals, in which KCC2 is completely absent, die postnatally due to respiratory failure.
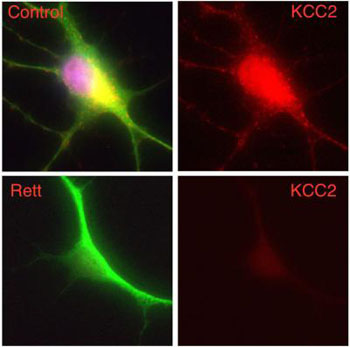
Image: A human nerve cell derived from a patient with Rett syndrome shows significantly decreased levels of KCC2 compared to a control cell (Photo courtesy of Gong Chen laboratory, Pennsylvania State University).
Investigators at Pennsylvania State University (University Park, USA) worked with cultures of neurons that had been established by inducing skin cells from Rett syndrome patients to regress to stem cells and then differentiate into neurons. Rett syndrome is a severe form of autism spectrum disorder, mainly caused by mutations of a single gene, methyl CpG binding protein 2 (MeCP2) on the X chromosome. Patients with Rett syndrome exhibit a period of normal development followed by regression of brain function and the emergence of autistic behaviors.
The investigators reported in the January 5, 2016, online edition of the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America (PNAS) that neuron-specific KCC2 was a critical downstream gene target of MeCP2. They found that human neurons differentiated from induced pluripotent stem cells from patients with Rett syndrome showed a significant deficit in KCC2 expression and consequently a delayed GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid) functional switch from excitation to inhibition. Overexpression of KCC2 in MeCP2-deficient neurons rescued GABA functional deficits, suggesting an important role of KCC2 in Rett syndrome.
As KCC2 is a slow onset molecule with expression level reaching maximum later in development, the functional deficit of KCC2 may offer an explanation for the delayed onset of Rett symptoms.
"The most exciting part of this research is that it directly uses human neurons that originated from Rett syndrome patients as a clinically-relevant disease model to investigate the underlying mechanism," said senior author Dr. Gong Chen, professor of biology at Pennsylvania State University. "Therefore, the new drug target discovered in this study might have direct clinical implication in the treatment of Rett syndrome and potentially for other autism-spectrum disorders as well."
"KCC2 controls the function of the neurotransmitter GABA at a critical time during early brain development," said Dr. Chen. "Interestingly, when we put KCC2 back into Rett neurons, the GABA function returns to normal. We therefore think that increasing KCC2 function in individuals with Rett syndrome may lead to a potential new treatment."
Related Links:
Pennsylvania State University













