New Culture Technique Will Promote the Study of Leukemic Stem Cells
By LabMedica International staff writers
Posted on 02 Apr 2014
A multidisciplinary team of cancer researchers has developed a method for maintaining leukemic stem cells (LSCs) in culture, which will aid in the study of this class of cancer cells and the development of new drugs.Posted on 02 Apr 2014
It has proven difficult to study LSCs, as currently available culture conditions do not prevent their spontaneous differentiation into full-blown acute myeloid leukemia (AML) cells. To overcome these constraints the “Leucégène” research group of investigators at the Université de Montréal (Canada) conducted a high-throughput chemical screen to identify small molecules that could inhibit differentiation and support LSC activity in vitro.
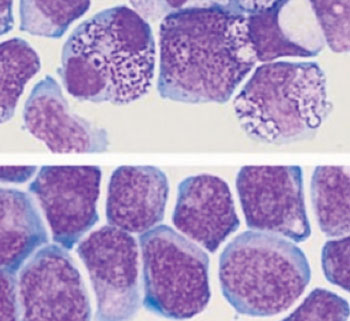
Image: Acute myeloid leukemia cells presenting anomalies in standard growth conditions (top). Acute myeloid leukemia cells preserving their leukemic cell features following in vitro culture with the two chemical molecules referred to in the study (below) (Photo courtesy of the Université de Montréal).
They reported in the February 23, 2014, online edition of the journal Nature Methods that they were able to identify two chemical compounds that, when added to the culture medium, could maintain functional human LSCs alive for at least seven days in vitro. One of the compounds suppressed the aryl-hydrocarbon receptor (AhR) pathway, which is inactive in vivo but rapidly activated ex vivo in AML cells. The other compound, UM729, collaborated with AhR suppressors in preventing AML cell differentiation.
These findings provide newly defined culture conditions for improved ex vivo culture of human LSCs and primary AML cells. “This research breakthrough demonstrates the advantage of working in a multidisciplinary team like the “Leucégène” research group,” said senior author Dr. Guy Sauvageau, professor of medicine at the Université de Montréal. “Access to cells of leukemia patients and to IRIC’s [The Institute for Research in Immunology and Cancer of the Université de Montréal] state-of-the-art facilities are also key factors in pursuing ground-breaking research.”
Related Links:
Université de Montréal













