Small Molecule TWEAK-Fn14 Inhibitors Block Cancer Growth
By LabMedica International staff writers
Posted on 21 Nov 2013
Drug developers have identified a series of small molecules that block the interaction of the cytokine TWEAK (TNF-related weak inducer of apoptosis) with its receptor Fn14 (fibroblast growth factor-inducible 14), which slows growth of brain, breast, pancreatic, esophageal, lung, and liver cancers.Posted on 21 Nov 2013
TWEAK is a cytokine protein that belongs to the tumor necrosis factor (TNF) family and is a ligand for the Fn14/TWEAKR receptor. This cytokine has overlapping signaling functions with TNF, but displays a much wider tissue distribution. TWEAK can induce apoptosis via multiple pathways of cell death in a cell type-specific manner. This cytokine is also found to promote proliferation and migration of endothelial cells, and thus acts as a regulator of angiogenesis. Overexpression of TWEAK-Fn14 activation has been linked to tissue damage and degradation, including autoimmune diseases, as well as the survival, migration, and invasion of cancer cells.
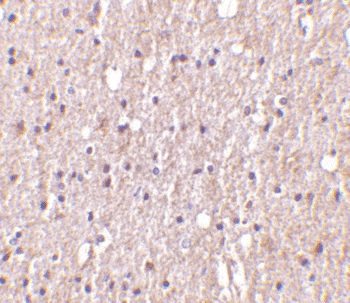
Image: Immunohistochemistry of TWEAK in human brain tissue (Photo courtesy of Sigma-Aldrich Inc.).
Investigators at the Translational Genomics Research Institute (Phoenix, AZ, USA) used computer-generated protein-protein docking models to design a targeted library of small molecules predicted to disrupt the TWEAK-Fn14 interaction.
Results published in the November 8, 2013, issue of the Journal of Biological Chemistry described a group of 129 small molecules that produced up to 37% inhibition of TWEAK-Fn14 binding. Four molecules were found to be particularly potent; including compound L524-0366, which completely suppressed TWEAK-induced brain cancer-cell migration without any potential cytotoxic effects.
"Our results show that the TWEAK-Fn14 interaction is a viable drug target, and they provide the foundation for further exploration of this system in researching invasive cancers," said co-senior author Dr. Nhan Tran, associate professor of cancer and cell biology at the Translational Genomics Research Institute. "Because of its unique qualities and association with acute injuries, this drug-like molecule not only could benefit cancer patients, but also might be applied to patients with autoimmunity, heart disease like atherosclerosis, and rheumatoid arthritis."
Related Links:
Translational Genomics Research Institute








 Analyzer.jpg)