Cord Blood and Matched Related Donor Transplantation Compared in Acute Myeloid Leukemia
|
By LabMedica International staff writers Posted on 19 Jan 2022 |
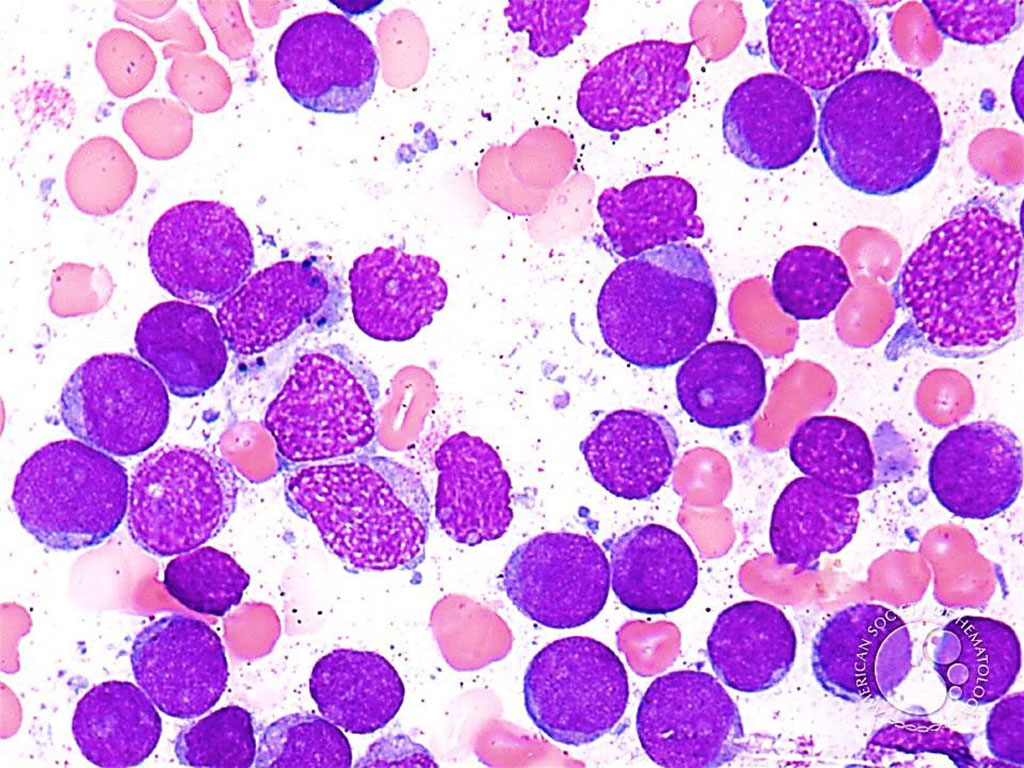
Image: Bone marrow aspirate from a patient with Acute Myeloid Leukemia: Blasts are the predominant population and have a high nuclear to cytoplasmic ratio and generally lack granules. (Photo courtesy of Professor Peter G. Maslak, MD)
The prognosis of primary refractory and relapsed acute myeloid leukemia is poor, with a five-year overall survival of less than 10%. Allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) is the only curative treatment option for these patients.
Cord blood transplantation (CBT) is an alternative donor transplantation method and has the advantages of rapid availability and the possibility of inducing a more potent graft-versus-leukemia effect, leading to a lower relapse rate for patients with non-remission relapse and refractory acute myeloid leukemia (R/R AML).
A large team of Hematologists at the Graduate School of Medicine Kyoto University (Kyoto, Japan) and their colleagues investigated the impact of CBT, compared to human leukocyte antigen-matched related donor transplantation (MRDT). The study included 2,451 adult patients with non-remission R/R AML who received CBT (1,738 patients) or MRDT (713 patients) between January 2009 and December 2018. The median age was 55 years (interquartile range, 43–63 years), with 1,484 patients (61%) being male. Karyotype risk, was estimated as 190 (8.2%), 1,352 (59%), and 768 (33%) patients had favorable, intermediate, and poor karyotypes, respectively.
There were 1,499 (61%) patients with primary induction failures and 952 (39%) with relapses. Among these patients, 1,576 (65%) had blasts in the peripheral blood. The myeloablative conditioning regimen (MAC) and reduced-intensity conditioning regimen were defined as previously described. HLA match was defined as the same serologically identified HLA-A, HLA-B, and HLA-DRB1 between the donor and recipient. Comparisons were made by examining the 5-year progression-free survival (PFS) rates of these Japanese patients.
The investigators reported that the primary endpoint, the 5-year PFS, was 22.2% (95% CI: 20.1–24.3%) in the CBT group and 19.9% (95% CI: 16.8–23.1%) in the MRDT group. The adjusted hazard ratio (HR) was 0.83 (95% CI: 0.69–1.00); this was due to a more pronounced decrease in the relapse rate (HR: 0.78, 95% CI: 0.69–0.89) than an increase in the non-relapse mortality (NRM: 1.42, 1.15–1.76). The CBT group had more patients with infection-related death and fewer patients with graft-versus-host disease (GVHD)-related deaths and death due to primary diseases.
Yoshimitsu Shimomura, MD, a Hematologist and the lead author of the study, said, “We believe CBT would be a great treatment option for R/R AML patients in non-remission given the circumstances. However, there are currently limited data for how this subset of patients would respond to CBT. Before comparing PFS rates, we performed propensity score matching. This took into account factors such as patient age, sex, years of treatment, and others to ensure all comparisons were as fair as possible and no biases were introduced. CBT compared with MDRT that had a more pronounced decrease in relapse rate than increase in NRM.”
The authors concluded that their data support CBT as a potential superior alternative to MRDT for patient prognosis and thus provide evidence which may influence clinical guidelines on R/R AML treatment. Future studies will investigate if genetic factors play any roles in patients’ responses to these two transplantation methods. Additionally, patient quality of life will be considered to optimize therapeutic development for this deadly disease. The study was originally published on November 21, 2021 in the journal Leukemia.
Related Links:
Graduate School of Medicine Kyoto University
Cord blood transplantation (CBT) is an alternative donor transplantation method and has the advantages of rapid availability and the possibility of inducing a more potent graft-versus-leukemia effect, leading to a lower relapse rate for patients with non-remission relapse and refractory acute myeloid leukemia (R/R AML).
A large team of Hematologists at the Graduate School of Medicine Kyoto University (Kyoto, Japan) and their colleagues investigated the impact of CBT, compared to human leukocyte antigen-matched related donor transplantation (MRDT). The study included 2,451 adult patients with non-remission R/R AML who received CBT (1,738 patients) or MRDT (713 patients) between January 2009 and December 2018. The median age was 55 years (interquartile range, 43–63 years), with 1,484 patients (61%) being male. Karyotype risk, was estimated as 190 (8.2%), 1,352 (59%), and 768 (33%) patients had favorable, intermediate, and poor karyotypes, respectively.
There were 1,499 (61%) patients with primary induction failures and 952 (39%) with relapses. Among these patients, 1,576 (65%) had blasts in the peripheral blood. The myeloablative conditioning regimen (MAC) and reduced-intensity conditioning regimen were defined as previously described. HLA match was defined as the same serologically identified HLA-A, HLA-B, and HLA-DRB1 between the donor and recipient. Comparisons were made by examining the 5-year progression-free survival (PFS) rates of these Japanese patients.
The investigators reported that the primary endpoint, the 5-year PFS, was 22.2% (95% CI: 20.1–24.3%) in the CBT group and 19.9% (95% CI: 16.8–23.1%) in the MRDT group. The adjusted hazard ratio (HR) was 0.83 (95% CI: 0.69–1.00); this was due to a more pronounced decrease in the relapse rate (HR: 0.78, 95% CI: 0.69–0.89) than an increase in the non-relapse mortality (NRM: 1.42, 1.15–1.76). The CBT group had more patients with infection-related death and fewer patients with graft-versus-host disease (GVHD)-related deaths and death due to primary diseases.
Yoshimitsu Shimomura, MD, a Hematologist and the lead author of the study, said, “We believe CBT would be a great treatment option for R/R AML patients in non-remission given the circumstances. However, there are currently limited data for how this subset of patients would respond to CBT. Before comparing PFS rates, we performed propensity score matching. This took into account factors such as patient age, sex, years of treatment, and others to ensure all comparisons were as fair as possible and no biases were introduced. CBT compared with MDRT that had a more pronounced decrease in relapse rate than increase in NRM.”
The authors concluded that their data support CBT as a potential superior alternative to MRDT for patient prognosis and thus provide evidence which may influence clinical guidelines on R/R AML treatment. Future studies will investigate if genetic factors play any roles in patients’ responses to these two transplantation methods. Additionally, patient quality of life will be considered to optimize therapeutic development for this deadly disease. The study was originally published on November 21, 2021 in the journal Leukemia.
Related Links:
Graduate School of Medicine Kyoto University
Latest Hematology News
- Rapid Cartridge-Based Test Aims to Expand Access to Hemoglobin Disorder Diagnosis
- New Guidelines Aim to Improve AL Amyloidosis Diagnosis
- Automated Hemostasis System Helps Labs of All Sizes Optimize Workflow
- Fast and Easy Test Could Revolutionize Blood Transfusions
- High-Sensitivity Blood Test Improves Assessment of Clotting Risk in Heart Disease Patients
- AI Algorithm Effectively Distinguishes Alpha Thalassemia Subtypes
- MRD Tests Could Predict Survival in Leukemia Patients
- Platelet Activity Blood Test in Middle Age Could Identify Early Alzheimer’s Risk
- Microvesicles Measurement Could Detect Vascular Injury in Sickle Cell Disease Patients
- ADLM’s New Coagulation Testing Guidance to Improve Care for Patients on Blood Thinners
- Viscoelastic Testing Could Improve Treatment of Maternal Hemorrhage
- Pioneering Model Measures Radiation Exposure in Blood for Precise Cancer Treatments
- Platelets Could Improve Early and Minimally Invasive Detection of Cancer
- Portable and Disposable Device Obtains Platelet-Rich Plasma Without Complex Equipment
- Disposable Cartridge-Based Test Delivers Rapid and Accurate CBC Results
- First Point-of-Care Heparin Monitoring Test Provides Results in Under 15 Minutes

Channels
Clinical Chemistry
view channel
Blood Test Tracks Transplant Health Using Donor DNA
Organ transplantation offers life-saving treatment for patients with end-stage disease, but complications such as rejection remain a constant risk. Monitoring transplanted organs typically relies on invasive... Read more
AI Sensor Detects Neurological Disorders Using Single Saliva Drop
Neurological disorders such as Parkinson’s disease and Alzheimer’s disease often develop gradually and present subtle symptoms in their early stages. Because early signs are frequently vague or atypical,... Read moreMolecular Diagnostics
view channel
Blood Test Predicts Dementia in Women 25 Years Before Symptoms Begin
Dementia and Alzheimer’s disease often develop silently over many years before symptoms appear. Detecting risk earlier could allow preventive strategies to begin long before memory problems interfere with... Read more
Serial Liquid Biopsies Reveal Therapy Resistance in Metastatic Prostate Cancer
Metastatic Prostate cancer can rapidly adapt under treatment, making it difficult to detect resistance before clinical progression. Genomic results from archival tumor tissue may no longer reflect the... Read moreImmunology
view channel
Cancer Mutation ‘Fingerprints’ to Improve Prediction of Immunotherapy Response
Cancer cells accumulate thousands of genetic mutations, but not all mutations affect tumors in the same way. Some make cancer cells more visible to the immune system, while others allow tumors to evade... Read more
Immune Signature Identified in Treatment-Resistant Myasthenia Gravis
Myasthenia gravis is a rare autoimmune disorder in which immune attack at the neuromuscular junction causes fluctuating weakness that can impair vision, movement, speech, swallowing, and breathing.... Read more
New Biomarker Predicts Chemotherapy Response in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
Triple-negative breast cancer is an aggressive form of breast cancer in which patients often show widely varying responses to chemotherapy. Predicting who will benefit from treatment remains challenging,... Read moreBlood Test Identifies Lung Cancer Patients Who Can Benefit from Immunotherapy Drug
Small cell lung cancer (SCLC) is an aggressive disease with limited treatment options, and even newly approved immunotherapies do not benefit all patients. While immunotherapy can extend survival for some,... Read moreMicrobiology
view channel
Study Highlights Accuracy Gaps in Consumer Gut Microbiome Kits
Direct-to-consumer gut microbiome kits promise personalized insights by profiling fecal bacteria and generating health readouts, but their analytical accuracy remains uncertain. A new study shows that... Read more
WHO Recommends Near POC Tests, Tongue Swabs and Sputum Pooling for TB Diagnosis
Tuberculosis (TB) remains one of the world’s leading infectious disease killers, yet millions of cases go undiagnosed or are detected too late. Barriers such as reliance on sputum samples, limited laboratory... Read morePathology
view channel
Novel mcPCR Technology to Transform Testing of Clinical Samples
DNA methylation is an important biological marker used in the diagnosis and monitoring of many diseases, including cancer. These chemical modifications to DNA influence gene activity and can reveal early... Read more
Sex Differences in Alzheimer’s Biomarkers Linked to Faster Cognitive Decline
Sex differences in Alzheimer’s disease present ongoing diagnostic challenges, with women often experiencing a disproportionate disease burden even when preclinical amyloid-beta levels are similar to men.... Read moreTechnology
view channel
AI Model Outperforms Clinicians in Rare Disease Detection
Rare diseases affect an estimated 300 million people worldwide, yet diagnosis is often protracted and error-prone. Many conditions present with heterogeneous signs that overlap with common disorders, leading... Read more
AI-Driven Diagnostic Demonstrates High Accuracy in Detecting Periprosthetic Joint Infection
Periprosthetic joint infection (PJI) is a rare but serious complication affecting 1% to 2% of primary joint replacement surgeries. The condition occurs when bacteria or fungi infect tissues around an implanted... Read moreIndustry
view channel
MGI Tech Strengthens Sequencing Portfolio with Dual Acquisition
MGI Tech Co., Ltd. (Shenzhen, China) announced the acquisition of STOmics and CycloneSEQ on March 3, 2026, as part of its “SEQALL+GLI+Omics” strategy. According to the company, the combined portfolio spans... Read more
Agilent Technologies Acquires Pathology Diagnostics Company Biocare Medical
Agilent Technologies (Santa Clara, CA, USA) has entered into a definitive agreement to acquire Biocare Medical (Pacheco, CA, USA), expanding its pathology portfolio through the addition of highly complementary... Read more