Clinical Chemistry

Automated Urine Microscope Verified for Regional Laboratories
Automated Urine Microscopy examines a sample of urine under a microscope. It can check cells from the urinary tract, blood cells, crystals, bacteria, parasites, and cells from tumors. This test is often used to confirm the findings of other tests or add information to a diagnosis. More...03 Feb 2021

UPLC-MS/MS Method Simultaneously Determines Plasma Catecholamines and Their Metabolites
Phaeochromocytomas and paragangliomas (PPGLs) are rare tumors of adrenal chromaffin cells or extra-adrenal paraganglia. They are difficult to diagnose because of the non-specific clinical symptoms such as hypertension, palpitations, flushing and sweating. More...27 Jan 2021
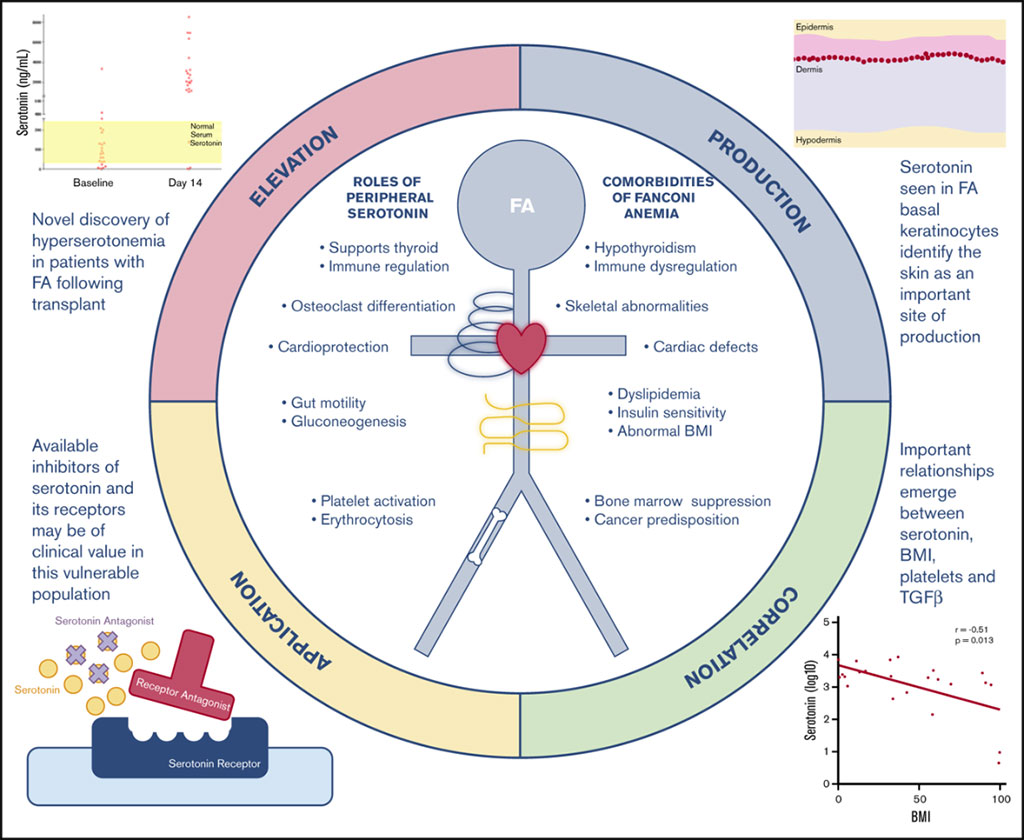
Tryptophan Metabolism Is Dysregulated in Individuals with Fanconi Anemia
Fanconi anemia (FA) is a complex genetic disorder frequently associated with progressive marrow failure and a strong predisposition to early malignancies, particularly squamous cell carcinomas and hepatocellular carcinomas. More...20 Jan 2021
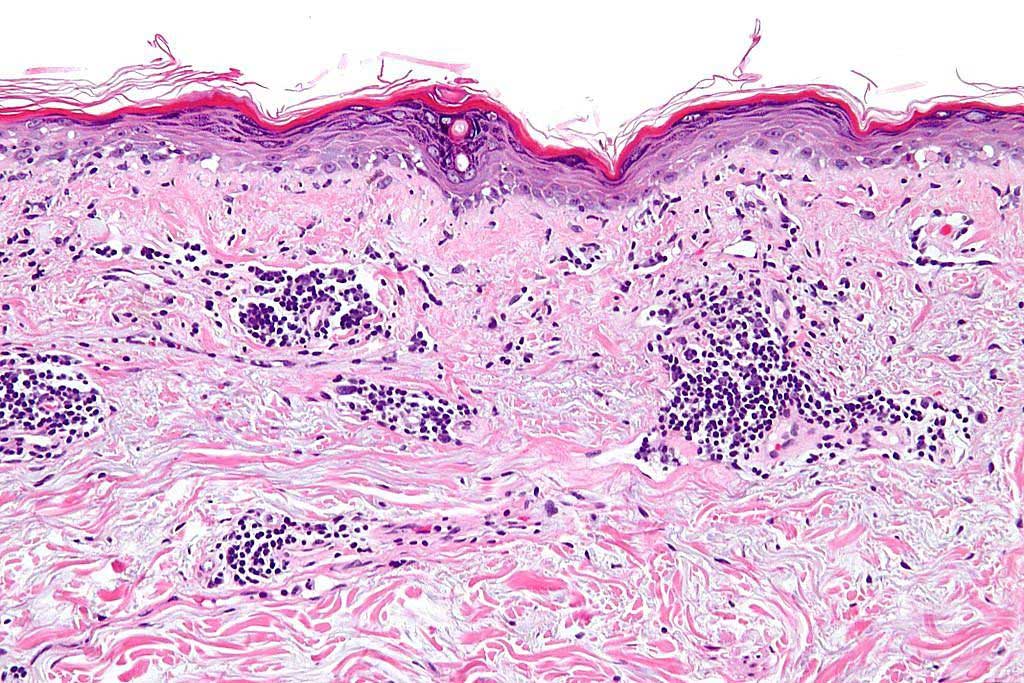
Serum Pentosidine Levels Measured in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), is the most common type of lupus. SLE is an autoimmune disease in which the immune system attacks its own tissues, causing widespread inflammation and tissue damage in the affected organs. It can affect the joints, skin, brain, lungs, kidneys, and blood vessels. More...14 Jan 2021
Angiopoietin-Like 2 Is a Biomarker for Diabetic Foot Patients
Diabetic foot ulcers (DFUs) are one of the common complications in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients and are chartered by lower extremity vascular obstructions, persistent foot infections, ulcers, and deep tissue destruction. More...14 Jan 2021

Gestational Lipid Profiles Associated with Adverse Cardiovascular Risk
Pregnancy has been proposed as a natural ‘stress test’ to predict the risk of cardiovascular disease (CVD) later in life. The long-term effect of high blood pressure during pregnancy has been well established. Women who develop a hypertensive disorder of pregnancy such as gestational hypertension or pre-eclampsia have a 2–8 times higher risk of developing chronic hypertension and other diseases. More...12 Jan 2021
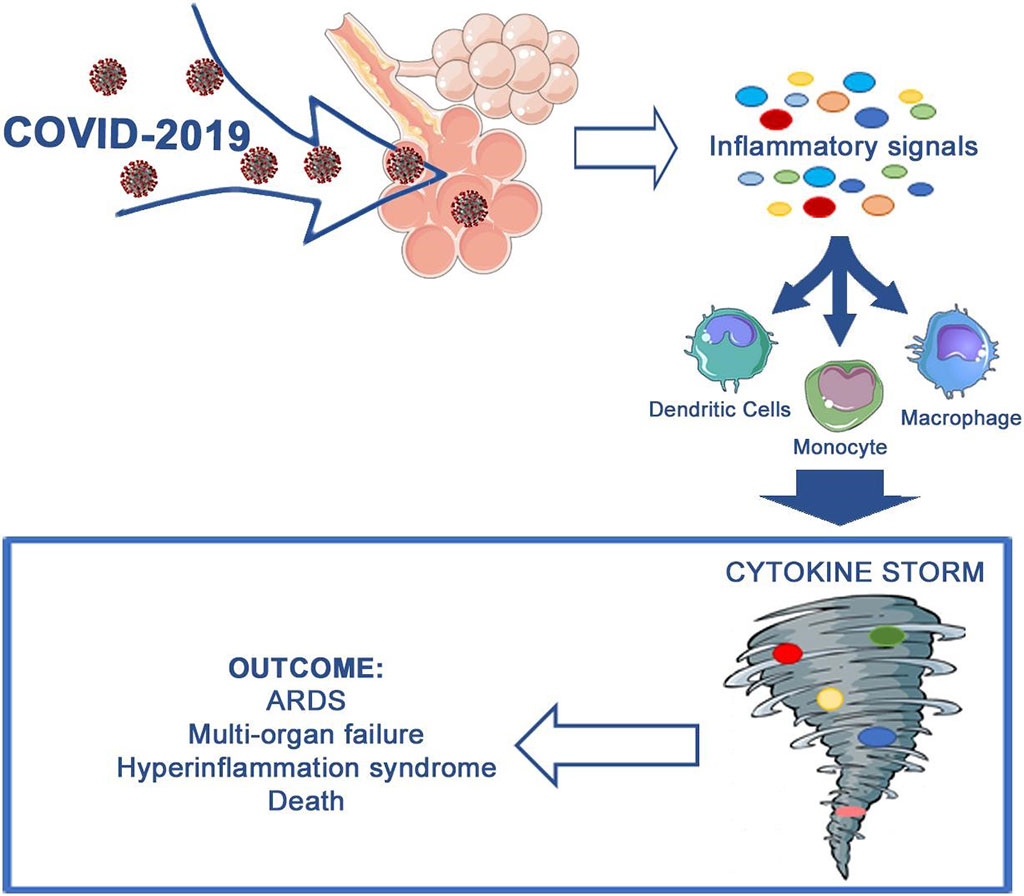
Preliminary Predictive Criteria Identified for COVID-19 Cytokine Storm
While most of cases of COVID-19 are mild, a sizeable number of patients develop a severe acute hyperimmune response characterized by a cytokine storm (CS). Two forms of CS, hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (HLH) and macrophage activation syndrome (MAS), rely on well-established criteria to identify their occurrence. More...05 Jan 2021
In Other News
Plasma Serglycin Levels Evaluated for Diabetic Retinopathy Diagnosis
Novel Biomarkers Predict the Development of Incident Heart Failure
Hyperglycemia and Hypoglycemia Associated with Poor Outcomes in COVID-19 Patients
Novel Biomarker Candidate for Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis Explored
Biomarker Evaluated for Early Detection of Congenital Heart Disease
Interstitial Fluid Sampled from Skin Using a Microneedle Patch
HDL-Cholesterol Predicts Survival in Cirrhotic Patients with Gastrointestinal Bleeding
Diagnostic Assays Evaluated for Vitamin B12 and Folate Deficiency
Kininogen-1 Protein Linked to Early Cognitive Impairment in Parkinson’s
Single-Tube Multimarker Assay Estimates Preeclampsia Risk
Spot Urine Sample Evaluated for Renal Potassium Loss
Incretin Hormone Levels Linked to Arteriosclerosis
Biomarker Detects Early Alzheimer’s Disease
Elevated Fructosamine Levels Associated with Increased PJI Risk
Biomarkers Predict Whether RA Patients Will Respond to DMARDs
Breath Ammonia Biomarker Predicts Kidney Function in CKD Patients
Metabolomics Profiles Associated with Diabetic Retinopathy
High-Sensitivity C-Reactive Protein Investigated in Acute Myocardial Infarction Patients
Novel Fecal Calprotectin Test Validated in Pediatric Population
Serum Creatinine-to-Cystatin C Ratio Predicts AKI Mortality
Glycosylated Hemoglobin Predicts Coronary Artery Disease in Non‐Diabetic Patients
Breath Test Developed for Head and Neck Cancer Diagnosis
Glycated Albumin Levels in Tears Allow Noninvasive Glucose Testing
The Clinical Chemistry channel updates the reader on tests, techniques, and research in the field - from routine assays to specialized tests on blood, urine, enzymes, lipids, hormones and more.










