Microbiology

New Test Developed For Early Detection Of Lyme Disease
A new test for early detection of Lyme disease (borreliosis) is being developed and this will improve the ability to detect an active infection more easily than before so that healthy people with Lyme disease antibodies in their blood do not receive unnecessary antibiotic treatment and so that appropriate treatments can be initiated at an early stage. More...12 May 2016
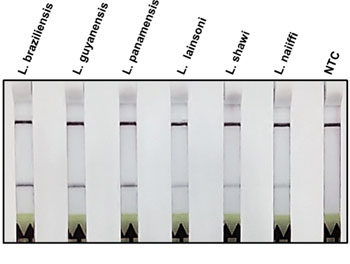
Field-Applicable Molecular Test Diagnoses Tegumentary Leishmaniasis
Cutaneous and mucosal leishmaniases are widely distributed in Central and South America. Leishmania of the Viannia subgenus are the most frequent species infecting humans. L. (V.) braziliensis, L. (V.) panamensis are also responsible for metastatic mucosal leishmaniasis. More...11 May 2016
Bacterial Vaginosis Assessed By Molecular Methods
Bacterial vaginosis (BV) is an aberrant state of the vaginal microbiota, which is characterized by a depletion of lactobacilli, an increased diversity of the bacterial population and an elevated pH. It is one the most common vaginal syndromes in fertile, premenopausal and pregnant women. More...11 May 2016
Zika Test Authorized by FDA for Emergency Use
The first test from a commercial lab provider to receive the US Food & Drug Administration (FDA)’s Emergency Use Authorization (EUA) for testing patients in the USA, including Puerto Rico, for Zika infection. The molecular test is intended for the qualitative detection of RNA from the Zika virus in human serum specimens from certain individuals. More...10 May 2016
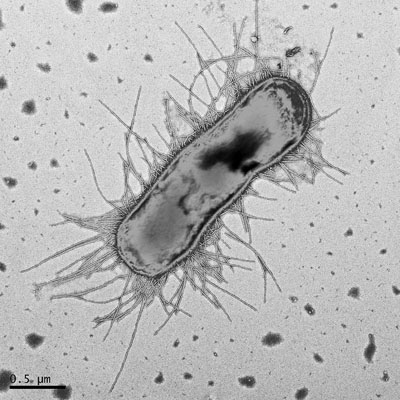
Study Improves Understanding of E. coli H30 Epidemiology, Persistent Infections Remains Unexplained
Researchers have identified populations more vulnerable to infection with pandemic E. coli strain H30, however improved testing is needed to monitor patients due to the high rate of treatment failure. Antibiotic resistance and weakened immunity only partially explain persistent infection. More...05 May 2016

Blood Transfusions in Malaria Zones Made Safer
Patients, especially children, who undergo blood transfusions in sub-Saharan Africa, are at high risk of transfusion-transmitted malaria. Every year, approximately 214 million people worldwide are infected with acute malaria, the majority of whom are in Africa and the disease is caused by the parasite Plasmodium. More...03 May 2016
In Other News
MALDI-TOF Mass Spectrometry Differentiates Streptococcus Species
Molecular Diagnostics Identify Resistance Biomarkers of Bloodstream Infection
New Assay Improves Detection Of Deadly Prion Diseases
Prototype Rapid Diagnostic Test Detects Human African Trypanosomiasis
Group A Streptococcus Rapid Immunoassay Evaluated
Tuberculosis Elimination at Stake
Multiple STIs Could Be Detected with A Single Rapid Test
Immunoassay Detects Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome Virus
On-the-Go Microfluidics Device May Provide Better Diagnostics of HIV/HCV
Novel Multiplex Immunoassay Developed for Chagas Disease
Profiling Persistent Tubercle Bacilli Predicts Early Drug Efficacy
Acid-Fast Stain Identifies Schistosoma Eggs
Immunoassay for Human Cystic Echinococcosis Evaluated
Dedicated Blood Culture Diagnostics Cartridge Set for CE-IVD Marketing Release
Uninfected or Asymptomatic? – Key to Forecasting Infectious Disease Epidemics
Automated Ebola Blood Test Performs Well in Field Evaluation
Genomic Sequencing Identifies Deadly Bloodstream Infection
Shiga Toxin Direct Test Receives FDA Clearance
High Risk HPV Multiplex Assay Clinically Validated
Emerging Blood-Borne Bacteria Found in Blood Donors
Novel Malaria Test Sets a New Gold Standard for Diagnosis
Dried Cerebrospinal Fluid Spots Detect Anti-Japanese Encephalitis IgM
Uropathogenic Bacteria Linked to Deadly Disease in Preterm Infants
The LabMedica Microbiology channel provides the latest news in the fields of epidemiology, bacteriology, virology, and parasitology, all viewed from the unique perspective of Laboratory Medicine.










