Low Cost Point-of-Care DNA Amplification Test for Chlamydia Infection Demonstrated at the 2015 AACC Annual Meeting
|
By LabMedica International staff writers Posted on 29 Jul 2015 |
![Image: Human pap smear showing H&E stained Chlamydia in the vacuoles (500x) (Photo courtesy of the [US] National Cancer Institute). Image: Human pap smear showing H&E stained Chlamydia in the vacuoles (500x) (Photo courtesy of the [US] National Cancer Institute).](https://globetechcdn.com/mobile_labmedica/images/stories/articles/article_images/2015-07-29/GMS-250.jpg)
Image: Human pap smear showing H&E stained Chlamydia in the vacuoles (500x) (Photo courtesy of the [US] National Cancer Institute).
Researchers have demonstrated a low cost, point-of-care NAAT (nucleic acid amplification testing) platform that meshes with a smartphone application for rapid diagnosis of Chlamydia infection at the 2015 AACC Annual Meeting & Clinical Lab Expo (Atlanta, GA, USA).
Chlamydia trachomatis causes sexually transmitted genital and eye infections in humans. Chlamydia infection is one of the most common sexually transmitted infections worldwide; it is estimated that about one million individuals in the United States are infected with Chlamydia. C. trachomatis is naturally found living only inside human cells. It can be transmitted during vaginal, anal, or oral sex, and can be passed from an infected mother to her baby during childbirth. Between half and three-quarters of all women who have a chlamydial infection of the cervix have an inflamed cervix without symptoms and may not realize they are infected. In men, infection by C. trachomatis can lead to inflammation of the penile urethra causing a white discharge from the penis with or without a burning sensation during urination.
Over the past decade, the emergence of highly sensitive method NAAT-based tests has expanded screening programs for Chlamydia. However, these types of tests are too complex and expensive to perform in point-of-care settings such as physicians’ offices, health fairs, school clinics, or other sexual health outreach venues.
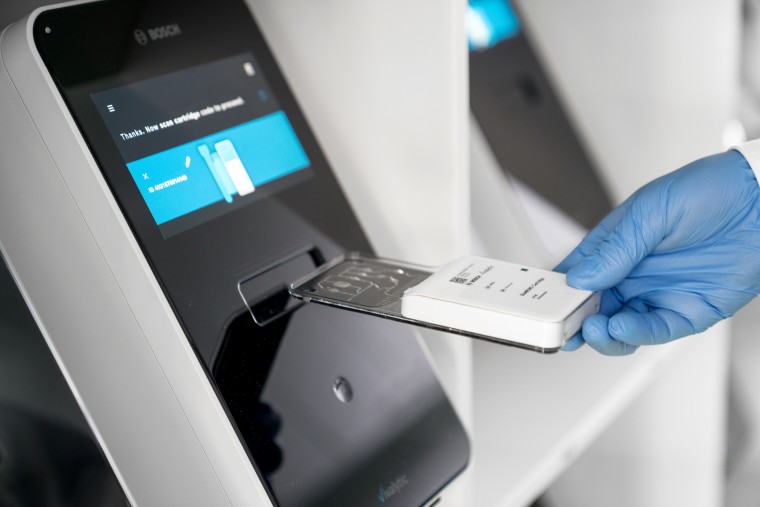
Investigators from Johns Hopkins University (Baltimore, MD, USA) have taken advantage of the Annual AACC Meeting venue to demonstrate their novel point-of-care NAAT/smartphone platform. Their coffee mug sized "mobiLab" instrument is battery powered. The device works by using a microfluidics cartridge to detect the DNA of Chlamydia bacteria in genital swab samples. The DNA analysis unit with its automated sample preparation mechanism is meshed with a smartphone, which enables the user to control the instrument and process test data through an application.
The developers of mobiLab validated the device's performance by comparing its accuracy on 20 patient samples with that of the Hologics (Bedford, MA, USA) GenProbe Aptima Combo 2 assay, the gold standard test for Chlamydia. Results indicated that both tests identified the same 10 positive and 10 negative cases, demonstrating that mobiLab could be used for Chlamydia diagnosis in place of standard NAATs.
“We now have these pretty accurate, sensitive, and specific molecular assays to detect very few numbers of organisms in biological samples,” said Dong Jin Shin, a research student in mechanical engineering at Johns Hopkins University. “But a lot of these technologies are confined to being used in centralized lab settings. If we are able to bring molecular diagnostic technology closer to the clinic and deliver accurate results to clinicians sooner, then we will be able to improve our standard of care for patients with Chlamydia while also saving costs.”
Related Links:
2015 AACC Annual Meeting & Clinical Lab Expo
Johns Hopkins University
Hologics
Chlamydia trachomatis causes sexually transmitted genital and eye infections in humans. Chlamydia infection is one of the most common sexually transmitted infections worldwide; it is estimated that about one million individuals in the United States are infected with Chlamydia. C. trachomatis is naturally found living only inside human cells. It can be transmitted during vaginal, anal, or oral sex, and can be passed from an infected mother to her baby during childbirth. Between half and three-quarters of all women who have a chlamydial infection of the cervix have an inflamed cervix without symptoms and may not realize they are infected. In men, infection by C. trachomatis can lead to inflammation of the penile urethra causing a white discharge from the penis with or without a burning sensation during urination.
Over the past decade, the emergence of highly sensitive method NAAT-based tests has expanded screening programs for Chlamydia. However, these types of tests are too complex and expensive to perform in point-of-care settings such as physicians’ offices, health fairs, school clinics, or other sexual health outreach venues.
Investigators from Johns Hopkins University (Baltimore, MD, USA) have taken advantage of the Annual AACC Meeting venue to demonstrate their novel point-of-care NAAT/smartphone platform. Their coffee mug sized "mobiLab" instrument is battery powered. The device works by using a microfluidics cartridge to detect the DNA of Chlamydia bacteria in genital swab samples. The DNA analysis unit with its automated sample preparation mechanism is meshed with a smartphone, which enables the user to control the instrument and process test data through an application.
The developers of mobiLab validated the device's performance by comparing its accuracy on 20 patient samples with that of the Hologics (Bedford, MA, USA) GenProbe Aptima Combo 2 assay, the gold standard test for Chlamydia. Results indicated that both tests identified the same 10 positive and 10 negative cases, demonstrating that mobiLab could be used for Chlamydia diagnosis in place of standard NAATs.
“We now have these pretty accurate, sensitive, and specific molecular assays to detect very few numbers of organisms in biological samples,” said Dong Jin Shin, a research student in mechanical engineering at Johns Hopkins University. “But a lot of these technologies are confined to being used in centralized lab settings. If we are able to bring molecular diagnostic technology closer to the clinic and deliver accurate results to clinicians sooner, then we will be able to improve our standard of care for patients with Chlamydia while also saving costs.”
Related Links:
2015 AACC Annual Meeting & Clinical Lab Expo
Johns Hopkins University
Hologics
Latest AACC 2015 News
- Automated Molecular Diagnostics System Presented at AACC 2015
- Portable Molecular Diagnostics System Unveiled At 2015 AACC
- Expanded Steroid Control Launched at the 2015 AACC Annual Meeting
- Innovative New Technology to Provide Plastic-Exterior Components with Glass Interior, Presented at AACC 2015
- Eco-Friendly Immunoassay Reagents Featured at AACC 2015
- Inexpensive Multipurpose Point-of-Care Analyzer Unveiled at 2015 AACC Annual Meeting
- State-of-the-Art Automated Laboratory Systems Highlighted at the 2015 AACC Annual Meeting
- Siemens Showcases Multiple New IVD Solutions at AACC 2015
- New HPLC Quadruples Clinical Throughput Capabilities, Displayed at AACC 2015
- Diagnostic Test that Measures Active Renin in Hypertension Displayed at the 2015 AACC Annual Meeting
- Hair Testing May Offer Insights into Asthma-Related Complications in Pregnancy
- Two Newly Developed Tests May Better Diabetes Diagnosis and Monitoring
- CE Marking of Theranostic Monitoring Test Announced at 2015 AACC Annual Meeting
- Ebola Rapid Lateral Flow Test Previewed at the 2015 AACC Annual Meeting
- AACC: Better Quality and Patient-Friendliness Needed in Direct Testing
- Clinical Chemistry Instruments and Reagents Under Scrutiny at the 2015 AACC Annual Meeting
Channels
Clinical Chemistry
view channel
3D Printed Point-Of-Care Mass Spectrometer Outperforms State-Of-The-Art Models
Mass spectrometry is a precise technique for identifying the chemical components of a sample and has significant potential for monitoring chronic illness health states, such as measuring hormone levels... Read more.jpg)
POC Biomedical Test Spins Water Droplet Using Sound Waves for Cancer Detection
Exosomes, tiny cellular bioparticles carrying a specific set of proteins, lipids, and genetic materials, play a crucial role in cell communication and hold promise for non-invasive diagnostics.... Read more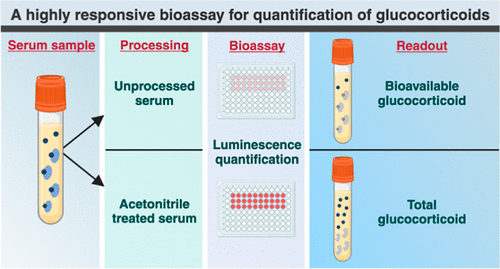
Highly Reliable Cell-Based Assay Enables Accurate Diagnosis of Endocrine Diseases
The conventional methods for measuring free cortisol, the body's stress hormone, from blood or saliva are quite demanding and require sample processing. The most common method, therefore, involves collecting... Read moreMolecular Diagnostics
view channel.jpg)
First of Its Kind NGS Assay for Precise Detection of BCR::ABL1 Fusion Gene to Enable Personalized Leukemia Treatment
The BCR::ABL1 fusion gene plays a key role in the pathogenesis of several blood cancers, particularly chronic myeloid leukemia (CML). This gene results from a chromosomal translocation that causes constitutive... Read more
Urine Test to Revolutionize Lyme Disease Testing
Lyme disease is the most common animal-to-human transmitted disease in the United States, with around 476,000 people diagnosed and treated annually, and its incidence has been increasing.... Read more
Simple Blood Test Could Enable First Quantitative Assessments for Future Cerebrovascular Disease
Cerebral small vessel disease is a common cause of stroke and cognitive decline, particularly in the elderly. Presently, assessing the risk for cerebral vascular diseases involves using a mix of diagnostic... Read more
New Genetic Testing Procedure Combined With Ultrasound Detects High Cardiovascular Risk
A key interest area in cardiovascular research today is the impact of clonal hematopoiesis on cardiovascular diseases. Clonal hematopoiesis results from mutations in hematopoietic stem cells and may lead... Read moreHematology
view channel
Next Generation Instrument Screens for Hemoglobin Disorders in Newborns
Hemoglobinopathies, the most widespread inherited conditions globally, affect about 7% of the population as carriers, with 2.7% of newborns being born with these conditions. The spectrum of clinical manifestations... Read more
First 4-in-1 Nucleic Acid Test for Arbovirus Screening to Reduce Risk of Transfusion-Transmitted Infections
Arboviruses represent an emerging global health threat, exacerbated by climate change and increased international travel that is facilitating their spread across new regions. Chikungunya, dengue, West... Read more
POC Finger-Prick Blood Test Determines Risk of Neutropenic Sepsis in Patients Undergoing Chemotherapy
Neutropenia, a decrease in neutrophils (a type of white blood cell crucial for fighting infections), is a frequent side effect of certain cancer treatments. This condition elevates the risk of infections,... Read more
First Affordable and Rapid Test for Beta Thalassemia Demonstrates 99% Diagnostic Accuracy
Hemoglobin disorders rank as some of the most prevalent monogenic diseases globally. Among various hemoglobin disorders, beta thalassemia, a hereditary blood disorder, affects about 1.5% of the world's... Read moreImmunology
view channel
Diagnostic Blood Test for Cellular Rejection after Organ Transplant Could Replace Surgical Biopsies
Transplanted organs constantly face the risk of being rejected by the recipient's immune system which differentiates self from non-self using T cells and B cells. T cells are commonly associated with acute... Read more
AI Tool Precisely Matches Cancer Drugs to Patients Using Information from Each Tumor Cell
Current strategies for matching cancer patients with specific treatments often depend on bulk sequencing of tumor DNA and RNA, which provides an average profile from all cells within a tumor sample.... Read more
Genetic Testing Combined With Personalized Drug Screening On Tumor Samples to Revolutionize Cancer Treatment
Cancer treatment typically adheres to a standard of care—established, statistically validated regimens that are effective for the majority of patients. However, the disease’s inherent variability means... Read moreMicrobiology
view channelEnhanced Rapid Syndromic Molecular Diagnostic Solution Detects Broad Range of Infectious Diseases
GenMark Diagnostics (Carlsbad, CA, USA), a member of the Roche Group (Basel, Switzerland), has rebranded its ePlex® system as the cobas eplex system. This rebranding under the globally renowned cobas name... Read more
Clinical Decision Support Software a Game-Changer in Antimicrobial Resistance Battle
Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) is a serious global public health concern that claims millions of lives every year. It primarily results from the inappropriate and excessive use of antibiotics, which reduces... Read more
New CE-Marked Hepatitis Assays to Help Diagnose Infections Earlier
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), an estimated 354 million individuals globally are afflicted with chronic hepatitis B or C. These viruses are the leading causes of liver cirrhosis, liver... Read more
1 Hour, Direct-From-Blood Multiplex PCR Test Identifies 95% of Sepsis-Causing Pathogens
Sepsis contributes to one in every three hospital deaths in the US, and globally, septic shock carries a mortality rate of 30-40%. Diagnosing sepsis early is challenging due to its non-specific symptoms... Read morePathology
view channel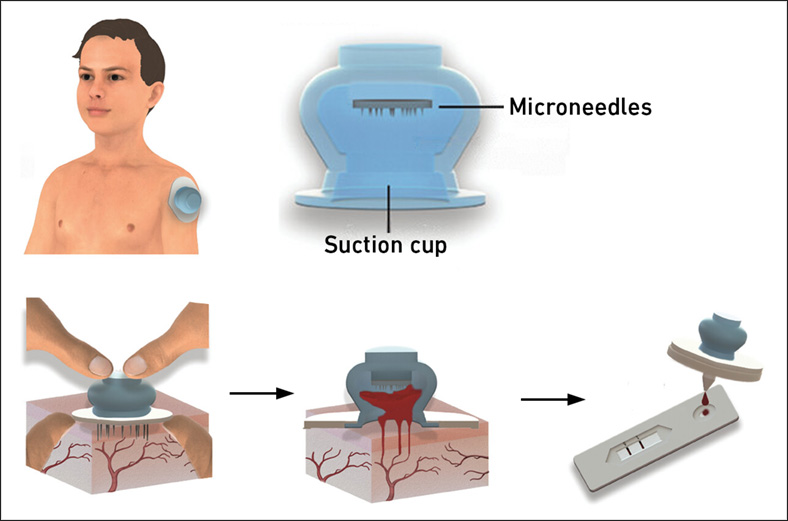
New Blood Test Device Modeled on Leeches to Help Diagnose Malaria
Many individuals have a fear of needles, making the experience of having blood drawn from their arm particularly distressing. An alternative method involves taking blood from the fingertip or earlobe,... Read more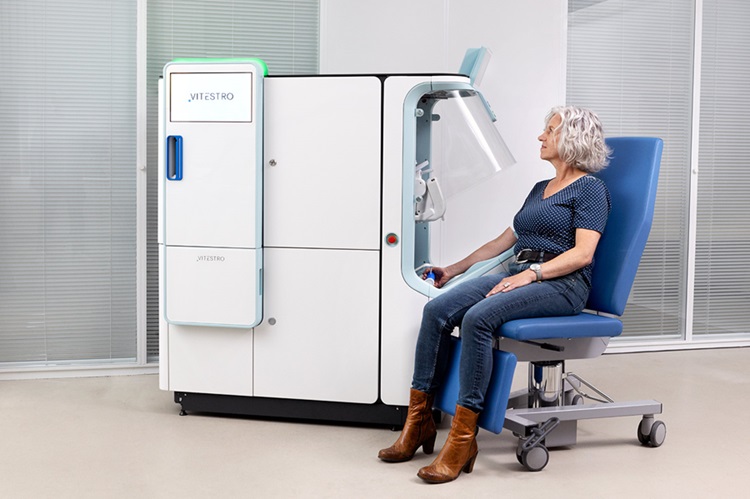
Robotic Blood Drawing Device to Revolutionize Sample Collection for Diagnostic Testing
Blood drawing is performed billions of times each year worldwide, playing a critical role in diagnostic procedures. Despite its importance, clinical laboratories are dealing with significant staff shortages,... Read more.jpg)
Use of DICOM Images for Pathology Diagnostics Marks Significant Step towards Standardization
Digital pathology is rapidly becoming a key aspect of modern healthcare, transforming the practice of pathology as laboratories worldwide adopt this advanced technology. Digital pathology systems allow... Read more
First of Its Kind Universal Tool to Revolutionize Sample Collection for Diagnostic Tests
The COVID pandemic has dramatically reshaped the perception of diagnostics. Post the pandemic, a groundbreaking device that combines sample collection and processing into a single, easy-to-use disposable... Read moreTechnology
view channel
New Diagnostic System Achieves PCR Testing Accuracy
While PCR tests are the gold standard of accuracy for virology testing, they come with limitations such as complexity, the need for skilled lab operators, and longer result times. They also require complex... Read more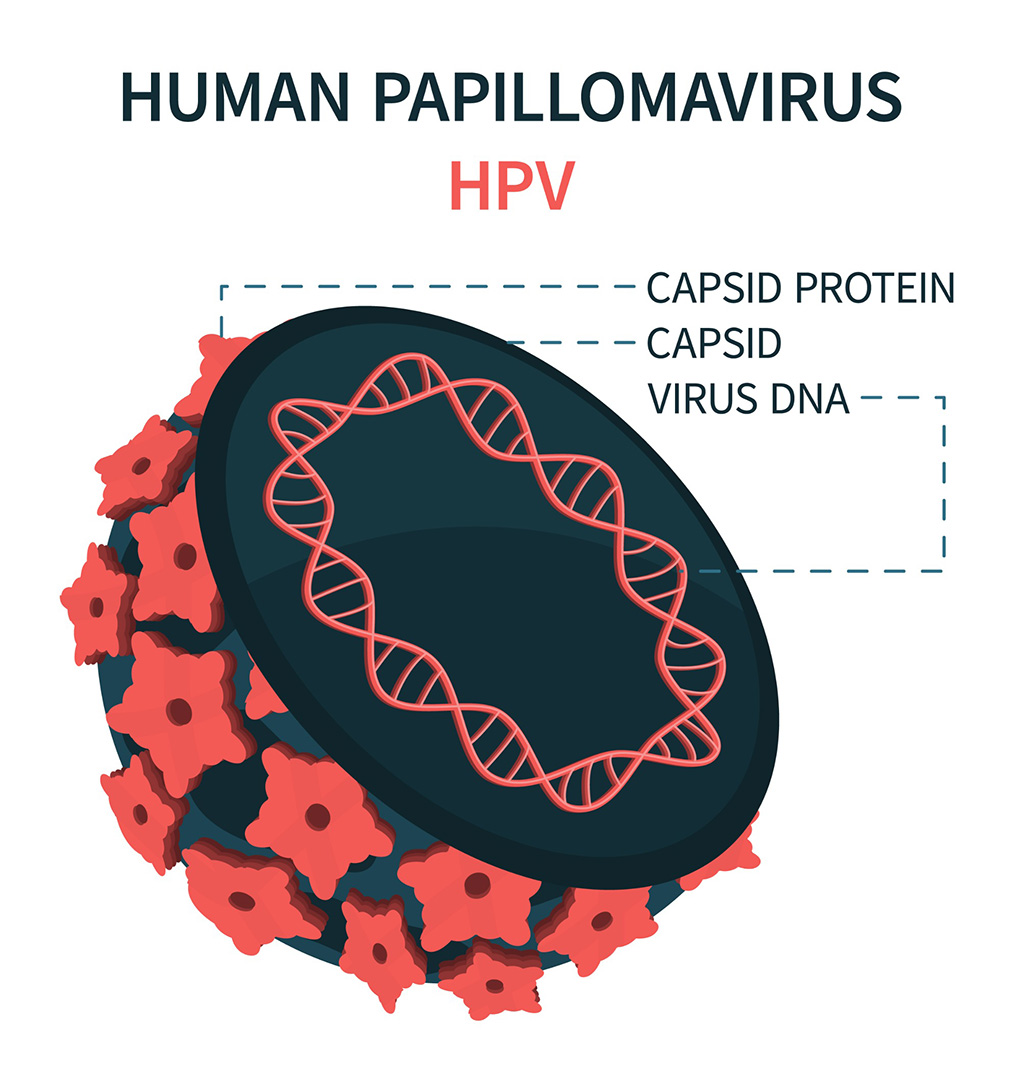
DNA Biosensor Enables Early Diagnosis of Cervical Cancer
Molybdenum disulfide (MoS2), recognized for its potential to form two-dimensional nanosheets like graphene, is a material that's increasingly catching the eye of the scientific community.... Read more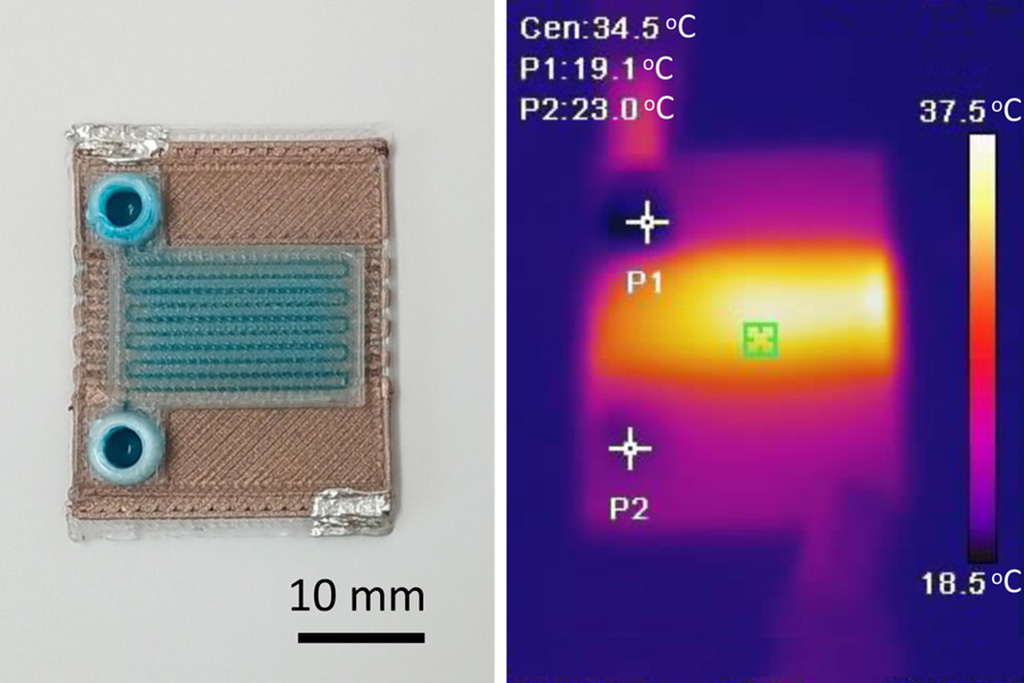
Self-Heating Microfluidic Devices Can Detect Diseases in Tiny Blood or Fluid Samples
Microfluidics, which are miniature devices that control the flow of liquids and facilitate chemical reactions, play a key role in disease detection from small samples of blood or other fluids.... Read more
Breakthrough in Diagnostic Technology Could Make On-The-Spot Testing Widely Accessible
Home testing gained significant importance during the COVID-19 pandemic, yet the availability of rapid tests is limited, and most of them can only drive one liquid across the strip, leading to continued... Read moreIndustry
view channel_1.jpg)
Thermo Fisher and Bio-Techne Enter Into Strategic Distribution Agreement for Europe
Thermo Fisher Scientific (Waltham, MA USA) has entered into a strategic distribution agreement with Bio-Techne Corporation (Minneapolis, MN, USA), resulting in a significant collaboration between two industry... Read more
ECCMID Congress Name Changes to ESCMID Global
Over the last few years, the European Society of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases (ESCMID, Basel, Switzerland) has evolved remarkably. The society is now stronger and broader than ever before... Read more